A REVIEW ON SYNTHESIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF SUPERHYDROPHOBIC COATING
Ajmal Ubaid1, Manu Harilal2 1Ajmal Ubaid, Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, Amal Jyothi College of Engineering, Kerala, India 2Manu Harilal, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, Amal Jyothi College of Engineering, Kerala, India
2Manu Harilal, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, Amal Jyothi College of Engineering, Kerala, India
***
Abstract - Superhydrophobic surfaces are high water repellent surfaces having a water contact angle greater than 150°.These surfaces were developed by scientists by taking inspiration from nature. There are various methods to manufacture a superhydrophobic surface, such as chemical etching, dip coating, spin coating, spray coating, sol-gel processing, electrochemical deposition, chemical vapour deposition, etc. The superhydrophobic surface shows excellent self-cleaning, anti-corrosive, antifogging properties. Also has good chemical, mechanical and thermal stability. The applications of the surfaces are in the fields of aerospace, automobile, ships, medical, solar panels etc. This article contains the basics of Superhydrophobicity, the developing methods, and the experimental results obtained from different pieces of literature
Key Words: Superhydrophobic, Water repellent, Water contact angle, Self-cleaning, Coating
1. INTRODUCTION
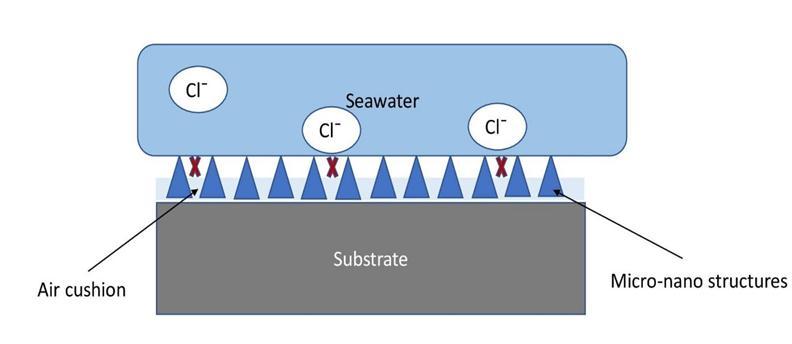
Humansaregeneratingenergybyexploitingrenewableandnon-renewableresourcesintheoceanoverthedecades.Inthe currentscenario,oilandgasindustriesandmarinerenewableenergycompaniesareholdingthedominationinthemaritime sector.However,theyarelosingahugepartoftheireconomytoitsmaintenance.AccordingtothereportsfromtheUS,the annualcostforrepairingthestructuresbythesecompaniesarebillionsofdollars[1].Corrosionandbiofoulingarethetwo majorproblemsforallmarinesectorsrangingfromshipstoturbinesandbuoysusedforoceanenergy[2].Inthecaseofoiland gasindustries,steelandlow-gradealloysaremostlyusedtoconveythemediaduetotheirgoodtensilestrengthandhigh weldability.Buttheyaresusceptibletocorrosiveattackundertheacidicenvironment[1].Anothermainissuefaced bythe maritimesectoristhehugefuelconsumptionbyshipswhichisduetothebiofoulingphenomenon.Mostofthematerialsused forbuildinghullstructuresarehighlycorrosionresistantbuttheyarenotmuchresistanttothemicroorganismintheseawater that causes biofouling. The adherence of microorganisms on the ship hull can leadto fouling influenced corrosion which graduallyreducesthelifespanofthematerial[3].Fromtheinternationalreports,corrosionconsumesabout3-4%oftheGDP ofindustrializedcountries[4].Totacklethisconsequentialfinanciallossinthesesectors,suitableprotectivemethodshave beendevelopingovertheyears.
In the case of corrosion protection in steel pipelines, cathodic protection, corrosion inhibitors, and various methods of protective coatings such as fusion bonded epoxy, three-layer polyolefin, bituminous enamel, asphaltic mastic have been applied.Inpractice,mostofthetechniquesareexpensiveandnoteffectivewhenusedinlargestructures.Topreventthe biofoulingactivity,somanymethodshaveemergedincludingpre-treatingthematerialsurfaceandalsoavarietyofprotective coatings[1].Amongthepreparationmethodsmentioned,nosuchcoatinghasprovenaneffectiveoneinreal-timeapplications [5].Overcomingthesechallengesisnowaglobaldiscussionbetweenthescientificcommunityandindustrialists.Becauseall coastalcountriesareinvestingmoreinthemaritimesectorincludingoffshorewindandoceanenergyforgeneratingenormous powerfromrenewablesourceswhichwillbeamajorassetinthecomingyears.Forthis,biofoulingonthemarinestructuresis the extensive challenge industries are facing [2]. With the advancement in surface coating technology, scientists have developedahigh-waterrepellentsurfacethatcanpreventcorrosiveagentsaswellassecedemicro-organismsinthemarine environment.
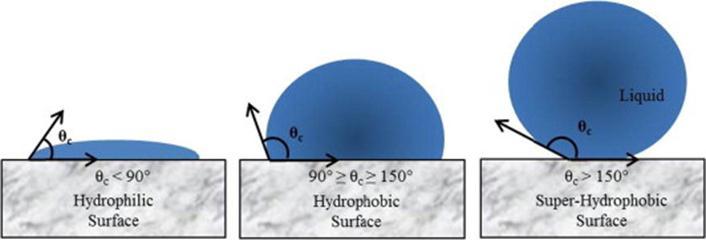
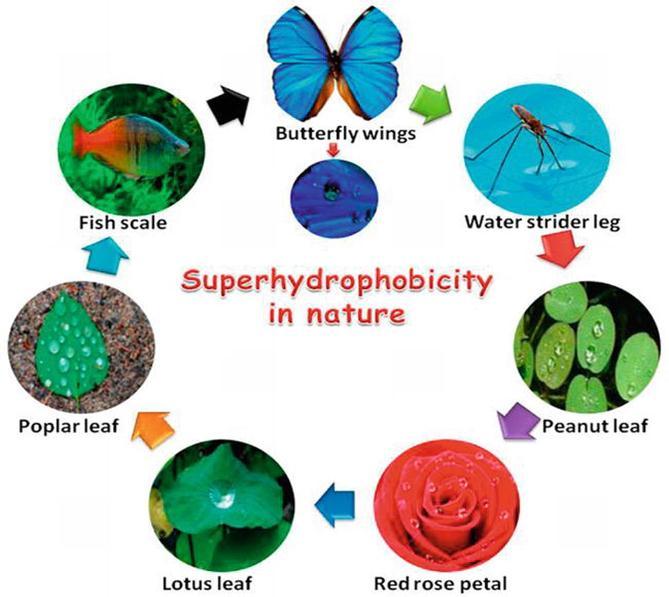
Byshowingsuperiorwater-repellingproperty,superhydrophobicsurfaceshavegainedmajorattentioninthefieldofsurface engineering[6].Thesesurfaceswereinspiredbynatureeg;Lotusleaf,butterfly,scalesofshark,geckofootetc.(Fig1.1)[7]. Superhydrophobicityistechnicallydefinedasthesurfaceshowingawatercontactanglegreaterthan150°asseeninFig1.2 [6].CassieandBaxterwerethetwoscientistswhofirstreportedthisphenomenoninreferencetotheworkdonebyWenzelin 1936.Comparisonstudiesweredonebycassie –Baxterbetweenporousandflatsurfaces,andtheyreportedthatporous surfacesshowhighapparentcontactanglethanflatsurfacesbecauseofthemaintenanceofairatthisinterface[8].
Overtheyears,tremendousresearchhasbeencarriedoutbecauseofitsbroadapplicationinindustriesaswellasinbiological sectors [9]. Anti–biofouling paints for boats, coating for solar energy panels, self-cleaning exterior paints, blood vessel replacement,woundmanagementaresomeoftheexamplesfortheapplicationofsuperhydrophobiccoating.Toobtaina Superhydrophobicitycoatingsurfacetherearetwomainapproaches.,Bottom-upandTop-down.Intheformerapproach,low surfaceenergymaterialsarecoatedonthemicro/nanostructuredsurface.Thelatterinducewidespreadmicro/nanoroughness onahydrophobicsurfacehavinglowsurfacefreeenergy[10].
Thevariousfabricationtechniquestodevelopsuperhydrophobicsurfacesobtainedfromliteraturearechemicaletching,dip coating, spin coating, spray coating, Electro-chemical deposition, Sol-gel processing, Chemical vapour deposition, Phase separation,wetchemicalreaction,Lithography,andothers.Amongthese,someareindustriallypreferredduetotheirlowcost ofprocessing,easyprocedure,andhighdurabilitycoatings.Scientistsareworkingonthemethodswhicharecomplicatedand havinglessernumberofdatatoobtainoptimumresultssothatitcanbeappliedcommerciallyinthenearfuture[11]
2. EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
2.1 Etching
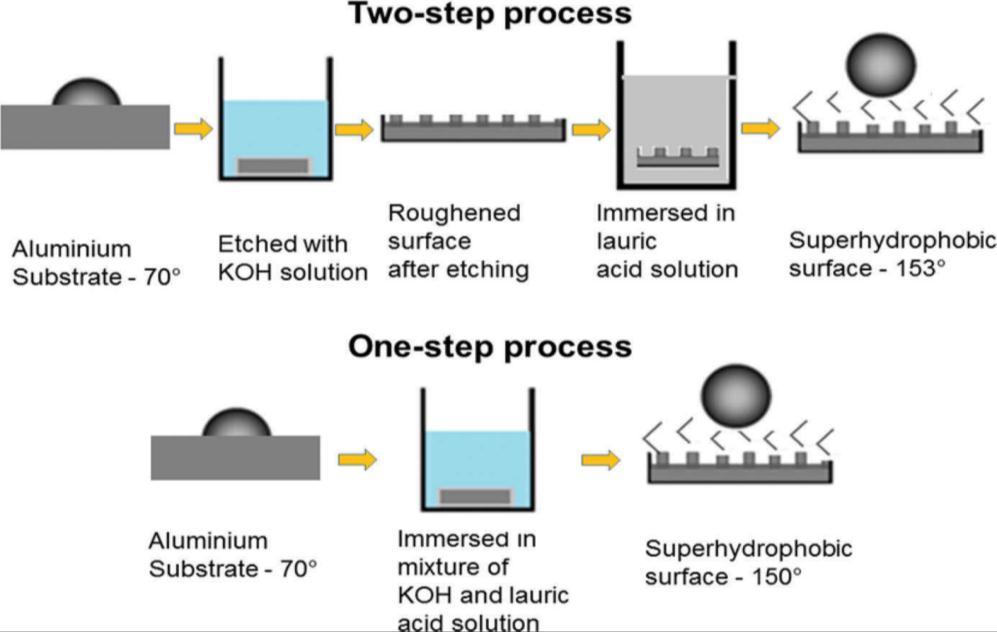
Itistheconventional coatingtechniqueinwhichthemetal isimmersedina mixtureforsometime[11].Therearetwo approachesinetchinga)One-stepprocessand2)Two-stepprocessasshowninfig.2.1.Varshneyetal.[13]studiedthetwo-step processbyimmersingAlsubstrateinKOHsolutionandtheninLauricacidsolution.Inaone-stepprocess,theyimmersedthe substrateinamixtureofKOHandLauricacidsolutionfor5–60min.HerebothrougheningandloweringsurfaceenergyofAl doneinasinglestep.Wangetal.[14]reportedasynthesisofsuperhydrophobicfilmonpureMgsurfacethroughchemical
© 2023, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page618

