A Comparative Study on Image Contrast Enhancement Techniques
Amanpreet Kaur1 , Kamaljit Singh2
1Assistant Professor, Dept of CSE, SSIET, Derabassi, Punjab, India

2Assistant Professor, Dept of CSE, SSIET, Derabassi, Punjab, India
Abstract - Intheprocessofenhancementofimagequalityof different types of images which have huge applications in the number ofareasofreal worldthecontrastandbrightnessare two main concerns. For the sake of human interpretation not only the objective as well as subjective quality also matters. For subjective quality evaluation main parameter is the contrast present in every part of the image. Contrast rises if there is a contrast variation in the amount of luminance reflected from the two adjacent surfaces. Researchers have proposed various techniques for contrast enhancement in image processing while ignoring the illumination parameter present in the digital images. Main aim for the contrast enhancement of the images is for enhancing the details present of the objects present in the image. Image contrast enhancement is possible if stretching of pixel values is performedofaparticularrangewherecontrastimprovement is needed. In tonal enhancement, there are many regions present in the digital image where darkness and brightened regions are more prone to variations and this scenario accurateandsmoothcontrastenhancementisrequired.Inthis present research work, there is a comparative analysis of various contrast enhancement of different color images is performed. Various techniques like Histogram equalization, brightness preserving technique and other techniques outcomes are discussed in detail with the help of various objective parameters.
Key Words: Image contrast enhancement, image processing,colorimages,histogramequalization,entropy
1. INTRODUCTION
Therearevariouscolorspacesintherealworldandoutof thesetwoprimecolorspacesareRGBandCMYKandwhich are intended for various engineering and science communications.
1.1 RGB
ThisRGBcolormodelisassociatedwiththered,greenand blue receptor is the retina of the eye of living beings. This color model is based on the additive color process where mixingofthesecolorsproducesothercomplimentarycolors oftherealworld.Itisthefundamentalcolormodelandwhich istheintegralpartofthecolorprojectedwiththesunlight.In the world of digital electronics, this model is used for graphics and also in printing applications. The secondary colorlike cyan, magenta and yellowarecreatedby mixing twocolorsatatimefromthered,greenandbluecolors.Cyan
isproducedbymixinggreenandblue,magentaisproduced bymixingblueandred,yellowisproducedbymixingredand green. If red, green and blue are mixed in full proportions thenwhitecolorisproducedandifthereisnovalueofthese colorsthenblackcolorisproduced.
Therearevarioustechniqueswhichareutilizedtoimprove thecontrastofthedigitalimage.Someofthetechniquesthat are utilized for implementation of present research work havebeendiscussedbelow.
1.2 HE (Histogram Equalization)
Histogram equalization is one of the contrast adjustment techniquesthatisutilizedindigitalimageprocessing.Inthis processpixelvaluesareadjustedsothathistogramoforiginal imageisuniformedandnormalized.Thistechniqueisusedto improvetheoverallcontrastoftheinternalpartsoftheimage whereeitherthepixelshaveloworhighvaluesregions.Since this method normalized the pixel values with the help of histogram way so this method is known as histogram equalization.Thismethodisgenerallyusedtoimprovethe overallcontrastofthedigitalimageincomparisontoother region-basedcontrastimprovementmethods.
1.3 Gamma Correction
Gamma correction is a methodology that is helpful in obtainingenhancedbrightnessandluminanceofthepixelby using some mathematical functions. This mathematical functionisnonlinearinnatureandmonotonicthatisusedto affectthewhiteandgreyvaluesaswellasdarkshadowspixel valuesinthedigitalimage.Gammacorrectionisoneofthe testedtechniquesforparticularapplications.
1.4 Brightness Preserving Bi-Histogram Equalization (BBHE)
ThistechniquewasproposedbyY.T.Kim.Inthismethod, author used the concept of dividing the histogram of the inputdigitalimageintotwodifferentparts.Thisprocessis basedontheaverageoftheimage.So,thistechniquetriesto equalizethetwopartsbasedontheirrespectivehistograms independently.Thismethodisusedtoincreasethecontrast of the image where output image has brightness near to averageandmeangreylevel.Thistechniquehasnumerous applications in various areas of image processing. This techniqueisprimarilyusedtoenhancingthecontrastofthe imageinadditiontopreservingthemeanbrightnessofthe inputdigitalimage.
