2 minute read
Type Four stoke, water cooled diesel
Vimal Patel1, Sneh Patel2, Soham Patel3 , Jignesh Patel4 , Alok Choudhary5 1, 2, 3Students of B.Tech (Mechanical Engineering), Merchant Engineering Collage Basna, Gujarat, India 4Assistant Professor, Mechanical Department, Merchant Engineering Collage Basna, Gujarat, India 5Head Of Department, Mechanical Department, Merchant Engineering Collage Basna, Gujarat, India
Advertisement
Abstract: Variable Compression Ratio (VCR) engine test can be used to determine the effect of Compression Ratio (CR) on the performance and emissions of the engine. The combustion situation, when provided with a pressure transducer. The performance frequency parameters like efficiencies, power, and specific fuel consumption are determined. The combustion phenomenon is also observed through this work, we can find the optimum compression ratio for which the best performance is possible. In order to find out the optimum compression ratio, experiments were carried out on a single-cylinder four-stroke variable compression ratio engine. Tests were carried out at compression ratios of 18, 17, and 16 at different loads the performance characteristics of the engine like Brake power (BP), Thermal Efficiency, Brake Specific Fuel Consumption (BSFC). A variable compression ratio engine is able to operate at different compression ratios, depending on particular vehicle performance needs. The VCR engine is optimized for the full range of driving conditions, as acceleration, speed, and load. Keywords: Performance, Compression ratio, Load, Break Power, William Line’s Method, Emission, Thermal Efficiency, Diesel Engine, Fuel Consumption
I. INTRODUCTION
Each year, the ultimate goal of emission legislation is to force technology to the point where practically viable zero-emission vehicles become a reality. The path to reach this target is a formidable challenge. The ever-increasing demand for petroleum-based fuels and their availability has lead to extensive research on Diesel fuelled engines. A better design of the engine can significantly improve the combustion quality and in turn, will lead to better brake thermal efficiencies and hence saves fuel. India though rich in coal abundantly and endowed with renewable energy in the form of solar, wind, hydro, and bio-energy has a very small hydrocarbon reserve. India is a net importer of energy. Nearly 25% of its energy needs are met through imports mainly in the form of crude oil and natural gas. The rising oil bill has been the focus of serious concerns due to the pressure it has placed on scarce foreign exchange resources and is also largely responsible for energy supply shortages. The sub-optimal consumption of commercial energy adversely affects the productive sectors, which in turn hampers economic growth. The present work deals with finding the better compression ratio for the Diesel fuelled C.I. engine at variable load and constant speed operation. All over the world, the reduction of automotive fuel consumption and emissions is leading to the introduction of various new technologies in engines.
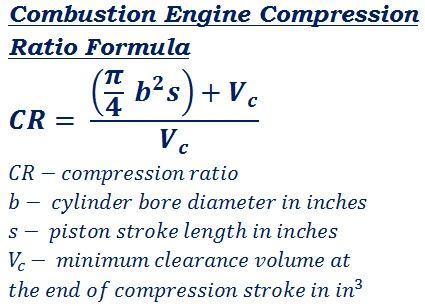
Fig. 1 Compression Ratio Terminology