etchingmethod.Theyachievedawatercontactangleof154°andaslidingangleof3°withprominentwaterrepellencyandgood chemicalstabilityduetoitsflowerlikestructuresandchemicalbonding.
2.2 Dip Coating
Thedipcoatingisacontinuousprocessinwhichthesubstrateissubmergedintothesolutionataconstantimmersionrateand thecoatingisdevelopedbywithdrawingthemetalsubstrateaftersometimeofimmersionasshowninfig.2.2.Drainingof excesssolutionfromthesurfaceandevaporationofthesolventduringwithdrawingresultsinasurfacecoating[1].XiaZhang andhisco-workersfabricatedthesuperhydrophobicsurfacefromamixtureofTiO2nanowires,Tetrahydrofluran,andPDMSon apieceofglass.HerePDMSactsaslowsurfaceenergymaterial[15].Thespeedofpullingorwithdrawingplaysamajorrolein determiningthefilmthickness.Lowspeedproducesthickfilmswhilehighspeedgeneratesthinfilms[1].

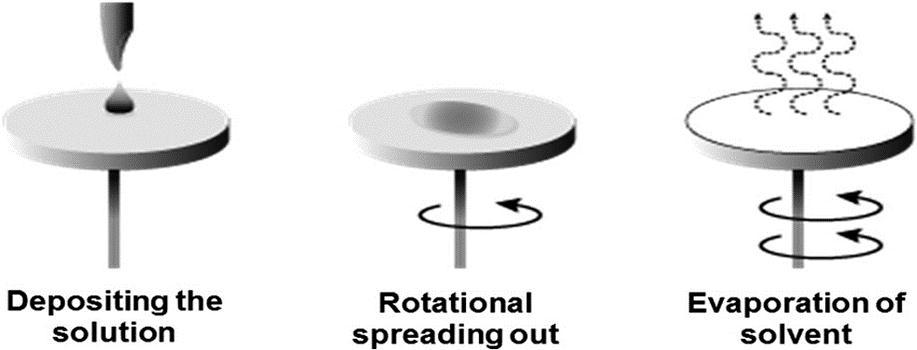
2.3 Spin Coating
Itisoneofthesimplecoatingtechniquesinwhichasolutionisdepositedonasubstratethatisspunoffatahigh-velocityrate as seen in fig. 2.3. Here spinning speed describes the film thickness [11]. Mukesh Kumar Meena et al. [7] prepared polyurethane-basedsuperhydrophobiccoatingonsteelsurfacethroughspincoatingtechnique.Thesolutionwasprepared fromamixtureofPU,2–Propanol,SiO2HDTMS.Surfaceroughnesswascreatedbysimpleetchingpriortothecoatinginwhich improvestheadhesionstrengthofthecoating.Generally,thecoatingisdonein3steps;1000rpmfor30s,1500rpmfor30s, andfinally2000rpmforthe60s.Thistechniquepossessessimpleapproachandisanexcellentmethodonlaboratoryscale.
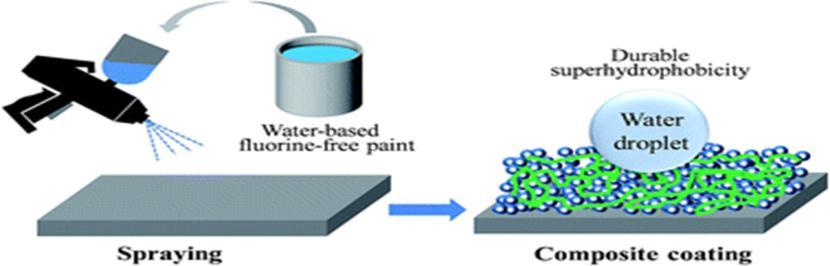
2.4 Spray Coating
Inthistechnique,the solutionwhichisto becoatedis sprayed onto a substrateas seenin fig.2.4.Thecoating precursor requiresheatingormeltingpriortothesprayingprocess[11].KonXuetal[18]havedevelopedacolourfulsuperhydrophobic concretecoatingonanordinaryconcretebysimplespraycoatingtechnique.Theyusedamixtureofament,sand,water,based stoneprotector,anddyesforconcretecolouring.Themixturewasgroundintopowdersandsprayedontothesubstratebya sprayerwithhighforce.Polizosetal[19]havedevelopedaspraycoatingsystemtodepositSHCtransparentsilicananoparticle filmonglasssubstrates.

