https://ebookmass.com/product/lexical-variation-and-change-
Instant digital products (PDF, ePub, MOBI) ready for you
Download now and discover formats that fit your needs...
Language Change, Variation, and Universals Culicover
https://ebookmass.com/product/language-change-variation-anduniversals-culicover/
ebookmass.com
An Anatomy of Chinese Offensive Words: A Lexical and Semantic Analysis 1st ed. 2021 Edition Adrian Tien
https://ebookmass.com/product/an-anatomy-of-chinese-offensive-words-alexical-and-semantic-analysis-1st-ed-2021-edition-adrian-tien/
ebookmass.com
Visual Experience: A Semantic Approach 1st Edition Wylie Breckenridge
https://ebookmass.com/product/visual-experience-a-semanticapproach-1st-edition-wylie-breckenridge/
ebookmass.com
The Irish Rogue (The Billionaire's Club Book 3) Elizabeth Lennox
https://ebookmass.com/product/the-irish-rogue-the-billionaires-clubbook-3-elizabeth-lennox/
ebookmass.com
Cummings Review of Otolaryngology 1st Edition Harrison W. Lin
https://ebookmass.com/product/cummings-review-of-otolaryngology-1stedition-harrison-w-lin/
ebookmass.com
Cupid's Love (Seasonal Paranormal and Fantasy Romances Book 3) Amelia Shaw
https://ebookmass.com/product/cupids-love-seasonal-paranormal-andfantasy-romances-book-3-amelia-shaw/
ebookmass.com
(eTextbook PDF) for Liberty, Equality, Power: A History of the American People 7th Edition
https://ebookmass.com/product/etextbook-pdf-for-liberty-equalitypower-a-history-of-the-american-people-7th-edition/
ebookmass.com
Discovering Psychology Eighth Edition – Ebook PDF Version
https://ebookmass.com/product/discovering-psychology-eighth-editionebook-pdf-version/
ebookmass.com
Banks and Fintech on Platform Economies Paolo Sironi
https://ebookmass.com/product/banks-and-fintech-on-platform-economiespaolo-sironi/
ebookmass.com
Strategic Management: Theory & Cases: An Integrated Approach, 13e 13th Edition
Charles W. L. Hill
https://ebookmass.com/product/strategic-management-theory-cases-anintegrated-approach-13e-13th-edition-charles-w-l-hill/
ebookmass.com
LexicalVariationandChange
LexicalVariation andChange
ADistributionalSemanticApproach
DIRKGEERAERTS
DIRKSPEELMAN
KRISHEYLEN
MARIANAMONTES
STEFANODEPASCALE
KARLIENFRANCO
MICHAELLANG
GreatClarendonStreet,Oxford,OX26DP, UnitedKingdom
OxfordUniversityPressisadepartmentoftheUniversityofOxford. ItfurtherstheUniversity’sobjectiveofexcellenceinresearch,scholarship, andeducationbypublishingworldwide.Oxfordisaregisteredtrademarkof OxfordUniversityPressintheUKandincertainothercountries
©DirkGeeraerts,DirkSpeelman,KrisHeylen,MarianaMontes,StefanoDePascale, KarlienFranco,andMichaelLang2024
Themoralrightsoftheauthorshavebeenasserted Somerightsreserved.Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproduced,storedin aretrievalsystem,ortransmitted,inanyformorbyanymeans,forcommercialpurposes, withoutthepriorpermissioninwritingofOxfordUniversityPress,orasexpressly permittedbylaw,bylicenceorundertermsagreedwiththeappropriate reprographicsrightsorganization.
Thisisanopenaccesspublication,availableonlineanddistributedunderthetermsofa CreativeCommonsAttribution—NonCommercial—NoDerivatives4.0 Internationallicence(CCBY-NC-ND4.0),acopyofwhichisavailableat http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
Enquiriesconcerningreproductionoutsidethescopeofthislicence shouldbesenttotheRightsDepartment,OxfordUniversityPress,attheaddressabove
PublishedintheUnitedStatesofAmericabyOxfordUniversityPress 198MadisonAvenue,NewYork,NY10016,UnitedStatesofAmerica
BritishLibraryCataloguinginPublicationData Dataavailable
LibraryofCongressControlNumber:2023937657
ISBN9780198890676
DOI:10.1093/oso/9780198890676.001.0001
Printedandboundby
CPIGroup(UK)Ltd,Croydon,CR04YY
LinkstothirdpartywebsitesareprovidedbyOxfordingoodfaithand forinformationonly.Oxforddisclaimsanyresponsibilityforthematerials containedinanythirdpartywebsitereferencedinthiswork.