1.5 Brightness Preserving Dynamic Histogram Equalization
Thistechniqueisimplementedtosolvethelimitationsofthe histogram equalization method. Histogram equalization showssaturationeffectinelectronicsdevicessothiscanbe solvedbypreservingthebrightnessoftheinputimageinthe outputimagealso.BPDHEtriestopreservethebrightnessof inputimageintotheoutputimagealso.Methodusesgaussian filterandthenusespartitionmethodbasedonlocalmaxima. Here each partition of the image will have new dynamic range.Inthefinalstage,outputimageisnormalizedbasedon theinputimagemeanbrightnessvalue.
1.6 Region Based Adaptive Contrast Enhancement (RACE)
Thiswholealgorithmissplitintofollowingsteps
1)Acentralpointisconsideredbasedonthresholdofeach regionthatwillactasaseedpointforthatregion
2) Now this central point is used to split image into foregroundandbackgroundregions.
3) Foreground region is then enhanced by equalizing histogramadaptivelyandthenbackgroundregionisaddedto theenhancedforeground.
4)Inthelaststep,gradientoftheoriginalimageiscalculated and added to the step 3 output so that enhanced image is obtained.
2. LITERATURE SURVEY

A. M et al. [2] proposed an automatic transformation techniquethatimprovedthebrightnessofdimmedimages via the gamma correction and probability distribution of luminancepixelswhichusedanefficientmethodforcontrast andcolorenhancementofdigitalimagesascontrastofimage isveryimportantcharacteristicbywhichthequalityofimage canbejudgedasgoodorpoorquality.It wascomposedof three major steps. In the first primary step, histogram analysisprocesswasappliedontheoriginalimagesuchthat it was used to present the pixel data of the original image which was relied on probability as well as statistical transformation.Inthesubsequentsecondstep,theprocessof distribution of weights was followed which is helpful in smoothingthefluctuationofintensitiesandcomputingthe threshold of histogram so that stretching of pixels was achieved. In the third and final step, Adaptive gamma correctionandAdaptiveHistogramStretchingwithrespectto color constraint can automatically enhance the image contrast and color through use of a smoothing curve. The techniqueproposedhereperformedefficientlyindifferent dark and bright images by adjusting their contrast very frequentlyandproducedenhancedimagesofcomparableor higherqualitythanconventionalmethod.
A.Aggarwaletal.[3]proposedanalgorithmwhichachieves contrastenhancement,alsopreservesthebrightnesslevelof the images. It included the discussion regarding the developmentoftheimageenhancementtechniquesandtheir application in the field of image processing. To process an inputimagesothattheresultantimage wasmoresuitable thantheoriginalimageforspecificapplicationisaprincipal objective of image enhancement techniques. This new algorithm was developed to overcome the problems of excessivecontrastenhancementcausedbyTraditionalglobal histogram equalization and block effect caused by local histogramequalization.Inthis,theweightedaverageofthe histogramequalized,gammacorrectedandtheoriginalimage werecombinedtoobtainedtheenhancedprocessedimage.It had been shown by experimental results that proposed algorithmhadgoodperformanceonenhancingcontrastand visibilityforamajorityofimages.
S.C.Huangetal.[5]proposedanefficientmethodtomodify histograms and enhance contrast in digital images. Since enhancement plays a significant role in digital image processing, computer vision, and pattern recognition they presented an automatic transformation technique that improvesthebrightnessofdimmedimageswiththehelpof methods like gamma correction as well as the probability distribution of luminant image pixels. For improving the qualityoftheinputvideo,performtemporalinformationso thatcomputationalcomplexitycouldbelowered.Fromthe outcomeoftheexperiments,itwasshowedtheworthinessof the proposed method. They had presented a novel enhancementmethodforbothimagesandvideosequences.
T.Celiketal.[6]suggestedanalgorithmwhichimprovesthe contrast of the digital image by performing adaptive equalizationprocessonhistogramoftheoriginalimage.This method utilized the Gaussian mixture model on the image greylevelpixels.TheseGaussiancomponentswereutilizedto sectionedthedynamicrangeofinputoriginalimageintogrey level intervals of the pixels. From the outcome of the suggested algorithms, it was shown that the algorithm performedbetterincomparisontootheralgorithms.Theone of the most significant methods was not setting any parametermanuallyforsettingaparticulardynamicrangeas wellasitsapplicabilityonvarioustypesofdigitalimages.
3. PARAMETERS USED FOREVALUATIONOFIMAGE ENHANCEMENT TECHNIQUES
Fortheobjectivemeasurementofanyalgorithmforimage enhancement,therearevariousparametersonthebasisof which performance of the algorithms is evaluated. The various parameters that are used to evaluate the performanceoftechniquesareasfollows.