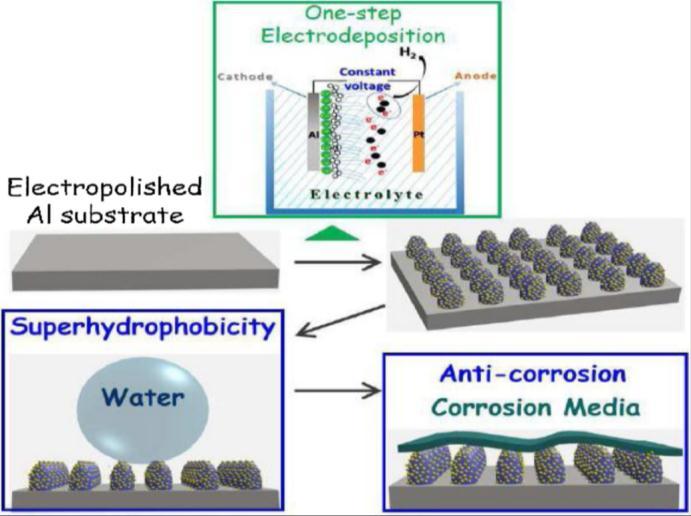
2.5 Electrochemical deposition
Inthis,SHCcoatingistheresultofchemicalreactionsofelectrolyticsolutionwhichistriggeredbytheapplicationofcurrent [1].SchematicrepresentationofElectrochemicaldepositionisshowninfig.2.5.Anodicoxidation,depositionusinggalvanic cell,polymerization,andelectrochemicalanodization,etc,aresomeoftheproductiontechniquesthat makeelectrochemical depositionawidemethodforthefabricationofSHC[9].
YanLiuet.al.[21]successfullyfabricatedSHConacopperplateviaelectrochemicaldeposition.Theyhadtaken2copperfor theanodeandcathode.Theelectrolyticmediumusedforthisprocesswasamixtureofceriumchloride,mystericacid,and ethanol.ZengguoBaiandBinZhang[22]havepreparedanovelreducedgrapheneoxiderGO/Nicompositecoatingonstainless steel through electrodeposition. They deposited a thin layer of Ni on the substrate before the application of the rGO/Ni compositelayer.TheelectrolytetheyusedasthemediumwaspreparedbyaddingNiCl2.6H2O,orthoboricacid,potassium chloride,sodiumdodecylbenzenesulfonate,andrGO.ThesuperhydrophobiccoatingsweregeneratedbythedepositionofNi onthestainless-steelsubstratefollowedbythedepositionofrGO/Nicompositemix.
2.6 Sol-gel process
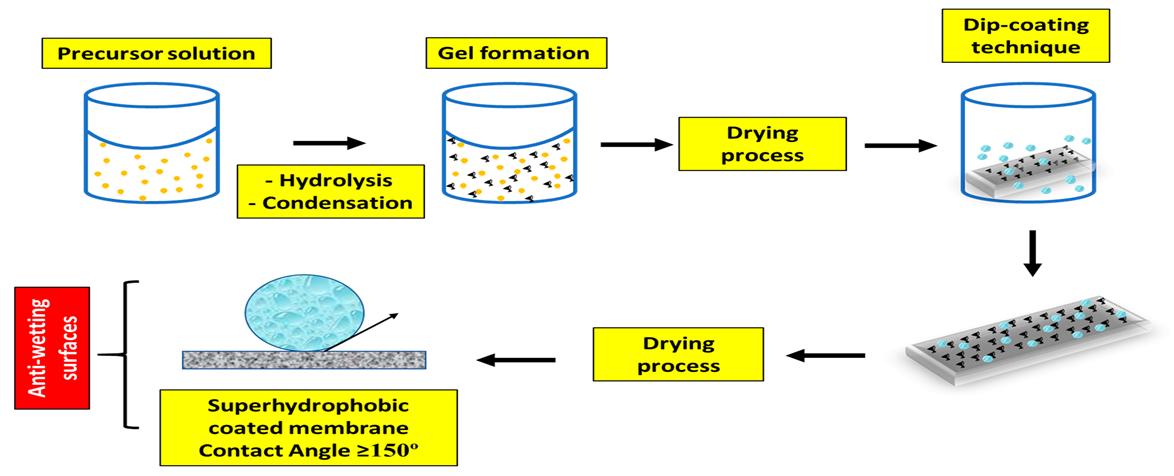
Thesol-gelprocessisthemostpreferredmethodfordevelopinggoodqualitycoatings.Theinorganicsilicaandorganically modifiedsilanescompriseahybridsol-gelthatformsa3Dnetworktoimpartsuperhydrophobiccharactertothecoatedsurface [1]. Spray coating, spin coating, and dip coating are the 3 techniques that can be used to deposit the sol-gel on various substrates [9]. Fig.2.6 showstheschematic representationoftheSol-gel coatingtechnique. S.Liu et al [23] reportedthe synthesisoftransparentSHCviasol-gelprocessingoflong-chainFluoroalkylsilane.Thecoatingmixwaspreparedbyadding ethanol(solvent),ammonia(catalyst),andwater.Thefinalsuperrepellentsurfacewasachievedbytheimmersionofglassin thepreparedsolutionfordifferentdepositiontimes.
2.7 Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD)
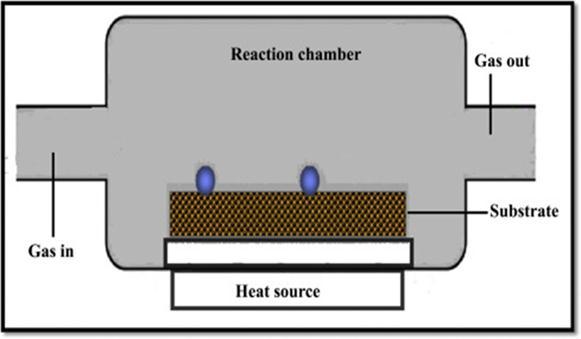
Itisaprocessinwhichgaseouselementsgetdepositedontoahotsubstratethatisplacedinachamberasshowninfig.2.7.A thin layer of coating is achieved under the reaction with the hot surface [11]. Zhengwei Cai et al [25] have successfully fabricatedtransparentSHConthecandlesootthroughCVD.TheprecursortheyhadtakenforthedepositionwasMTMSand theCVDprocesswasfollowedbycalcinationat450°C.