PARTI.THEORETICALPRELIMINARIES
PARTII.DISTRIBUTIONALMETHODOLOGY
3.Parametersandproceduresfortoken-baseddistributionalsemantics
5.Makingsenseofdistributionalsemantics
6.Theinterplayofsemasiologyandonomasiology
PARTIV.LECTOMETRICMETHODOLOGY
7.Quantifyinglectalstructureandchange
PARTV.LECTOMETRICEXPLORATIONS
1.1Researchperspectiveswithinthelexeme-lection-lecttriangle 5
2.1Semasiologicalstructureof vest 35
2.2Graphicalrepresentationofthestepsinthedistributionalworkflow
3.12DrepresentationofDutch hachelijk ‘dangerous/critical’ 70
3.2Syntactictreeofexample(3.1)
3.3Syntactictreeofexample(3.2)
4.1Two2DrepresentationsofthesamemodelofDutch hachelijk ‘dangerous/critical’ 90
4.2Portalof https://qlvl.github.io/NephoVis/ asofAugust2022 94
4.3Level1for heffen ‘tolevy/tolift’ 95
4.4Level2forthemedoidsof heffen ‘tolevy/tolift’ 96
4.5Level1for heffen ‘tolevy/tolift’.Theplotiscolour-codedwithfirst-order part-of-speechsettings;NAstandsformissingdata,inthiscasethe dependencybasedmodels 97
4.6Level1for heffen ‘tolevy/tolift’withmedoidshighlighted 98
4.7Level2forthemedoidsof heffen ‘tolevy/tolift’,colour-codedwith categoriesfrommanualannotation.Hoveringoveratokenshowsits concordanceline 98
4.8Heatmapofdistancesbetweenmedoidsof heffen ‘tolevy/tolift’againstthe backdropofLevel2 99
4.9Heatmapofdistancesbetweenmedoidsof haten ‘tohate’againstthe backdropofLevel2 100
4.10Level2forthemedoidsof heffen ‘tolevy/tolift’,colour-codedwith categoriesfrommanualannotation.Brushingoveranareainaplotselects thetokensinthatareaandtheirpositionsinothermodels 101
4.11Frequencytableofcontextwordsofselectedtokensagainstthebackdropof Level2(medoidsof heffen ‘tolevy/tolift’) 102
4.12Level3forthethirdmedoidof heffen ‘tolevy/tolift’,withparameters 10-10.ALL.BOUND.WEIGHT.SOCALL.FOC 104
4.13Level3forthesecondmedoidof heffen ‘tolevy/tolift’,withparameters 10-10.ALL.BOUND.WEIGHT.SOCALL.FOC 104
4.14StartingviewoftheShinyAppdashboard,extensionofLevel3 106
4.15Topboxesofthe‘t-SNE’taboftheShinyAppdashboard,withactivetooltips
4.16Token-levelplotandbottomfirst-ordercontextwordsplotofthe‘t-SNE’ taboftheShinyAppdashboard,withonecontextwordselected
4.17Heatmapoftype-leveldistancesbetweenrelevantcontextwordsinthe ShinyAppdashboard 108
5.1Variableimportancepredictingdistancesbetweenallmodels 116
5.2Variableimportancepredictingaccuracyofmodels 117
5.3Conditionaltreepredictingtheaccuracyof herinneren ‘toremember/to remind’modelsaskNN 118
5.4Conditionaltreepredictingtheaccuracyof huldigen ‘tobelieve/tohonour’ modelsaskNN 118
5.5Modelsof heet ‘hot’and stof ‘substance,dust…’withparameters 5-5.LEX.BOUND.SELECTION.SOCALL.FOC 119
5.6Modelsof dof ‘dull’and huldigen ‘tobelieve/tohonour’withparameters 5-5.LEX.BOUND.SELECTION.SOCALL.FOC 120
5.7Modelsof haten ‘tohate’and hoop ‘hope,heap’withparameters 5-5.LEX.BOUND.SELECTION.SOCALL.FOC 121
5.8Modelof heilzaam withparameters10-10.ALL.BOUND.WEIGHT.SOCALL.FOC. Circlesare‘healthy,healing’,trianglesare‘beneficial’ingeneral 128
5.9Modelof herstructureren withparameters
3-3.ALL.BOUND.SELECTION.SOCALL.FOC
5.10Modelof grijs withparameters5-5.ALL.BOUND.ASSOCNO.SOCALL.FOC
5.11Modelof herroepen withparameters3-3.ALL.BOUND.SELECTION.SOCALL.FOC
5.12Modelof blik withparameters5-5.ALL.BOUND.WEIGHT.SOCNAV.5000
5.13Modelof schaal withparameters5-5.ALL.NOBOUND.WEIGHT.SOCALL.FOC
5.14Modelof herhalen withparametersREL1.SELECTION.SOCALL.FOC
5.15Modelof haken withparameters10-10.LEX.BOUND.SELECTION.SOCNAV.FOC
5.16Modelof huldigen withparameters 3-3.LEX.NOBOUND.SELECTION.SOCALL.FOC
5.17Networkofcontextwordsofthe huldigen ‘tohonour’cluster
5.18Modelof heffen withparameters10-10.ALL.BOUND.WEIGHT.SOCNAV.FOC
5.19Modelof hachelijk withparameters5-5.ALL.BOUND.WEIGHT.SOCALL.FOC
5.20Modelof herinneren withparameters 10-10.ALL.BOUND.WEIGHT.SOCNAV.5000
5.21Modelof heet withparameters5-5.ALL.BOUND.ASSOCNO.SOCALL.FOC
5.22Modelof stof withparameters5-5.LEX.BOUND.SELECTION.SOCALL.FOC
5.23Modelof horde withparameters5-5.ALL.BOUND.SELECTION.SOCALL.FOC
5.24Modelof geldig withparameters10-10.LEX.BOUND.SELECTION.SOCALL.FOC
6.1Modelsfor woedend and laaiend 157
6.2Modelsfor briljant and geniaal 158
6.3Scatterplotoft-SNEvisualizationofonemodelof vernielen and vernietigen, colouredbyfourclustersandshape-codedbyvariant 164
6.4Scatterplotwithcoloursformanualcodingofagenttypeandshapesfor variants 165
6.5Scatterplotwithcoloursformanualcodingofpatienttypeandshapesfor variants 166
6.6Clusteranalysesof vernielen and vernietigen inthefourdiachronic subcorpora 172
7.1Hierarchicaldestandardizationasincreasingdistancebetweenstrata 192
7.2Informalizationastop-downdecreasingdistancebetweenstrata 192
7.3Dehomogenizationasincreasingvariationwithinonestratum 193
8.1VisualizationofamodelforSECONDARY 211
8.2Exampleworkflowforcalculatingdistributionaltokenstability 216
9.1Hierarchical(de)standardizationscoresinBelgianDutch(caterpillarplot with‘models’ony-axis) 239
9.2Hierarchical(de)standardizationinNetherlandicDutch(caterpillarplot with‘models’ony-axis) 240
9.3Hierarchical(de)standardizationscoresinBelgianDutch(caterpillarplot with‘concepts’ony-axis) 241
9.4Hierarchical(de)standardizationscoresinNetherlandicDutch(caterpillar plotwith‘concepts’ony-axis) 241
9.5Hierarchical(de)standardizationscoresacrosssemanticfields
9.6(In)formalizationscoresforBelgianDutch(caterpillarplotwith‘models’ ony-axis) 245
9.7(In)formalizationscoresforNetherlandicDutch(caterpillarplotwith ‘models’ony-axis) 245