(i)
where,h(s)isthenormalizedhistogramoftheoutputdigital image.Thisparameterisutilizedtomeasurethecontentof theimage,withhavinghigherrangevaluesshowingdigital imagesarericherininformation.
(ii)

Absolute Contrast Error is the difference between the deviationsoftheoriginalimageandtheenhancedimage.ACE shouldbeaslessaspossible;itmeansthedeviationofthe output image should be more means the contrast enhancementismore.
(iii) PeakSignalto
2 10 255 10log
(PSNR) MSE
PeakSignaltoNoiseRatioparametervalueshouldbehigh.It meansthatthecontentofimageintheoutputishighwith lessnoise.
4. RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
Thischapteraimsatprovidingtheresultsofthealgorithmsof imageenhancementtechniqueslikeHistogramEqualization (HE),GammaCorrection(GC),BBHE,BPDHE,Regionbased Adaptive Contrast Enhancement (RACE Approach), which have been described in previously and determine the best oneforimageenhancement.
All the enhancement techniques are implemented using MATLAB-2009a and its image processing toolbox. Enhancementtechniquesareappliedonxrayboneimagesof differentsizelike512512,256256,etc.
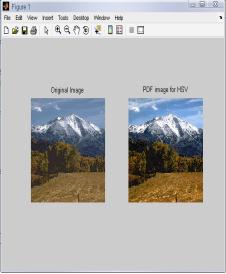
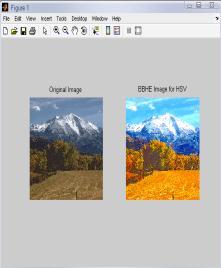
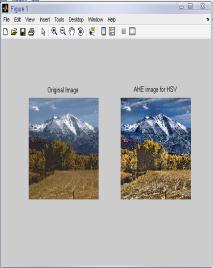
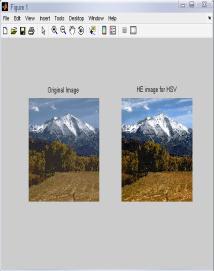
4.1 ResultsforHSVColor Model for ‘Landscape’ Image
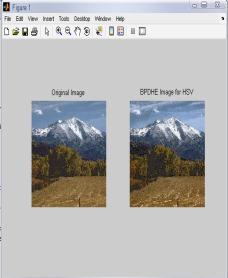
Table -1: ResultsofVariousParametersfor“LANDSCAPE” ImageusingHSVColorModel
Input entropy of Landscape Image: R=7.2382, G=7.3182, B=7.4802
IntheTable1,differenttechniquesarecomparedonthebasis ofvariousparametersforHSVcolormodel.Fromthistable,it is clear that value of error color for BPDHE is less as comparedtotheothertechniques.Itmeansthatthereisvery littledifferenceinthecolorsoftheoutputimageascompared to the input image even after enhancement. The value of CPSNR is more for BPDHE which is also desirable for any techniquetoworkefficiently.MoreCPSNRmeanslessnoise enteredduringenhancement.Intermsofentropy,theoutput entropy of R and G components are more as compared to input entropyincase ofall the techniques exceptBBHEin which all component output entropy is less than input entropy.
FromtheFig.1,itisclearthatthevisualqualityofHE,BPDHE andRACEapproachisgoodascomparedtotheothers.But, only BPDHE is showing the best quality image in terms of colorasthecolorsoftheinputandoutputimagearealmost same,whileinothersthereislotofvariationinthecolorof theoutputimage.
Input entropy of Landscape Image: R=7.2382, G=7.3182, B=7.4802
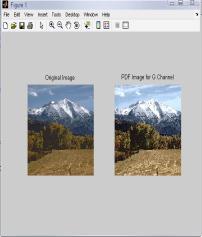
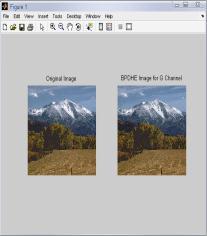
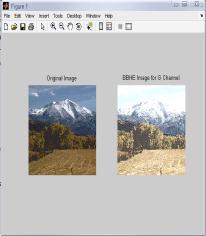
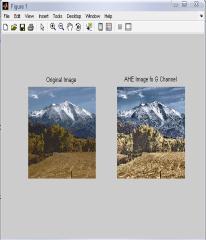
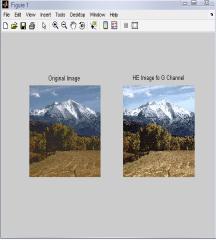
IntheTable2,differenttechniquesarecomparedonthebasis ofvariousparametersforG-Channelcolormodel.Fromthis table,itisclearthatvalueoferrorcolorforBPDHEislessas comparedtotheothertechniques.Itmeansthatthereisvery littledifferenceinthecolorsoftheoutputimageascompared totheinputimageevenafterenhancement.Eventhevalueof CPSNR is more for BPDHE which is also desirable for any techniquetoworkefficiently.MoreCPSNRmeanslessnoise enteredduringenhancement.Intermsofentropy,theoutput entropy of R component is more as compared to input entropyincaseofallthetechniquesexceptBBHEinwhichall componentoutputentropyislessthaninputentropyandin caseofBPDHE,inwhichoutputentropyofBcomponentis alsomore.ItmeansonlyRcomponentshowmoredetailsin theimageafterenhancementusingG-Channelcolormodel.