TakahiroIshizakietal.[26]reportedasynthesisofSuperhydrophobiccoatingonAZ31MgalloyusingMicrowavePlasma
Enhanced Chemical Vapour Deposition (MPECVD). The raw materials used in the chamber were a gas mixture of trimethylmethoxysilane(TMMOS)andAr.Toobtainsmoothdepositiononthesubstrate,theyhadkeptthepartialpressuresof bothArandTMMOSconstant.Theyalsostudiedtherelationshipbetweenwatercontactangleanddepositiontimebyvarying thetimeparameterfrom10to30minutes. © 2023, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 |
2.8 Hydrothermal Method
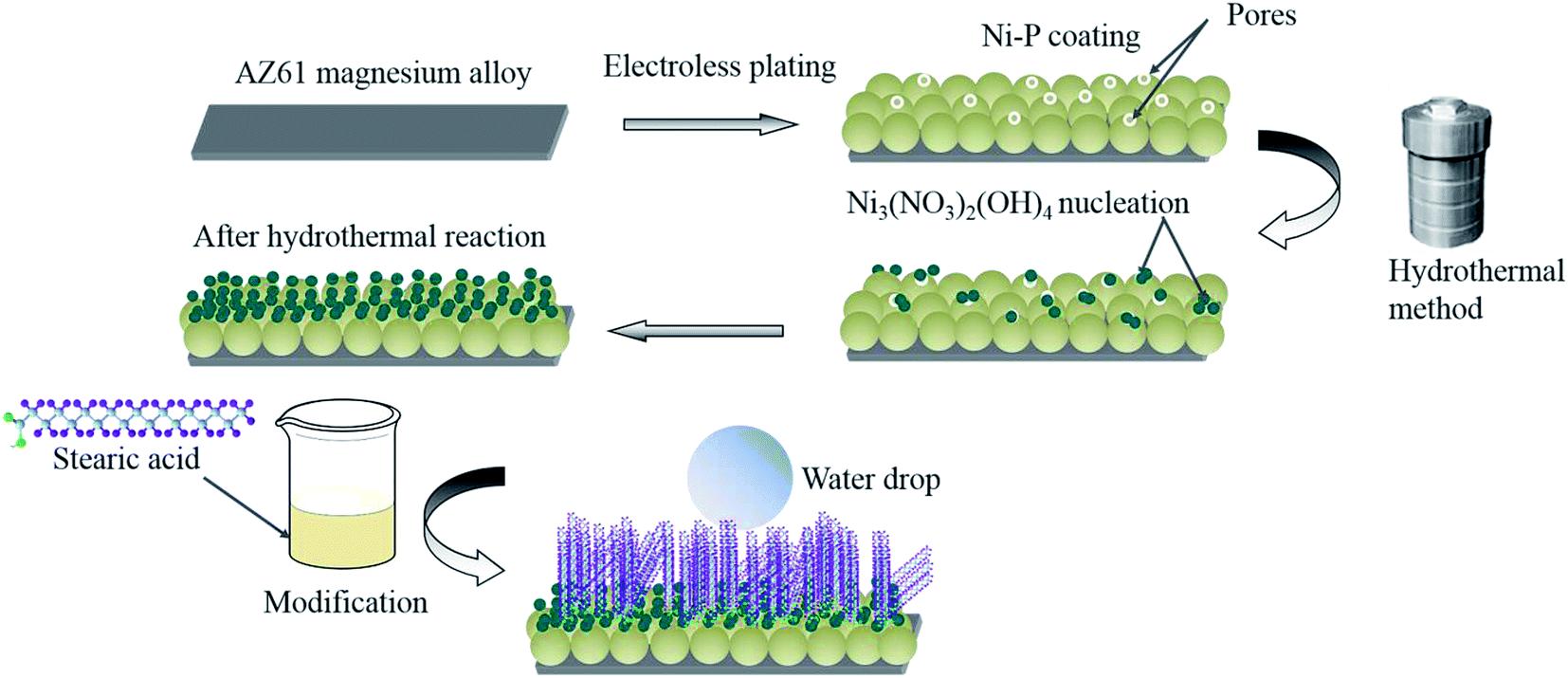
Itisanin-situcoatingtechniquethatisusedtoproducecrystallinesubstancesfromhotaqueoussolutionsathighvapour pressure [9]. This method can be applied to get micro nanostructured superhydrophobic features on a variety of metal substratessuchasstainlesssteel,carbonsteels,magnesiumalloys,Aluminiumalloys,andpurecopper[1].Thisreproducible techniqueisveryeffectiveforrougheningthesurfacebyentrappingairinthevalleysbetweenthestructure,thusmigratingthe corrosionionsleadstoimprovedcorrosionresistance[9].JingYuanetal.[28] haddevelopedasuperhydrophobiccoatingon an electroless plated magnesium alloy via hydrothermal method followed by immersion in stearic acid solution. The homologoussolutionwaspreparedbymixingNi(NO3)2.6H2Oandethanol.TheTeflonlinedstainlesssteelautoclavehadbeen heatedupto160°Cfor9-24hoursafterimmersingthenickel-platedmgalloyinthesolution.Finally,thesamplewasimmersed inethanolstearicacidsolutionfornanostructuremodification.ShijunHeetal.[29]hadfabricatedasuperhydrophobicsurface by developing micro nanostructured Fe3O3 on N80 steel through the hydrothermal method. They treated it at different temperature ranges from 120°C to 180°C for different reaction times. The superhydrophobic surface was obtained after annealingat500°Cfor2hoursandawaterbathinODAethanolsolutionfor12hours.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 SHP coating by chemical etching technique
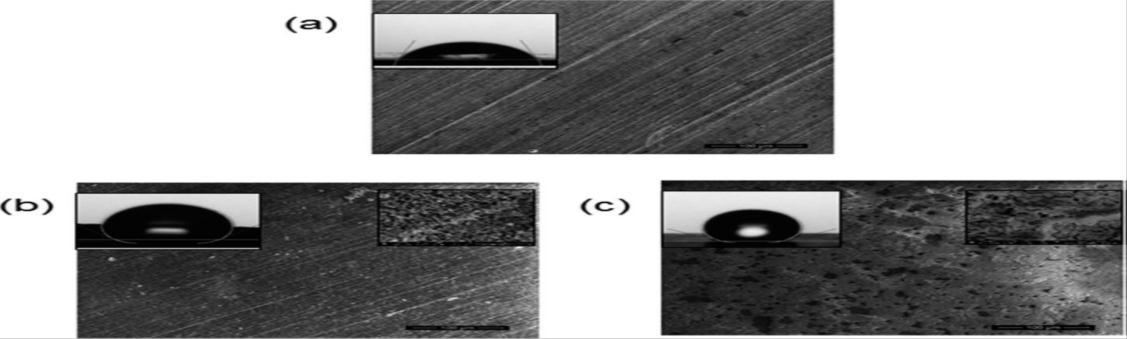
Varshneyandhisco-workers[13]couldobtainawatercontactangleof150°fromtheone-stepetchingprocessand153°from thetwo-stepprocess.Theyhadobservedtheas-receivedaluminiumandcoated(modified)surfacesbySEMandtheimagesare shownhereinfig.3.1.
Slightmorphologicalchangeswereobservedonthealuminiumwhenimmersingfor30sec(fig.3.1.(b)).Whentheyincreased theimmersingtimeto60sec,craterlikemicrofeatureswereseenclearlyinhighmagnifiedSEMimagesasshowninfig.3.1(C). Themajorincreaseinwatercontactanglewasnoticedwiththeincreaseinimmersingtimeforbothprocesses[13].
© 2023, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008
Certified Journal | Page622

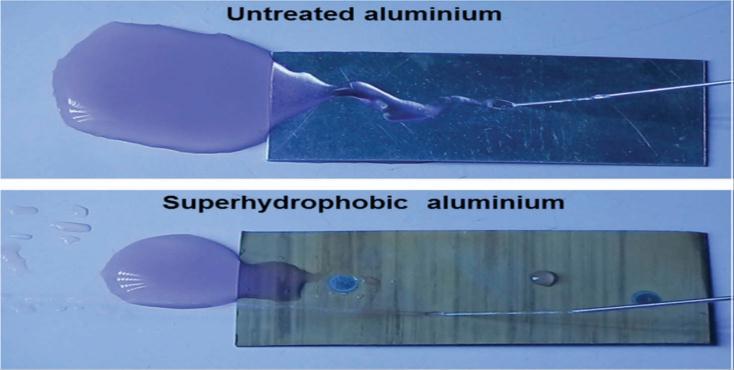
Theeffectivewaterrepellencyofthesuperhydrophobiccoatingwasexhibitedunderahigh-speedwaterjettestasshowninfig. 3.2.Thewatergetsspreadontheas-receivedaluminium,butitbouncesintheoppositedirectiononthecoatedaluminium surface[13].
3.2 SHP surface by dip-coating technique
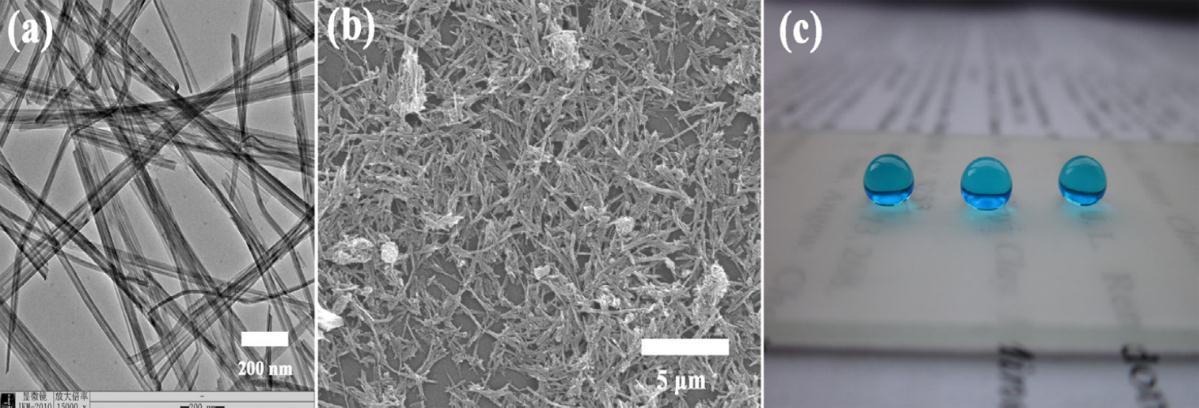
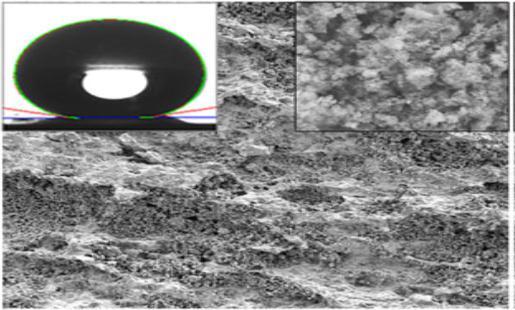
Xia Zhang et al could successfully generate SHP coating with a water contact angle of 158 ± 2° and a sliding angle of 5° [15].TheyhadcharacterizedthecoatedsurfaceusingTEMandSEManalysis.Fig.3.3displayedhereshowstheTEMimageof theTiO2 nanowires.Fromthestudies,itwasconfirmedthesolidstructureofthenanowireswithadiameterof20–30nm rangeandlengthofabout5µmtomorethan10µm.Thefig.3.3b)showstheSEMimagesofthecoatedsurfaceandcouldsee theaccumulation ofTiO2 nanowiresthatform dendritestomake the surface roughened. Thesuperhydrophobicityofthe surfacewasclearlydefinedbytheimageofsphericaldropletsofwaterontheTiO2 nanowirecoatingasucanseeinfig.3.3C).