9.8(In)formalizationscoresforBelgianDutch(caterpillarplotwith‘concepts’ ony-axis)
9.9(In)formalizationscoresforNetherlandicDutch(caterpillarplotwith ‘concepts’ony-axis) 246
9.10(In)formalizationscoresacrosssemanticfields
9.11(De)homogenizationscoresforBelgianDutch(caterpillarplotwith ‘models’ony-axis)
9.12(De)homogenizationscoresforNetherlandicDutch(caterpillarplotswith ‘models’ony-axis)
9.13(De)homogenizationscoresforBelgianDutch(caterpillarplotswith ‘concepts’ony-axis) 250
9.14(De)homogenizationscoresforNetherlandicDutch(caterpillarplotwith ‘concepts’ony-axis)
9.15(De)homogenizationscoresacrosssemanticfields
ColourversionsoffigurescanbeconsultedviathefreePDFdownloadat https://global.oup.com/academic/product/lexical-variation-and-change-978019 8890676orviaOUP’sonlineplatformathttps://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780198 890676.001.0001.
1.1Terminologicaldistinctionsindenotationallyexpandedlexicology: phenomena 11
1.2Terminologicaldistinctionsindenotationallyexpandedlexicology:subfields
1.3Differencesinconceptualonomasiologicalsalienceamongco-hyponyms
1.4Structuralandusage-orientedperspectivesinlexicalresearch 15
1.5OnomasiologicalprofilesforNONSENSEinthefictitiousTzaraandBall dialects 18
1.6OnomasiologicalprofilesforNONSENSEinthefictitiousArpandPicabia dialects
2.1Partialmatrixunderlyingtheanalysisof vest inFigure2.1
3.1Exampleoftype-levelvectors
3.2Smallexampleoftoken-levelvectorsofthreeinstancesof
5.1Examplesofsyntagmatic(columns)andparadigmatic(rows)perspectives onthelinguisticinterpretationofclouds 125
6.1Codingschemaforagentandpatientexpression
6.2Clustersinthemodelfor vernielen and vernietigen incontemporarydata 164
6.3Inflectedformsandspellingvariantsoccurringfor vernielen and vernietigen inthediachroniccorpus 169
6.4Frequencyof vernielen and vernietigen,andtotalnumberoftokensper century 170
6.5Parametersettingsinthecontemporarystudycomparedtoparameter settingsinthediachronicstudy 171
6.6Clustersinthemodelfor vernielen and vernietigen inthe16thand17th centuries 173
6.7Clustersinthemodelfor vernielen and vernietigen inthe18thcentury 174
6.8Clustersinthemodelfor vernielen and vernietigen inthe19thcentury 175
6.9Clustersinthemodelfor vernielen and vernietigen inthe20thcentury 176
6.10Summaryoftheclusteranalysesof vernielen and vernietigen inthe subcorpora 177
9.1CorpuscompositionfortheDutchstandardizationstudy
9.3OverviewofparametersfortheDutchstandardizationstudy
9.4Downsamplingschemeforconceptsizes
9.5OverviewofdestandardizationscoresinBelgianDutchandNetherlandic Dutch
9.6Summaryofstandardlanguagechangescoresacrosssemanticfields
10.1SizesofthesixlectsintheWeb/DialectscorpusintheCorpusdelEspañol
10.3OverviewofparametersfortheSpanishpluricentricitystudy
10.4Conceptsforwhichnomodelswereretained
10.5Completelyuniformconceptsresultingfromtheapplicationofa significancetesttothelectalcomparisons
10.6Overviewoftheconceptsbymodelretention
10.7U-valuesforallthree AnyMod tokensetsfrombothapan-Hispanicand pan-Americanperspective
10.8U-valuesforallthree 19+Mod tokensetsfrombothapan-Hispanicand pan-Americanperspective
10.9U-valuesforallthree<18Mod tokensetsfrombothapan-Hispanicand pan-Americanperspective
10.10Characteristicsofthethreegroupsbasedonmodelretention
Introduction
Incorpuslinguistics,distributionalsemanticsembodiestheideathatthecontext inwhichawordoccursrevealsthemeaningofthatword.Bywayofillustration,considerthewords underground and subway,bothreferringtosubterranean railwaysystems.Thesynonymyrelationshipthatexistsbetweenthewordsmay berecognizeddistributionallybecausetheybothco-occurfrequentlywithwords like line, station, terminal, urban, crosstown, northbound, passenger, transit, train, run, operate.Thatistosay,thesimilardistributionofthewords underground and subway overcontextsfeaturingitemslike line, station, terminal,andsoon tellsussomethingaboutthemeaningofthetwowords.Importantly,thereare computationaltechniquesthatallowustoidentifythesimilarityinthedistributionalpatterningof underground and subway.Thosetechniquescanrecognize that underground and subway aresemanticallycloserthan,say, subway and sunshine.But underground alsohasthemeaning‘asecretorganizationfightingthe establishedgovernmentoroccupationforces’,whichco-occurswithwordslike clandestine,resistance,insurrection,attack,army,hidden,andwhichthusblursthe synonymyrelationshipwith subway. Amorefine-graineddistributionalapproach thentriestomodel,nottheoverallsimilaritybetween underground and subway, butthesimilaritybetweentheoccurrencesof underground inthesense‘subterraneanrailway’andthoseinthesense‘resistancemovement’.Suchamoredetailed typeofdistributionalsemanticsiscalleda token-based approach,whereatokenis anyofthespecificoccurrencesofthewords,incontrastwithatype-basedapproach thatonlylooksatthelevelofthewordsasawhole.Computationally,token-based approachesgroupoccurrencestogetherbasedontheirsemantic(read:distributional)similarity,justlikeatype-basedapproachgroupswordsassuchtogether. Sointhecaseof underground,youexpecttocomeacrossagroupoftokensfor the‘subterraneanrailway’senseandanotherforthe‘resistancemovement’sense, andwhenyouaddtheoccurrencesof subway tothemodel,youexpecttofind themintermingledwiththegroupof underground tokensthatrepresentsthe‘subterraneanrailway’sense.Ifwerefertosuchclustersofgrouped-togethertokens asclouds—tokenclouds—thenthedistributionalapproachconsistsofanalysing configurationsoftokencloudstoseewhatlighttheyshedonthemeaningsofthe expressions.