FromtheFig.2,itisclearthatthevisualqualityofHE,GC, BPDHE and RACE approach is good and particularly only BPDHEisshowingthebestqualityimageintermsofcoloras the colors of the inputand output image are almost same, while in others there is lot of variation in the color of the outputimage.
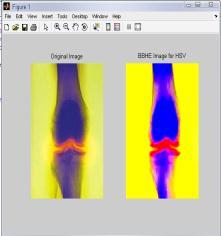
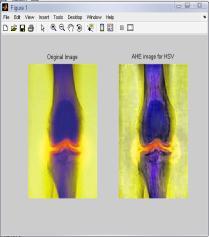
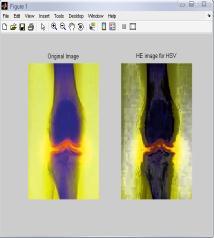

4.3
Table -3: ResultsofVariousParametersfor“BONESCAN” ImageusingHSVColorModel
Input entropy of Bonescan Image: R=6.9825, G=6.6600, B=6.8148
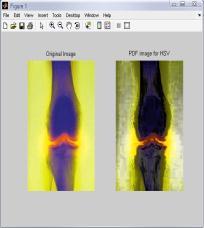
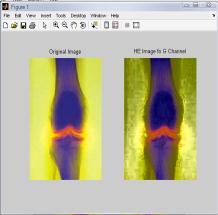
IntheTable3,differenttechniquesarecomparedonthebasis ofvariousparametersforHSVcolormodel.Fromthistable,it is clear that value of error color for BPDHE is less as comparedtotheothertechniques.Itmeansthatthereisvery littledifferenceinthecolorsoftheoutputimageascompared totheinputimageevenafterenhancement.Eventhevalueof CPSNR is more for BPDHE which is also desirable for any techniquetoworkefficiently.MoreCPSNRmeanslessnoise enteredduringenhancement.Intermsofentropy,theoutput entropyofR,GandBcomponentsismoreascomparedto input entropyincase ofall the techniques exceptBBHEin which all component output entropy is less than input entropy.Itmeansallthecomponentsshowmoredetailsin the image after enhancement using HSV Color model for medicalimage.
(d)BPDHEImage (e)RACEApproach
FromtheFig.3,itisclearthatthevisualqualityofBPDHEis goodascomparedtotheothers.TheresultsfromBPDHEis showingthebestqualityimageintermsofcolorasthecolors of the input and output image are almost same, while in others there is lot of variation in the color of the output image.
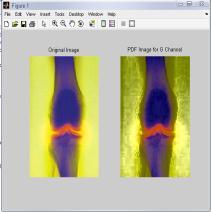
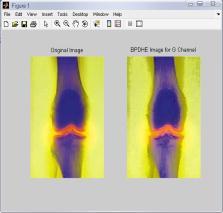
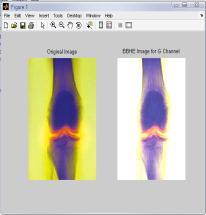
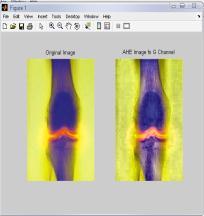
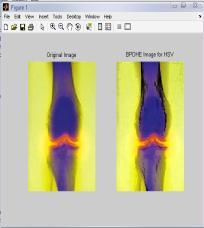
4.4 Results for G-channel of RGB Color Model for ‘Bonescan’ Image
IntheTable4,differenttechniquesarecomparedonthebasis ofvariousparametersforG-Channelcolormodel.Fromthis table,itisclearthatvalueoferrorcolorforBPDHEislessas comparedtotheothertechniques.Itmeansthatthereisvery littledifferenceinthecolorsoftheoutputimageascompared totheinputimageevenafterenhancement.Eventhevalueof CPSNR is more for BPDHE which is also desirable for any techniquetoworkefficiently.MoreCPSNRmeanslessnoise enteredduringenhancement.Intermsofentropy,theoutput entropy of component R is more as compared to input entropyincaseofallthetechniquesexceptBBHE,incaseof which all the output entropy values are less than input entropyvalues.OnlyincaseofGCandBPDHEallcomponents are having more value. It means only component R show moredetailsintheimageafterenhancementusingG-Channel Colormodel
(d)BPDHEImage (e)RACEApproach
Fig.-4: Imagesof“BONESCAN”AfterEqualizationUsingGChannelofRGBColorModel

FromtheFig.4,itisclearthatthevisualqualityofBPDHEand GCisgoodascomparedtotheothers.But,theresultsfrom BPDHEisshowingthebestqualityimageintermsofcoloras the colors of the inputand output image are almost same, while in others there is lot of variation in the color of the outputimage.