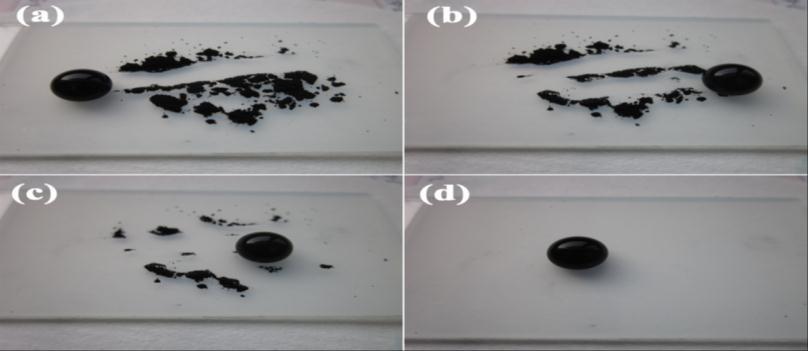
Theself-cleaningfunctionofthesuperhydrophobiccoatingsurfacewasstudiedwithgraphitepowderascontaminants.The self-cleaningprocessisshowninfig3.4.Thecoatingwhichisbeingscratchedbymechanicalmeanscanberegeneratedby immersing in TiO2 nanowire suspension and drying. The regeneration was easy and it will meet the future needs in the applicationofsuperhydrophobicity[15].

Thetransformationstudiesofthesuperhydrophobiccoatingweredoneusingultravioletlightandcouldconcludethatthe conversion of a superhydrophobic surface to a hydrophilic one was mainly due to the surface composition and not the microstructure.Thebenefitsofthedippingmethodincludeeasyrepairability,anindustrialmethodofimplementation,and applicabilitytomakeapromisingpracticalapplicationpotential[15].
3.3 SHP surface by the spin method
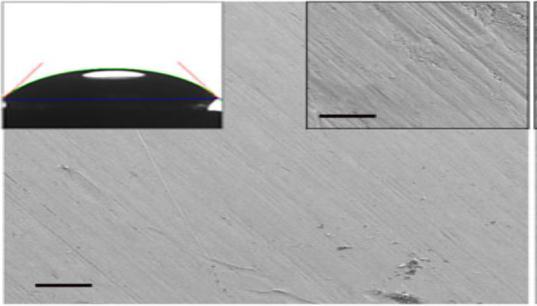
TheSHPcoatedsamplepreparedbyMukeshKumarMeenaetal[7]showedexcellentwaterrepellencywithawatercontact angle(WCA)of165±5°andatiltangleof4°±2°.TheSEMimagesofbothuncoatedandcoatedsteeltogetherwithcontact anglesareshowninfig.3.5.
Thefloatingtestwasdonetoexaminethefloatingabilityofthecoatedsample,theuncoatedsamplesunkrapidlyandthe coatedsampletofloatonthesurfaceofthewaterasshowninfig.3.6.Theyhadstudiedtheanti-corrosionpropertyofthe superhydrophobiccoatingthroughanelectrochemical experimentinPotentiostatbyusing3.5(w/v)%NaCl solutionfor 30min. The coated sample had shown an increase in corrosion potential and a decrease in current density as that from uncoatedsteelwhichconfirmedtheanti-corrosionpropertiesofthesuperhydrophobicsteel.TheSHPcoatedsteelexhibited excellent self-cleaning, anti-fogging and anti-corrosion properties, which makes the coating useful for many industrial applications[7].
3.4
TheSuperhydrophobiccoatedsurfacefabricatedbyKonXuetal.[18]showedawatercontactangleof158±0.5°andasliding angle of 5 ± 0.8° as shown in fig 3.7. The coating showed high robustness and retained superhydrophobicity even after abrasion,knifescratchandtapepeel.Itexhibitedexcellentchemicalstabilityandgooddurabilityandcouldresistextreme weather conditions showing anti-icing, anti-irradiation, anti-corrosion and self-cleaning capabilities. The CSC (Colourful SuperhydrophobicConcrete)coatingcouldbeeasilyappliedonlargestructuresandisexpectedtohavepromisingapplications inconcretearchitectures.
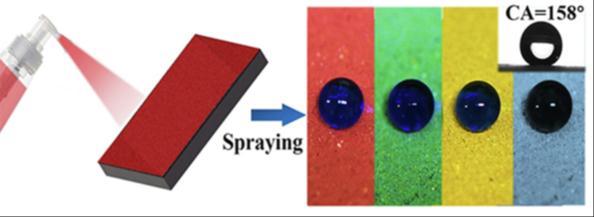
Thehighlytransparent,anti-soilingSHPcoatingdevelopedbyPolizosetal.[19],exhibitedawatercontactangleof166°.Their studiesshowedamajordependenceonwatercontactangleandtheratioofthepolymerbindertothenanoparticle.Theycould achievehighresistancetofallingsandwhichcanreducethecostsofperiodiccleaningofsolarenergyconversionsystems[18].
3.6
Coating by Electro-Chemical Deposition method
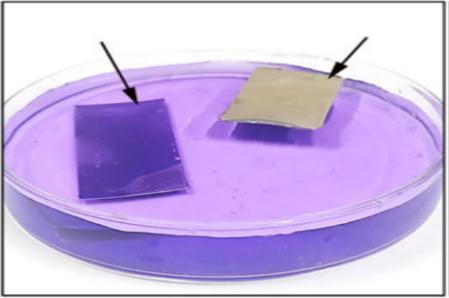
YanLiuet.al.[21]fabricatedasuperhydrophobicsurfaceonacopperplatethroughtheelectrodepositionmethod,witha maximumwatercontactangleof161.7°±2°.Theyhadnoticedthegradualincreaseincontactanglewhentimeincreasedfrom 5 to 30min. The SEM images below show the transition from irregular rod-like microstructures to hierarchical micro –nanostructures.Fig.3.8(c)showslargerpapillaestructuresafter40minofdeposition.

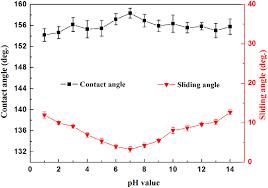
Thechemicalstabilityoftheas-preparedsurfacewasexaminedbyimmersingthesampleindifferentsolutionswherePH rangingfrom1to14.Theyobservedonlyasmalldecreaseinwatercontactanglewhichconfirmedthechemicalstabilityofthe superhydrophobiccoating[21].
ZengguoBaietal.[22]achievedawatercontactangleof162.7°±0.8°andaslidingangle2.5°±1.0fromasuperhydrophobic stainlesssteelsurfaceviaelectrodeposition.Thecoatingwasabletowithstandthedurabilitytestwithasmallchangeinthe WCAfor100cyclesofmechanicalabrasion.Theas-preparedsurfaceshowedexcellentself–cleaningpropertiesandcorrosion resistance.Itisoneofthesimple,controllable,andeconomicaltechniquestofabricatewaterrepellentcoatingwithoptimum surfaceproperties.
3.5 SHP coating by sol-gel processing
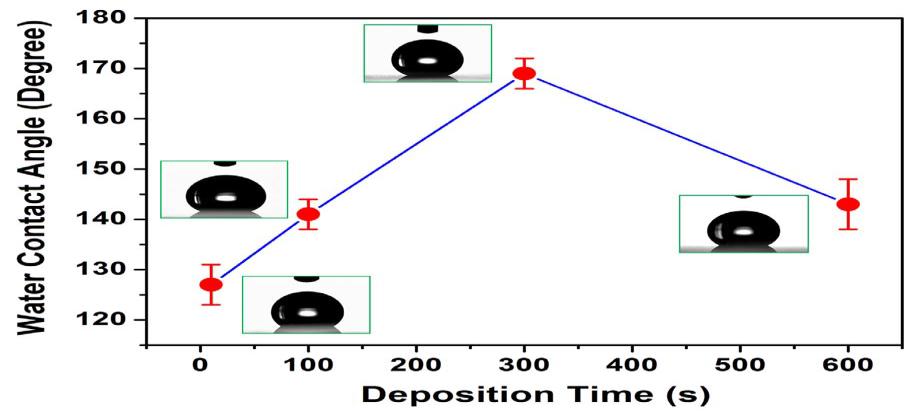
S.Liuetal.[23]hadsuccessfullydevelopedasuperhydrophobiccoatingwithawatercontactangleof169°andaslidingangle oflessthan5.Thepreparedsurfaceexhibitedarough,wrinkled,hilllikemorphologywherethewaterdropscouldforma sphericalshape.Thedepositiontimeofcoatingplaysamajorroleindeterminingthewettabilityofthesurface.Theyhad observedagradualincreaseinWCAwithrespecttotheincreaseindepositiontimeof10s,100s,300s,buttherewasadecrease inWCAwhentimeincreasedto600sasshowninfig.3.9.
AsweallknowthatthemajorconcernofSHPcoatingisitsmechanicalstability.Thepropertiesexhibitedbythesurfacecanbe easilyaffectedbyscratches,abrasionetc.Theenhancementinthemechanicalstabilityofthecoatingwasachievedbyadding variousmicro/-nanoparticlesinthesol-gelmatrix.
© 2023, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page626