Onemajorgoalofthepresentmonograph,then,istoexploretheinsandouts ofadistributional,token-cloud-basedapproachtowordmeaning.Whatdoesit involve,inwhatflavoursdoesitcome,howefficientlycanitbeimplemented,and whatexactlyisitssemanticimport?Thestakesforcorpussemanticsarehigh:if
distributionalmodellingatthelevelofindividualtokensofwordsworkswell,the automatedorsemi-automatedanalysisofmeaninginlargetextcorporacanbe broughttoanextlevelofdetailandprecision.Thereisalsoaverypracticalside tothemethodologicalobjectivesofthebook.Thetoolsandalgorithmsthatwe willusearemadeavailableforpublicuse,andsothebookcanalsobeseenas aportfolioofsamplestudiesthatmightinspireotherresearchers.Atthesame time,wewillpointouttherestrictionsonthekindofdistributionalmodelling thatwehaveimplementedandargueforsomecautionregardingitsintroduction inlinguisticsemantics.Itturnsoutthatthesemanticinformationpickedupbydistributionalmodelsdoesnotcorrespondinastableandstraightforwardwaywith theinformationalinguistmaybelookingforandthisrecognitioncallsforspecific measuresastohowdistributionalmodelsmaybeincorporatedintoalinguistic workflow.
Butapartfromthismethodologicalpurpose,thebookhasanequallyimportant theoreticalgoal.Ourexplorationofdistributionalsemanticscontinuesalexicologicallineofresearchthatwasdevelopedoverthepastquartercenturyinthe QuantitativeLexicologyandVariationalLinguistics(QLVL)researchgroupat theUniversityofLeuven.Situatedwithinthebroadcontextofcognitivelinguistics,thisresearchlinetranslatesthecognitivelinguisticinterestincategorization phenomenaandsemanticvariabilityintoaresearchprogrammethattakesthe interplayofsemasiological,onomasiological,andlectalvariationasitscorequestion.Tobrieflyandsimplisticallyunpackthisterminologicaltriad(detailsfollow inaseparatechapter):semasiologicalvariationlooksfromawordtoitsmeanings;itstudiespolysemy,likethevarioussensesof underground.Onomasiology reversestheperspectiveanddescribeshowagivenmeaningcanbeexpressedby variouswords,likethesynonymyofundergroundandsubwayinthe‘subterranean railway’sense.Lectalvariationinvolvesthewayinwhichdiversityalongsociolinguistic,stylistic,geographical,andsoondimensionsinfluencessemasiologicaland onomasiologicalphenomena,liketheobservationthat underground istypically BritishEnglishand subway typicallyAmericanEnglish.Thislectalperspective includesaso-calledlectometricone:measuringthefrequenciesof underground andsubwayasexpressionsfor‘subterraneanrailway’inBritishandAmericantexts allowsustocalculatehowcloselexicalusageinthetwovarietiesiswithregard toeachother,andtoaddressthequestionwhethertheyaregrowingtogetheror apart.Thepresentvolumewilldetailthisframeworkandexaminehowtokenbaseddistributionaltechniquesmightbeusedtoscaleuptheresearchtothelevel oflarge-scalecorpora.Althoughwewillnotexhaustivelycoverallthedimensions oftheprogramme,thevariousstudiesshowcasingthedistributionalmethodwill treatcrucialcomponentsofthetheoreticalframeofreference:thedetectionof polysemy,theinterplayofsemasiologicalandonomasiologicalvariation,thetreatmentoflexicalvariationasasociolinguisticvariable,andtheuseofthosevariables tomeasureconvergenceordivergencebetweenlanguagevarieties.