4.5 Analysis of Computation Time of Image EnhancementTechniquesfor ColorImages
Table -5: ComputationTimeforColorImages
ItisclearfromtheTable 5thattheHSVcolormodel takes more time for processing than the G-Channel color model. This is because, for using HSV color model, first the RGB imageisconvertedintoHSVcolormodelusinglargenumber ofequationsandthenenhancementtechniqueisappliedon it.Then,afterthecompletionoftheenhancementtechnique HSVmodelisbackconvertedintoRGBcolormodel.Thus,the processingtimeismore.ButincaseofG-Channelcolormodel processingisdirectlydoneonRGBmodel.Thisisthereason that the processing time of HSV color model is more as comparedtotheG-Channelcolormodel.
3. CONCLUSIONS
Therearevarioustechniquesforenhancingthecontrastof thedigitalimage.Afterimplementingsomeofthesecontrast enhancement techniques, it is concluded that the enhancement of different types of digital images is dependentontypeofapplication.Fromthetableswhichare shown above, it is concluded that Brightness Preserving Dynamic Histogram Equalization is the most suitable techniqueintermsofAbsoluteContrastErrororErrorColor, Contrast Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (CPSNR). The visual qualityoftheimagesusingBPDHEisgoodascomparedto others with a limitation of high computation time for the implementation of BPDHE in comparison to all other techniques.
For color images, two different models are considered, they are HSV and G-Channel color model. All techniques are implemented on these two-color models. BPDHE technique provides good result both in terms of visual quality and objective performance parameters like Error Color and CPSNR. The computation time for implementinganytechniqueinthecaseofG-Channelisless ascomparedtoHSVcolormodel.Hence,itisconcludedthat enhancement techniques are dependent on type of application
Inthefuturework,forthecontrastenhancementpurpose, moretypesofdigitalimagescanbetakenfromthedifferent applicationfields,sothatitbecomesclearerthatforwhich applicationwhichparticulartechniqueispreferredbothfor gray scale images as well as color images. More new parameters can also be considered for the evaluation of enhancementtechniques.Newothercolormodelscanalso be chosen for better comparison purpose and also optimization techniques can be utilized to lower the complexity.
REFERENCES
[1] H. Mzoughi, I. Njeh, M. Ben Slima and A. Ben Hamida, "Histogramequalization-basedtechniquesforcontrast enhancement of MRI brain Glioma tumor images: Comparative study," 4th International Conference on AdvancedTechnologiesforSignalandImageProcessing (ATSIP),pp.1-6,2018.
[2] A. M and J. Simon, “Color Sensitive Adaptive Gamma CorrectionforImageColorandContrastEnhancement,” InternationalConferenceonHummingBird,2014.
[3] A. Aggarwal, R.S. Chauhan and K. Kaur,” An Adaptive ImageEnhancementTechniquePreserving,Brightness LevelUsingGammaCorrection,”AdvanceinElectronic andElectricEngineering,Vol.3,No.9,pp.1097-1108, 2013.
[4] T.CelikandT.Tjahjadi,“AutomaticImageEqualization and Contrast Enhancement Using Gaussian Mixture Modelling,”IEEETransactionsonImageProcessing,Vol. 21,No.1,2012.
[5] S.C.Huang,F.C.ChengandY.S.Chiu,“Efficientcontrast enhancementusingadaptive gammacorrectionwith weighting distribution,” IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,Vol.22,Issue3,2012.
[6] T. Celik and T. Tjahjadi, “Contextual and Variational Contrast Enhancement,” IEEE transactions on image processing,Vol.20,No.12,2011.