AnopticalphotographofsphericalwaterdropsonthesuperhydrophobicT-3coatingisshowninfig.3.10.Thedeveloped superhydrophobicsurfaceshowedaverygoodabilitytoself-cleanandsuchopticallytransparentsuperhydrophobiccoatings arevitalforself-cleaningapplications[23].
3.7 SHP coating by the chemical-vapour deposition method
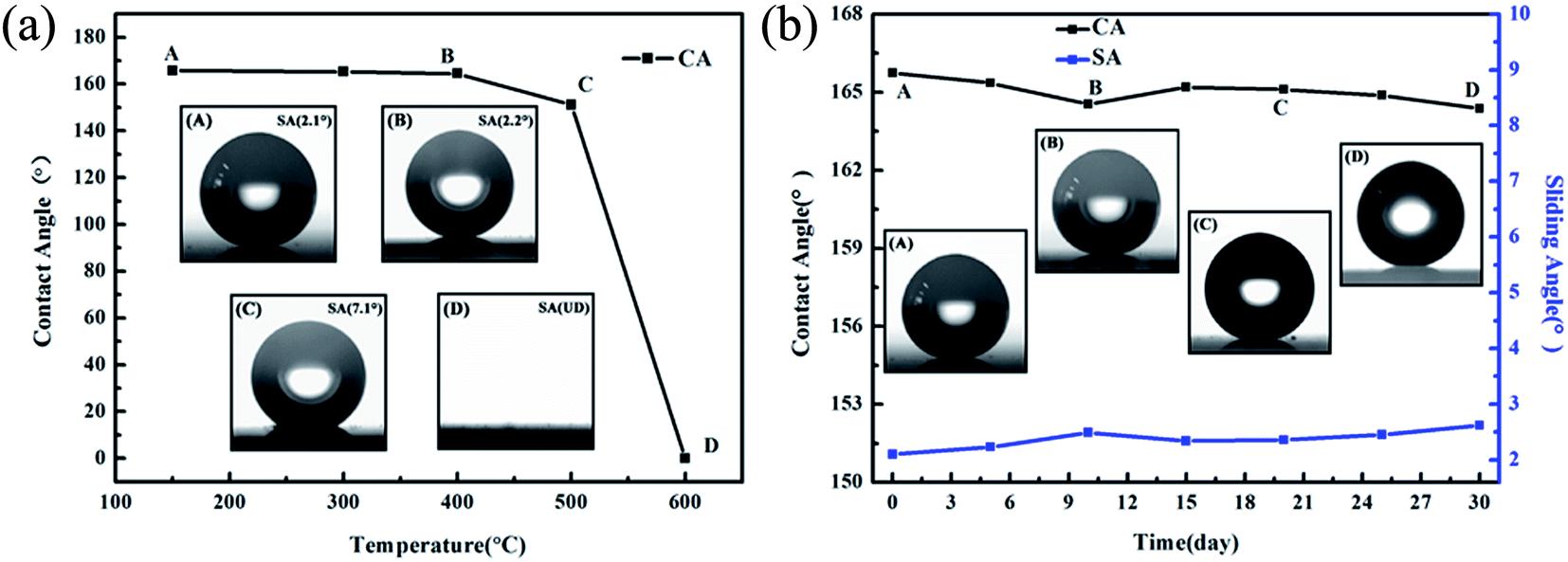

ZhengweiCaietal.[25]havefabricatedahighlytransparentsuperhydrophobichollowfilmsandachievedawatercontact angleof165.7°andaslidingangleof2.1°.Thedevelopedfilmsmaintainedgoodthermalstabilityupto500°Candturnedinto hydrophilicwhenthetemperaturehadbeenincreasedto600°C.Theyexaminedthemoistureresistanceofthecoatingby exposing it to an ambient condition for 30 days. The film had maintained the superhydrophobicity which confirmed the excellentmoistureresistancepropertyofthecoating.Boththermalstabilityandmoistureresistanceisgraphicallyshowninfig. 3.11.
Takahiro Ishizaki and his co-workers [26] had confirmed the superhydrophobicity of the film they had prepared by the topographicstudiesandhigherwettabilityofthesurface.Thedepositiontimeplaysamajorroleindeterminingthesurface roughness and the superhydrophobicity of the coating. As time increases, water contact angle increases resulting in superhydrophobicityasshowninfig.3.12.Thedecreaseincurrentdensityofthecoatedsurfacebymorethanthreeordersof magnitudeasthatofuncoatedAZ31alloyhadconfirmedtheimprovementincorrosionresistance.Thechemicalstabilityofthe coatingwasexaminedunderdifferentPH.Theresultsshowedexcellentstabilityinbothacidicandneutralaqueoussolutions, butlowerstabilityinalkalineaqueoussolutions.Higherchemicalstability,improvedcorrosionresistancewerethekeyresults theyhaveachievedtoexpandthecorrosion-resistantfilmsforvariousengineeringmaterials.