Thebookisstructuredinfivepartsoftwochapterseach.Thefirstsetoftwo chapters,Theoreticalpreliminaries,introducestheframework.Chapter1describes thevariousperspectivesthatmaybetakeninlexicalvariationresearch,andhow thesehavesofarbeencoveredinexistingresearch.Chapter2laysouttheconceptualfoundationsofatoken-baseddistributionalmethod.Theremainingeight chaptersfallintotwogroups.Afirstsetoftwotimestwochaptersdealswith semasiologyandonomasiology,thatis,withtherelationshipbetweenlexical expressionsandtheirmeanings,andhowthismaydifferoverchronologicalperiodsandlanguagevarieties.Asecondgroupoftwotimestwochaptersreverses theperspective.InChapters3to6,weareinterestedinhowlectalvariationmay influencelexicalvariation.InChapters7to10,weareinterestedinwhatlexical variationhastosayaboutlectalvariation.Ineachsetoftwotimestwochapters, thefirstpairofchaptersisdevotedtomethodologicalissueswhilethesecond pairillustratesthemethodologywithcasestudies.Accordingly,the Distributional methodology partintroduces,inChapter3,thetechnicalspecificsofthedistributionalsemanticworkflowwewilluse,andinChapter4thevisualizationtoolthat wehavedevelopedtoexploreitsoutcome.Thechaptersinthe Semasiologicaland onomasiologicalexplorations partputthisexplorationintopractice.UsingDutch materials,Chapter5examineshowfaradistributionalapproachcantakeusonthe pathofsemanticanalysis,andChapter6appliesthedistributionalmethodtothe interplayofsemasiologyandonomasiologyinlexicalsemanticchange.Thefinal fourchaptersaresimilarlysplitupbetweentwomethodologicalandtwodescriptivechapters.The Lectometricmethodology partintroducesthevariousstepsin alectometricworkflow.WhileChapter7introducestheformulaethatuselexical variationtoquantifytherelationshipbetweenlanguagevarieties,Chapter8specifieshowatoken-baseddistributionalmethodidentifiesthesetsofsynonymous expressionsthatprovidethebasisforthatquantification.Thechaptersinthefinal part,Lectometricexplorations,illustratethelectometricworkflow.Chapter9looks diachronicallyattheevolutionofDutch.Chapter10presentsasynchronicview ofinternationalvarietiesofSpanish.Thebookcloseswithaconclusiondetailinginwhatwaystheresearchprogrammecanbefurtherdeveloped—andreaders beware:thereareplentyofthem.
Inlightofthisoverview,webelievethebookoffersthefollowinguniqueand innovativefeatures.First,itpresentsa comprehensiveviewoflexicalvariation, basedonthedistinctionbetweensemasiologyandonomasiology,andtheaddition ofalectaldimension.Bydescribinghowthesedistinctionsdefinedifferentperspectivesforlexicalresearch,andhowthedifferentphenomenainteract,thebook drawsamoreadequatepictureoftherichnessandcomplexityoflexicalphenomenathancanbefoundintheexistingliterature.Inparticular,bytreatinglexical variationasasociolinguisticvariableinthesenseofvariationistsociolinguistics, therelationshipbetweenlanguagevarietiescanbequantifiedatanaggregatelevel
basedonsuchvariables.Themonographshowshowsuchalexicallectometrycan bedeveloped,andhowitcanprofitfromdistributionalmethods.
Second,bycomparingthesemanticclassificationsproducedbycount-based distributionalmodelswithmanuallyannotateddisambiguateddata,weoffera criticalinsightintothemachineryofdistributionalmodelling.Whereasacomputationalperspectiveondistributionalmethodsisprimarilyconcernedwiththeir successinmodellinglinguisticphenomena,weaimforadeeperunderstandingof themechanismsbehindthoseresults:howtechnicalchoiceswithregardtothedistributionalprocessinfluencewhichtextualinformationispickedupbythemodels, andhowthatrelatestoahumaninterpretationofthedata.Crucially,ouranalysisdemonstrates,first,thatthereisnoone-to-onerelationshipbetweenthetoken clustersthatfalloutofadistributionalmodellingandwhatwouldtraditionallybe considereddifferentsenses,andsecond,thatthereisnosinglechoiceofmodelbuildingparametersthatisoptimalacrosstheboard,thatis,thatyieldsthebest possiblesolution(theoneclosesttoahumanperspective)foranylexicalitem.
Third,thebookisaccompaniedbyasetof digitaltools supportingtheanalytic workflowsdemonstratedinthecasestudies.Ontheonehand,someofthesetools involvePython3andRpackagesusedtoextractinformationfromcorpora,create distributionalmodels,andapplyclusteringandotherstatistical,viz.lectometric, analyses.Ontheother,visualizationtoolshavebeendevelopedwithinthecontextofthesemasiologicalworkflowforthequalitativeexaminationoftoken-level models.Theavailabilityofthesetoolsgreatlyenhancestherelevanceofthebook asasourceoffurtherresearch.
Theseassetssuggestforwhichgroupsofreadersthemonographmaybeof interest.Semanticistsandlexicologistswillbeinterestedintheformulationof acomprehensiveviewoflexicalvariation,intheexplorationofthepossibilitiesandlimitsoftoken-baseddistributionalsemantics,andinthetoolswe offerfortheincorporationoftoken-baseddistributionalmodellinginlexicaland semanticresearch.Computationallinguistswillbeinterestedinthedistributional workflowsweoffer,withtheiraccompanyingtools,andourexplorationofthepossibilitiesandlimitsofatoken-baseddistributionalapproach.Sociolinguistsand historicallinguistswillbeinterestedinourtreatmentoflexicalvariationasasociolinguisticvariable,andthesynchronicanddiachroniclexicallectometrybased onit.
Becauseweintendtoreachadiverseaudienceoflinguists,thetextiswritten withminimalassumptionsregardingbackgroundknowledge.Specifically,thefirst twochaptersaremeanttobridgethegapbetweendescriptivelyorientedlinguists, whomayneedanintroductiontothemodusoperandiofdistributionalsemantics, andmoretechnicallymindedresearchers,whomaybeunfamiliarwiththevariety ofperspectivesindescriptivelexicalandsemanticresearch.Inaddition,because thetrajectorywewilldescribeisonewithmanyoptionalturnsandsideways,we
willendeachchapterwithasummarythatwillhelpthereadertotracktheprogress oftheargument.
