PAT E L
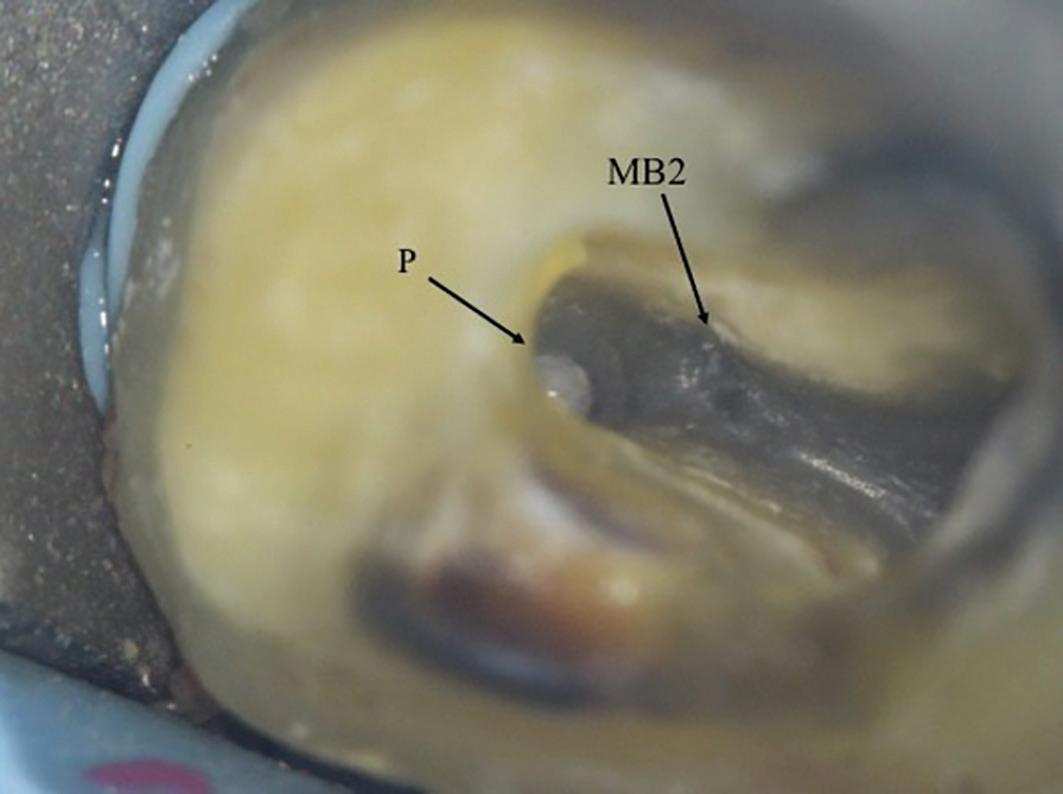
7a: MB2 orifice detected close to the palatal canal
7b: After obturation
of dentine, particularly in older patients. Therefore, the access cavity will need to be extended to remove this. In calcified cases, the MB2 may be slightly deeper apically.
Piezo-electric ultrasonic tips or long-neck burs used in a slow handpiece are very useful removing the dentine shelf and searching for MB2. They allow good vision during
8a: Preoperative radiograph. The tooth had previously been accessed by the referral dentist.
8d: Master cone radiograph taken with cone in MB2 d) Midfill radiograph shows MB1 and MB2 are separate canals
8b: MB2 was located within the MB1 orifice (mesial wall). The microscope photograph was taken after the MB1 and MB2 have been fully prepared
8e: Postoperative radiograph
8c: Master cone radiographs taken with a GP cone in MB1
8f: Post-obturation photograph showing one MB orifice. A trough line can be seen where MB2 was searched for in its ‘typical’ location
18 INTERNATIONAL DENTISTRY – AUSTRALASIAN EDITION VOL.16, NO. 1