3.8 SHP coating by Hydrothermal method

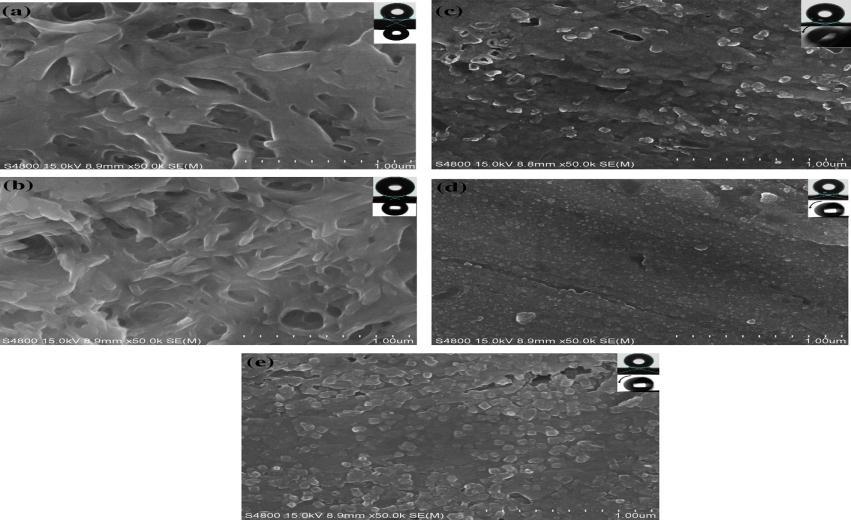
ThesurfacefabricatedbyJingYuanetal.[28]showedawatercontactangleof155.6±.3°at120°Candaslidingangleof2°, possessedgoodsuperhydrophobicity.TheSEMimagesofthepreparedfilmat120°Cfordifferentreactiontimesareshownin fig.3.13.Thefilmexhibitedhighmechanicalandchemicalstabilitywhichmakethemsuitableforvarietyofapplications.They hadinvestigatedself-cleaningabilityofthecoatingusingaluminapowderandthereportedperformancewasexcellent.
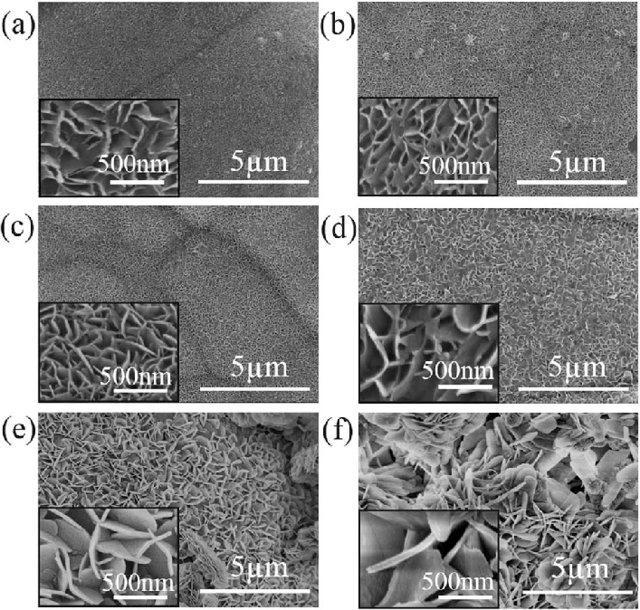
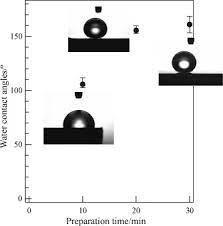
Fig -3.13: Surfacemorphologyofsampleshydrothermallypreparedat120°Cfordifferentreactiontimes:(a)9h,(b)12h, (c)15h,(d)18h,(e)21hand(f)24h[28].
ShijunHeandco-workers[29]haddevelopedathinFe3O4superhydrophobicfilmwithawatercontactangleof158.3°and slidingangleof3.3°.Thepreparedcoatingdisplayedexcellentself-cleaningproperties,andshowedgoodanti-wettingability whensubjectedtowaterjettingtests.Inaddition,theyfoundoutthatthesampleannealedinN2-O2couldpossessuperior corrosionresistanceinvarietyofsolutions.AlthoughthetestingsolutionswasunderindifferentpHrangingfrom2-13,there wasnosuchlargevariationinmeasuredcontactanglewhichisshowndetailedinfig.3.14.
3.9 Advantages and Disadvantages of Superhydrophobic coating techniques
Thetablebelowconcludesthemajoradvantagesanddisadvantagesofdifferentcoatingtechniquesthathavediscussedabove [7].
Methods
1.Chemical etching Industriallyfeasible lowcost Non-uniform Contaminationofthesubstrates
2.Dip coating Simultaneouscoating(Top-Bottom) Highlydurable Requiresmoretime Onlyforsolublepolymers
3. Spin coating Quick-drying controllablethickness Providesasmoothsurface Onlyforlaboratoryscale
4. Spray coating High-qualitycoating Repairable Requiresmorecapital Non-uniformthickness
5. Electro-Chemical Deposition Time-saving Eco-friendly Onlysuitablefortheselectedsize Lesscontrolingrowth
6. Sol-gel process Provideshigh-qualityfilms Synthesisatnormaltemperature Limitingthickness Lessdurabletomechanicalstress
7. Chemical-Vapour Deposition Uniformcoating Controllablethickness
8. Hydrothermal method Highqualitycoatings Industriallyfeasible Timeconsuming
3.10 Applications of Superhydrophobic coating
Scientistsandresearchershavebeenimmenselyworkingonthesuperhydrophobiccoatingduetotheincreasingdemandin differentsectors.Mostoftheresearchesarebasedonthecorrosionresistancecoatingbecauseitisoneofthemajorproperties needed by the engineering materials [6]. This coating is being used as a protective coating for the exposed materials in maritime industries as well as in the construction sector [18]. The resistance of corrosive agents under the sea by these coatingshaveshowninfig3.15.Theself-cleaningpropertyoftheSHPcoatingismainlyappliedinsolarpanels,mirrors,and lenses.Thisabilityishighlyexploitedbytheagricultureanddefencesectors.ThemajoradvantageofSHPcoatingisthatitcan be applied as a transparent coating especially in glass substrates, which is mostly used for architectural purposes. Antireflective superhydrophobic can be deposited on the covering of solar cell system and is also employed for automobile windowsandlensesetc.SHPcoatingpossesstheanti-icingpotential ofslowingdowntheadhesionofsnowor iceonthe surfacewhichisbeingutilizedbyairplanes,highways,powerlines,ships,etc.Theparamountpropertyofthiskind ofSHP
© 2023, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page629

surfaceisitsanti-fouling nature. Itisthemorepopular andcommerciallyacceptablecoating forshiphullstoprotectthe exterior surface of the ship’s exterior, as well as to reduce the growth of organisms results in less fuel consumption [3]. Superhydrophobiccoatingshavebeengainingmoreexposureinthemedicalsectoraswell.ThemainapplicationsofSHP coating in the medical field are drug delivery and non-adhesion of bacteria on implants, gloves, fabrics, etc. Moreover, Superhydrophobicmicrofiberedbandage,blood-repellentcoatings,advancedtextiles,andhigh-endfootweararesomeofthe emergingareasofsuperhydrophobiccoatingwhichwouldbecommerciallyavailableinthenearfuture[30].
4. Conclusion
Superhydrophobicityisdefinedbythewettabilityofthesurfacewhentheangleofcontactofwaterdroponthesolidisgreater than150°.Thisreviewdiscussedthefundamentals,synthesisprocesses,andachievementsofthesuperhydrophobiccoating. ThephenomenonwasdiscoveredbyWenzelin1936whichwaslaterfollowedbytwoscientistsnamedCassieandBaxter.Itisa bioinspiredsurface,eg;Lotusleaf,butterfly,scalesofshark,geckofootetc.Artificialsuperhydrophobicsurfacesaredeveloped bymakingthesubstratemoreroughenedwithlowsurfaceenergy.Thevariousfabricationtechniquesdiscussedaboveto developsuperhydrophobicsurfacesareChemicaletching,Dipcoating,Spincoating,Spraycoating,Electro-chemicaldeposition, Sol-gel processing, Chemical vapour deposition, and Hydrothermal method. Among these, Sol-gel and Electrochemical depositionarethemostpreferredmethodstofabricateSHPduetotheirsimplegeneration,cost-effectiveapproach,largescale production.ScientistsandresearchershavebeenworkingonSHPcoatingtodevelopamoreeco-friendlycoatingtechnique having low cost and large productivity. The superhydrophobic coating has intense applications in the field of aerospace, automotive,agriculture,defence,constructionandbiomedical.Recentprogressionsinthestudiesofsuperhydrophobicsurface wouldresultinadvancedtechnologiesthatwillhavethepotentialforvariousapplicationinthefuture.
REFERENCES
[1] Ijaola,AhmedOlanrewaju,PeterKayodeFarayibi,andEylemAsmatulu."Superhydrophobiccoatingsforsteelpipeline protectioninoilandgasindustries:acomprehensivereview." Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering (2020):103544.