TheprojectfromwhichthismonographemanateswasfundedbytheResearch CounciloftheUniversityofLeuven(projectC16/15/023,withDirkGeeraertsas principalinvestigator).Apartfromtheauthorsofthepresentvolume,participants intheprojectincludedBenediktSzmrecsanyi,StefaniaMarzo,WeiweiZhang,Tao Chen,ChristianAndersen,andKristinaGeeraert.Althoughthepresenttextisa collectiveproduct,resultingfromseveralyearsofjointresearchefforts,theauthors havecontributedindifferentdegreestothevariouschapters.DirkGeeraertswas leadauthorforChapters1,2,and7,MarianaMontesforChapters4and5,andfor Chapter3togetherwithKrisHeylen.KarlienFrancotooktheleadforChapter6, StefanoDePascaleforChapter9,andMichaelLangforChapter10.StefanoDe PascaleandKarlienFrancowerejointlyresponsibleforChapter8.
PARTI
THEORETICALPRELIMINARIES
Twointerwovenstrandsofresearchdeterminetheorganizationofourmonograph:adescriptiveone,focusingonlexicalvariation,andamethodologicalone, focusingondistributionalcorpussemantics.Inthisfirstpartofthebook,two chapterspresentthebasicsandthebackgroundofbothstrands,with Chapter1 introducingthedescriptiveframework,andChapter 2 informallyexplainingthe essentialsofdistributionalvectorsemantics.Bothchaptersnotonlylayoutthe conceptualgroundworkforthesetopics,butalsosituatetheminawidercontext ofexistinglinguisticresearch.
1
Lexicalvariationandthe lexeme-lection-lecttriangle
Asourinvestigationissituatedatthecrossroadsoflexicalvariationresearchand distributionalsemantics,wehaveadoublebackgroundtodescribe.Inthischapter, weintroducethefirstofthesetwobackdrops:whatmodeloflexicalvariationdo westartfrom,wheredowesituateourownresearchwithinthatfield,andhow dowerelatetopreviousresearch?Thefirstsectionofthechapterchartsvarious conceptualperspectivesthatmaybetakeninlexicalvariationstudies;specifiesthe focusofourresearchinlightofthosealternatives;andindicateshowourchoice ofperspectivetranslatesintothestructureofthemonograph.Thesecondand thirdsectionthendetailourchoiceoffocus.Thethirdsectioninparticularintroducesthelectometricperspectivethatplaysacentralroleinlaterchapters,from Chapter 7 onward.Thefinaltwosectionssketchtheresearchbackground:onone hand,lexicalstudiesinthebroadercontextoflinguisticvariationresearch,onthe other,ourlocalresearchcontext.Thepresentstudycontinuesalong-termresearch linewithintheQuantitativeLexicologyandVariationalLinguisticsresearchgroup attheUniversityofLeuven,andaccordingly,weneedtoprovidesomedetailabout previousworkandhowthepresentapproachbuildsonearlierachievements.
1.1 Choicesoflexicologicalperspective
Imagineapairoftrousersendingjustbelowtheknee,tightenedroundthelegso thatthebottomendisslightlybaggy.Howwouldtheybecalled?Severalterms exist: knickerbockers, knickers,and breeches.Atthesametime,theycouldsimplybereferredtoas trousers,butthentheiteminquestionwouldbecategorized differently.Itwouldthennotbeidentifiedasamemberofthespecificcategory BREECHES‘pairoftrousersendingjustbelowtheknee,tightenedroundtheleg (etc.)’thatreceivesaunique,category-specificnamewithknickerbockersorknickers or breeches,butitwouldbeidentifiedasamemberofthebroadercategory TROUSERS‘garmentextendingfromthewaistdowntothekneeortheankle, coveringeachlegseparately’.(Typographically,wewillbeusingsmallcapsfor conceptsorcategories,specificallywhentheyarerepresentedbyvarioussynonymousexpressions.Italicsareusedforlexicalforms,anddefinitions,glosses,or
LexicalVariationandChange.DirkGeeraerts,DirkSpeelman,KrisHeylen,MarianaMontes,StefanoDePascale,Karlien Franco,andMichaelLang,OxfordUniversityPress.©DirkGeeraerts,DirkSpeelman,KrisHeylen,MarianaMontes, StefanoDePascale,KarlienFranco,andMichaelLang(2024).DOI:10.1093/oso/9780198890676.003.0001
explanationswillappearwithinquotes.)Buthowuniquearetermslike knickerbockers and knickers?Atleastfor knickers,thereisapolysemytobeconsidered, becauseitmayalsosignify‘underpants’,andthesynonymybetween knickers and knickerbockersdoesnotextendtothissecondsenseofknickers.Asimilarsituation actuallyholdswithregardto trousers:itissynonymouswith pants,butinapolysemoussense, pants issynonymouswiththe‘underwear’readingof knickers.In addition,thereislectalvariationinthedistributionoftheterms.Withoutbeing toodetailedaboutit,wemaynotethattrousersistypicallyBritishEnglishwhereas itssynonym pants (like knickerbockers incomparisonto breeches)isAmerican English,andaccordingly,the‘underwear’senseof pants isnotcommoninAmericanEnglish(likethatof knickers).Termslike typically areimportanthere:the lexicalchoicesareseldomofablack-and-whitenature,butmoreofteninvolve preferentialpatterns.
Thisbriefexample,towhichwewillcomebackinSection1.2,isstructured alongtwobasicdimensions.Thefirstonelinkslinguisticformstoreadings, whereasthesecondonebringsindifferentlanguagevarietiesanddescribeshow theassociationbetweenformandsemanticsdiffersaccordingtothedialect(inthe broadestpossiblesenseoftheterm)underconsideration.Crucially,bothdimensionscanbetraversedintwodirections.Ifyoustartfromalexicalitemand describethesemanticsofhowitisused,youtakea semasiological perspectiveand yourinterestbasicallylieswithpolysemy.Butifyoufocusonsynonymy,youlook fromthesemanticleveltothelevelofforms,describinghowameaningcanbe expressedbyvariouslexicalitems;thisisanonomasiologicalperspective.Thevariationaldimensioncansimilarlybesubjectedtoaperspectivalswitch.Ontheone hand(andthisisthemostcommonview),youcantaketheassociationofforms andmeaningsasaresponsevariableandinvestigatehowthatassociationchanges whenyoucomparedifferentlanguagevarieties.Ontheotherhand,therelationshipbetweenthosevarietiescanbeyourresponsevariable:ifyouaggregateovera largerpartofthevocabularyanditssemasiological/onomasiologicalcharacteristics,whatdoesthattellyouaboutthelanguagevarietiesinwhichthatvocabulary appears?Howclosearethey,andifyoulookovertime,aretheygrowingapartor growingtogether?Thefirstoftheseperspectives,lookingfromvarietiestovariable word-meaningpairs,maybecalled variationist,becauseitsoutlookcorresponds withthatofvariationistlinguisticsasthemajorbranchofsociolinguisticsinitiatedbyLabov’sworkfromthe1960s.Thesecondperspectiveisa lectometric one, becauseitfocusesonmeasuringdistancesamonglects. Lect inthisdefinitionisa covertermforallkindsoflanguagevarieties.IntheterminologyofCoseriu(1981), thisvarietyofvarietiesmaybestructuredalongfourcross-classifyingdimensions: adiatopicone,involvingthedialects,regiolects,chronolects,nationalvarieties, andsoon,usedindifferentpartsandlocationsofalinguisticarea;adiastraticone, involvingsociolectsbelongingtodifferentsocialgroups;adiaphasicone,involvingthedifferencesofstyleandregisterthatshowupindifferentspeechsituations
andcommunicativecontexts;andadiachronicone,involvingthechronological developmentandthehistoricalstagesofalanguage.Lectometryhassofarprimarilybeenanenterprisewithadiatopicperspective,butinaccordancewitha genericconceptionof lect,wethinkofitasageneralizationofthatdialectometric tradition.(Ondialectometry,see Goebl2011, WielingandNerbonne2015,and thediscussioninSection1.3.)
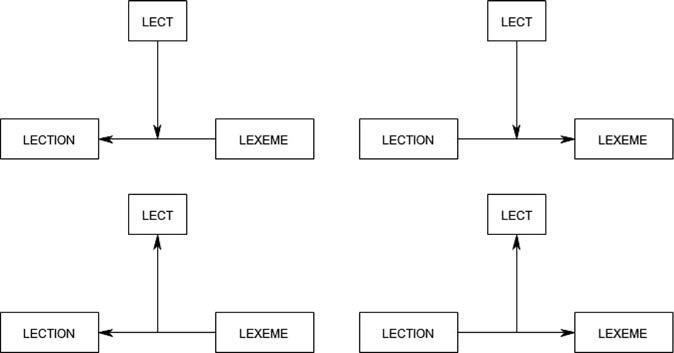
Giventhesetwodimensionsandtheassociatedperspectivalswitches (semasiological-onomasiological,variationist-lectometric),thescopeofourstudy canbedescribedintermsofwhatwewillcallthe lexeme-lection-lecttriangle.Terminologically,lexemesarethelexicalitemsunderinvestigation,andalectionisthe specificreadingwithwhichsuchawordappearsinatext(likewhether,tocome backtotheexample,knickersisusedinan‘underwear’readingora‘breeches’reading).Inthesenseintendedhere, lection isaratheroutdatedphilologicalterm,and weareadmittedlyselectingitlargelyforitsalliteratingqualities.Butthedefinition itreceivesinTheNewShorterOxfordEnglishDictionaryas‘aparticularwayof readingorinterpretingapassage;areadingfoundinaparticularcopyoredition ofatext’,adequatelycaptureswhatisofconcerntoushere,viz.themeaning-incontextofaword,theparticularinterpretationwithwhichitisusedinagiventext passage. Lect,asindicated,isageneraltermforallkindsoflanguagevarieties.
Lexemes,lections,andlectsinteract,andtalkingabouta lexeme-lection-lect triangle providesuswithahandyimagetoschematicallyrepresentthevarious aspectsofthatinteraction—orperhapsmoreprecisely,thecombinationsofthe twoperspectivaldimensionsthatweintroducedabove:seeFigure 1.1.Atthebase ofthetriangle,thedifferencebetweenasemasiologicalandanonomasiological perspectiveisexpressedbythedirectionofthearrowlinkinglexemeandlection.
Figure1.1 Researchperspectiveswithinthelexeme-lection-lecttriangle
Thepanelsontheleft-handsideembodyasemasiologicalperspective:looking fromlexemestotheirreadings.Thepanelsontherightembodytheconverse,onomasiologicalperspective:lookingfromreadingstotheformsthroughwhichthey areexpressed.Orthogonaltothesemasiological/onomasiologicaldimension,the perpendicularlinerepresentstheotherbasicperspective.Inthetoppanels,lectal variationisanexplanatoryvariable:ifyoulookateithersemasiologicaloronomasiologicalvariation,towhatextentisitinfluencedbylectaldiversity?Inthe bottompanels,theperspectiveisreversed,andlectalvariationbecomesaresponse variable:ifyouaggregateovereithersemasiologicaloronomasiologicalvariation, whichlectalstructureemerges?