[2] Vinagre,PedroAlmeida,TeresaSimas,EricaCruz,EmilianoPinori,andJohanSvenson."Marinebiofouling:Aeuropean databaseforthemarinerenewableenergysector." Journal of marine science and engineering 8,no.7(2020):495.
[3] Das,Sonalee,SudheerKumar,SushantaK.Samal,SmitaMohanty,andSanjayK.Nayak."Areviewonsuperhydrophobic polymernanocoatings:recentdevelopmentandapplications." Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 57,no.8(2018): 2727-2745.
[4] Prasad,AnupamaR.,AnupamaKunyankandy,andAbrahamJoseph."CorrosionInhibitioninOilandGasIndustry:Economic Considerations." Corrosion Inhibitors in the Oil and Gas Industry (2020):135-150.
[5] Ferrari,Michele,AlessandroBenedetti,andFrancescaCirisano."Superhydrophobiccoatingsfromrecyclablematerialsfor protectioninarealseaenvironment." Coatings 9,no.5(2019):303.
[6] Zhang,Dawei,LuntaoWang,HongchangQian,andXiaogangLi."Superhydrophobicsurfacesforcorrosionprotection:a reviewofrecentprogressesandfuturedirections." Journal of Coatings Technology and Research 13,no.1(2016):11-29.
[7] Meena,MukeshKumar,BalrajKrishnanTudu,AdityaKumar,andBharatBhushan."Developmentofpolyurethane-based superhydrophobic coatings on steel surfaces." Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A 378, no. 2167 (2020): 20190446.
[8] Falde, Eric J., Stefan T. Yohe, Yolonda L. Colson, and Mark W. Grinstaff. "Superhydrophobic materials for biomedical applications." Biomaterials 104(2016):87-103.
[9] Hooda, Amrita, M. S. Goyat, Jitendra Kumar Pandey, Adesh Kumar, and Rajeev Gupta. "A review on fundamentals, constraintsandfabricationtechniquesofsuperhydrophobiccoatings." Progress in Organic Coatings 142(2020):105557.[10] Erbil, H. Yildirim. "Practical applications of superhydrophobic materials and coatings: problems and perspectives." Langmuir 36,no.10(2020):2493-2509.
[11] Kumar, Aditya, and Debasis Nanda. "Methods and fabrication techniques of superhydrophobic surfaces." In Superhydrophobic Polymer Coatings,pp.43-75.Elsevier,2019.
[12] Gomes,DouglasJC,NaraC.deSouza,andJosmaryR.Silva."Usingamonocularopticalmicroscopetoassembleawetting contactangleanalyser." Measurement 46,no.9(2013):3623-3627.
[13] Varshney,Priya,SoumyaSanjeebMohapatra,andAdityaKumar."Superhydrophobiccoatingsforaluminiumsurfaces synthesizedbychemicaletchingprocess." International Journal of Smart and Nano Materials 7,no.4(2016):248-264.
[14] Wang,Yanhua,WeiWang,LianZhong,JiaWang,QuanliangJiang,andXiangyangGuo."Super-hydrophobicsurfaceonpure magnesiumsubstratebywetchemicalmethod." Applied Surface Science 256,no.12(2010):3837-3840.
[15] Zhang,Xia,YonggangGuo,ZhijunZhang,andPingyuZhang."Self-cleaningsuperhydrophobicsurfacebasedontitanium dioxidenanowirescombinedwithpolydimethylsiloxane." Applied surface science 284(2013):319-323.
[16]Neacşu,IonelaAndreea,AdrianIonuţNicoară,OtiliaRuxandraVasile,andBogdanŞtefanVasile."Inorganicmicro-and nanostructuredimplantsfortissueengineering."In Nanobiomaterials in Hard Tissue Engineering,pp.271-295.WilliamAndrew Publishing,2016.
[17] Amokrane,G.,C.Falentin-Daudré,S.Ramtani,andVéroniqueMigonney."AsimplemethodtofunctionalizePCLsurfaceby graftingbioactivepolymersusingUVirradiation." Irbm 39,no.4(2018):268-278.
[18] Xu,Kun,ShenzhuangRen,JinlongSong,JiyuLiu,ZiaiLiu,JingSun,andSiyingLing."Colorfulsuperhydrophobicconcrete coating." Chemical Engineering Journal 403:126348.
[19] Polizos, G., Gyoung Gug Jang, D. Barton Smith, F. A. List, Matthew G. Lassiter, Jaehyeung Park, and Panos G. Datskos. "Transparentsuperhydrophobicsurfacesusingaspraycoatingprocess." Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells 176(2018): 405-410.
[20] Ye, Hui, Liqun Zhu, Weiping Li, Huicong Liu, and Haining Chen. "Simple spray deposition of a water-based superhydrophobiccoatingwithhighstabilityforflexibleapplications." Journal of Materials Chemistry A 5,no.20(2017):98829890.
[21] Liu,Yan,ShuyiLi,JijiaZhang,YamingWang,ZhiwuHan,andLuquanRen."Fabricationofbiomimeticsuperhydrophobic surfacewithcontrolledadhesionbyelectrodeposition." Chemical Engineering Journal 248(2014):440-447.
[22] Bai,Zengguo,andBinZhang."Fabricationofsuperhydrophobicreduced-grapheneoxide/nickelcoatingwithmechanical durability,self-cleaningandanticorrosionperformance." Nano Materials Science 2,no.2(2020):151-158.
[23] Liu,Shanhu,XiaojingLiu,SanjayS.Latthe,LiGao,SeongpilAn,SamS.Yoon,BaoshunLiu,andRuiminXing."Self-cleaning transparentsuperhydrophobiccoatingsthroughsimplesol–gelprocessingoffluoroalkylsilane." Applied Surface Science 351 (2015):897-903.
[24] Sinha Ray,Saikat,Hyung-KaeLee,andYoung-Nam Kwon."Reviewon blueprintofdesigninganti-wettingpolymeric membranesurfacesforenhancedmembranedistillationperformance." Polymers 12,no.1(2020):23.
[25] Cai,Zhengwei,JinbinLin,andXinlinHong."Transparentsuperhydrophobichollowfilms(TSHFs)withsuperiorthermal stabilityandmoistureresistance." RSC advances 8,no.1(2018):491-498.
© 2023, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page631

[26] Ishizaki,Takahiro,JunkoHieda,NagahiroSaito,NaobumiSaito,andOsamuTakai."Corrosionresistanceandchemical stability of super-hydrophobic film deposited on magnesium alloy AZ31 by microwave plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition." Electrochimica Acta 55,no.23(2010):7094-7101.
[27] Kumar,Sanjay,SudhirSaralch,UzmaJabeen,andDineshPathak."Metaloxidesforenergyapplications."In Colloidal Metal Oxide Nanoparticles,pp.471-504.Elsevier,2020.
[28] Yuan, Jing, Jihui Wang, Kaili Zhang, and Wenbin Hu. "Fabrication and properties of a superhydrophobic film on an electrolessplatedmagnesiumalloy." RSC advances 7,no.46(2017):28909-28917.
[29] He, Shijun, Zhen Wang, Jun Hu, Jianbo Zhu, Liping Wei, and Zhong Chen. "Formation of superhydrophobic micronanostructuredironoxideforcorrosionprotectionofN80steel." Materials & Design 160(2018):84-94.
[30] Parvate, Sumit, Prakhar Dixit, and Sujay Chattopadhyay. "Superhydrophobic surfaces: insights from theory and experiment."TheJournalofPhysicalChemistryB124,no.8(2020):1323-1360.
[31] Gnedenkov, S. V., S. L. Sinebryukhov, V. S. Egorkin, D. V. Mashtalyar, A. M. Emelyanenko, and L. B. Boinovich. "Electrochemicalpropertiesofthesuperhydrophobiccoatingsonmetalsandalloys." Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers 45,no.6(2014):3075-3080.
[32] Zhang,Jing,WeidongZhang,NianchenZhou,YuyanWeng,andZhijunHu."Photoresponsivesuperhydrophobicsurfaces fromone-potsolutionspincoatingmediatedbypolydopamine." RSC advances 4,no.48(2014):24973-24977.
[33] Huang, Jian, Chang Lou, Dong Xu, Xin Lu, Zhong Xin, and Changlu Zhou. "Cardanol-based polybenzoxazine superhydrophobiccoatingwithimprovedcorrosionresistanceonmildsteel." Progress in Organic Coatings 136(2019):105191.
[34] Seyedmehdi, S. A., and M. Ebrahimi. "Superhydrophobic modified-polyurethane coatings for bushing of power transformers:Frommaterialtofabrication,mechanicalandelectricalproperties." Progress in Organic Coatings 123(2018): 134-137.
[35] Zhang,Fen,ShougangChen,LihuaDong,YanhuaLei,TaoLiu,andYanshengYin."Preparationofsuperhydrophobicfilms ontitaniumaseffectivecorrosionbarriers." Applied surface science 257,no.7(2011):2587-2591.
[36] Zhang,Fazhi,MengSun,SailongXu,LiliZhao,andBowenZhang."Fabricationoforientedlayereddoublehydroxidefilms byspincoatingandtheiruseincorrosionprotection." Chemical Engineering Journal 141,no.1-3(2008):362-367.
[37] Yeganeh,M.,andN.Mohammadi."SuperhydrophobicsurfaceofMgalloys:areview." Journal of magnesium and alloys 6, no.1(2018):59-70.
[38] Mertaniemi, Henrikki, Antti Laukkanen, Jan-Erik Teirfolk, Olli Ikkala, and Robin HA Ras. "Functionalized porous microparticlesofnanofibrillatedcelluloseforbiomimetichierarchicallystructuredsuperhydrophobicsurfaces." Rsc Advances 2,no.7(2012):2882-2886.
[39] Ye, Hui, Liqun Zhu, Weiping Li, Huicong Liu, and Haining Chen. "Simple spray deposition of a water-based superhydrophobiccoatingwithhighstabilityforflexibleapplications." Journal of Materials Chemistry A 5,no.20(2017):98829890.
[40] Rudnik,E.,andK.Chat."Abriefreviewonbio-inspiredsuperhydrophobicelectrodepositednickelcoatings." Transactions of the IMF 96,no.4(2018):185-192.
[41] Lv, Yan, and Mingyan Liu. "Corrosion and fouling behaviours of copper-based superhydrophobic coating." Surface Engineering 35,no.6(2019):542-549.