Thevariouspartsofthepresentmonographtaketheirstartingpointinthese perspectives.PartIII,Semasiologicalandonomasiologicalexplorations,focuseson thetop-leftandthetop-rightapproaches. PartV, Lectometricexplorations,deals withthebottom-rightapproach.Thebottom-leftperspective—semasiological lectometry—willnotfeatureseparatelyinthevolume(butsee Speelmanand Heylen2017 foranexample).Therearetworeasonsfortheomission.First,if youstudyasampleofthevocabularythatislargeenough,thelectalstructure thatemergeswillbethesame,regardlessofwhetheryousumoversemasiological differencesorwhetheryousumoveronomasiologicaldifferences:everysemasiologicaldifferencebetweenlectAandlectBwillalsoshowupifyoustartfromthe onomasiologicalside,andviceversa.Ofcourse,thisisonlyanargumentinprinciple,becausestudyingtheentirevocabularyisnotfeasible.Second,however,there isatraditionincontemporaryvariationistlinguisticstostudylectaldifferences fromaformalpointofview,thatis,toassumethatlinguisticdifferencesbetween dialects,sociolects,andwhathaveyouarebestseeninalternativelectalpreferencesforfunctionallyequivalentformsofexpression.Thisideaiscapturedbythe notionofsociolinguisticvariable.Putsimply,asociolinguisticvariableinthesense ofcontemporarysociolinguistics(see Labov1966)isasetofalternativewaysof expressingthesamelinguisticfunctionorrealizingthesamelinguisticelement, whereeachofthealternativeshassocialsignificance:‘Socialandstylisticvariationpresupposetheoptionofsaying“thesamething”inseveraldifferentways: thatis,thevariantsareidenticalinreferenceortruthvalue,butopposedintheir socialand/orstylisticsignificance’(Labov1972:271).Assuch,asociolinguistic variableisalinguisticelementthatissensitivetoanumberofextralinguisticindependentvariableslikesocialclass,age,sex,geographicallocation,ethnicgroup, orcontextualstyleandregister.Classicalcasesofsociolinguisticvariablesinvolve pronunciation.Pronouncingthet inbutter asaglottalstopisindicativeofaCockneyaccent,justlikeafullpronunciationofthe n in chemin istypicalofsouthern FrenchincontrastwithstandardFrench.Exampleslikethesehadbeenstudiedfor alongtimeintraditionaldialectology,butmodernsociolinguisticsasitemerged inthe1960senlargedthescopeofinvestigationbeyondthetraditionaldiatopic dialectstootherlects.Ifyouapplytheconceptofasociolinguisticvariabletothe
lexicon,youinevitablyreachanonomasiologicalperspective,becauseonomasiology(andmorespecifically,formalonomasiology)preciselyinvolvesalternative lexicalexpressionsforthesamesense.
Twomorethingsneedtobesaidaboutthewaywewillcovertheterrainoutlined above.Inthefirstplace,thesubsequentpartsofthetextbuildoneachother.PartI, Theoreticalpreliminaries,laysthegroundwork.PartsIIandIIIthenfocusonthe semasiologicalandonomasiologicalperspectivesthatbelongtotheupperlayerof Figure 1.1,whereas PartsIV andVtakealectometricpointofviewasinthelower layerofthefigure.Ineachofthesetwosets,thefirstpartisdevotedtomethodologicalissueswhilethesecondillustratesthemethodologywithcasestudies.Thus PartII,Distributionalmethodology,introducestheparticularsofthedistributional semanticworkflow,togetherwiththevisualizationtoolthatwewillusetoexplore itsoutcome. PartIII, Semasiologicalandonomasiologicalexplorations,putsthis explorationintopractice.Itexamineshowfaradistributionalapproachcantake usonthepathofsemanticanalysis(asweshallsee,thereareanumberofrestrictionsondistributionalinformationthatwillmakeusadoptacertainamountof cautionforthefurthersteps)andappliesthedistributionalmethodtotheinterplay ofsemasiologyandonomasiologyinlexicalsemanticchange. PartIV, Lectometricmethodology,introducesthevariousstepsinalectometricworkflow:howto determinetherelevantsetsofalternatingexpressionsandthecontextsinwhich theyalternateasequivalents(whatsociolinguisticsreferstoastheenvelopeofvariation),andhowtofeedthedistributionofthecompetingexpressionswithinthe envelopesintoacalculationoflectometricdistances. PartV, Lectometricexplorations,illustratesthisworkflow.Overallthen,thestructureofthetextembodiesa gradualbuild-up.ItisnotjustthatthechaptersinPartIIsmooththewayforthose in PartIII,andthosein PartIV for PartV,but(totheextentthatidentifyinglexicalsociolinguisticvariablesrequiresasemanticanalysis)PartsIIandIIItogether alsopreparethegroundforPartsIVandV.
Inthesecondplace,thedegreetowhichwewillcovertheperspectivallydefined domainsschematicallyrepresentedinFigure 1.1 willbynomeansbecomplete, evenapartfromtheabsenceofasemasiologicallectometricapproach.Ourpurposeistodefine,illustrate,andexplorearesearchprogramme,nottotreatit exhaustively—ifthatwouldbepossibleatall.Throughoutthechapters,wewill explicitlypointtoopenissuesandpossibilitiesforfurtherinvestigation.
Inthefollowingtwosectionsofthepresentchapter,wewilllookmoredeeply intothetwodimensionsandtheassociatedquestionsthatshapethestructureof thebookandthataregraphicallysummarizedinFigure 1.1.Alongthesemasiology/onomasiologydimension,Section1.2willconsiderthestatusofavectorspace approachfromthepointofviewofsemanticandconceptualanalysis.Alongthe variationist/lectometricdimension,Section1.3detailswhatitimpliestotreatlexicalvariationasasociolinguisticvariableintheLaboviansenseandtousethat variationasthebasisforlexicallectometry.