

P 38 – Three years on from its launch, the Cygnus 1 Ex UTG remains one of Cygnus Instruments’ most celebrated innovations, as revealed in a MEPCA exclusive interview.








P 38 – Three years on from its launch, the Cygnus 1 Ex UTG remains one of Cygnus Instruments’ most celebrated innovations, as revealed in a MEPCA exclusive interview.




Downtime costs more than lost hours. It erodes trust, safety and profitability. Use our free online Reliability Navigator to receive a personalized report with clear insights and actions to help you move from firefighting to future-proofing.














Editor
Oliver Batt oliver@cimltd.co.uk
Publication Manager
James Burke jb@mepca.com 01795 509105
Account Manager
Jim Bearden jim@mepca.com 01795 509105
Design & Production
Grant Waters grant@cimltd.co.uk
James Taylor james@cimltd.co.uk
Administration Manager
Natalie Woollin admin@cimltd.co.uk 01795 509103
Credit Facilities Manager
Gwen Lee creditcontrol@cimltd.co.uk 01795 509103
Head of Digital
Xhulio Bishtaja digital@cimltd.co.uk
Marketing Manager
Lucas Payne lucas@cimltd.co.uk
Director Tom Woollin tom@cimltd.co.uk
Managing Director
John Denning
© 2026 Cogent Multimedia Limited, 1st Floor, Saphir House, 5 Jubilee Way, Faversham, Kent, ME13 8GD. No part of this magazine may be reproduced or stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form – electronic, mechanical or physical – without express prior permission and written consent of the publisher. Contributions are invited and when not accepted will be returned only if accompanied by a fully stamped and addressed envelope. Manuscripts should be typewritten. No responsibility can be taken for drawings, photographs or literary contributions during transmission or in the editor’s hands. In the absence of an agreement the copyright of all contributions, literary, photographic or artistic, belongs to Cogent Multimedia Limited. The publisher accepts no responsibility in respect of advertisements appearing in the magazine and the opinions expressed do not necessarily represent the views of the publisher. The publisher cannot accept liability for any loss arising from the late appearance or nonpublication of any advertisement.

Greetings dear readers and welcome to the February edition of MEPCA magazine.
After weathering the January blues, 2026 year is well underway and picking up the pace. In this issue, we’re looking at strategies for seizing the year in our Business Operations focus (page 19), where Lloyds lead with a feature on the key factors that will influence manufacturing in the year ahead. Also in this section, MEPCA examines how to tackle the daunting talent shortage (page 24), while Gallagher addresses the impact of product recall on operations (page 30).

In our Cover Story this month (page 16), Epicor provides insights on the growing value of data, and further into this issue, we have an expensive Sensors & Sensing Systems section, within which I report on Turck Banner’s sensor to cloud solutions (40-41), aimed at addressing the IT-OT divide.
This month’s manufacturing champion (page 14) is building a community for industry as a strategy for tackling its most persistent challenges.
The MEPCA team looks forward to seeing many of you at Southern Manufacturing & Electronics. 16
Oliver Batt, Editor
To subscribe to MEPCA visit our website www.mepca.com or scan the QR code. @Mepca-magazine


















Mips AB (publ), a world-leader in helmetbased safety, has signed an agreement to acquire KOROYD. KOROYD is a pioneer in the development of advanced impact protection technology for head and body safety, which is complementary to Mips’ technology.
In December 2025, Mips announced its acquisition of KOROYD, strengthening the company’s world-leading helmet safety technology portfolio with complementary technology. Recognising the potential synergies between the two brands and their respective technologies, Mips and KOROYD will continue to operate separately under their respective leadership teams.
“The acquisition of KOROYD marks another important step in Mips’ long-term strategy to strengthen our position as the leader in helmet safety. This acquisition positions the group uniquely in the market and enables interesting entries into other adjacent product areas. The acquisition is in line with our strategy and also serves as a springboard into adjacent product safety areas”, says Max Strandwitz, CEO and President of Mips.
“From the beginning, KOROYD has been built on a culture of purposeful innovation, solving real problems with solutions that genuinely improve protection whilst putting the user experience first. In Mips, we have found

a partner who shares that ethos entirely”, says John Lloyd, Founder of KOROYD.
“Together, I am convinced that this combination will accelerate our diversification strategy. Our technologies are naturally complementary and together form a platform that strengthens partners, delivers on the strong demand for both brands and expands what is possible in protection,” adds John Lloyd.
koroyd.com
Famous for producing its Lucozade and Ribena brands, SBF GB&I has invested in data loggers added to water meters, to unlock further efficiency opportunities at its factory in Coleford. The data loggers feed information around water use into an online analysis portal, so use during the day and night can be reviewed and scrutinised.
An efficiency audit, also completed by Water Plus, identified a £500,000 saving for SBF GB&I in 2025. This was in addition to a previous £40,000 a month reduction in wholesaler charges1
Karl Ottomar, Supply Chain Director at Suntory Beverage & Food GB&I, said: “Whether its upgrading washout systems, quickly detecting leaks, or conducting regular audits, we know that every drop of water really does count to help us meet our target for reducing water intensity. Water Plus have been a great partner to help us identify where else we could deliver water efficiency in our operations.”
Suntory Beverage & Food GB&I has set science-based targets to reduce emissions and achieve Net Zero by 2050. For SBF GB&I, water is essential to the business and it works hard to protect this precious resource for future generations, as part of its purpose to create harmony with people and nature. Reducing water use reduces carbon

emissions, as less energy is needed to treat, pump and move water and improving water efficiencies also helps reduce water scarcity risks.
suntorybeverageandfood-europe.com
*£40,000 a month wholesaler charge reduction was secured by the Water Plus team for SBF GB&I since April 2025.




Wayne Rose, Chief Executive, British Pump Manufacturers Association, shares key trends defining the UK Pump Industry.
The UK pump industry is operating at a pivotal moment. Long recognised as a critical enabler of sectors ranging from water and energy to manufacturing and building services, the industry is now being reshaped by powerful forces including sustainability, regulation, skills shortages and digital transformation. While these trends present challenges, they also create opportunities for innovation and growth.
Energy efficiency continues to sit firmly at the top of the industry agenda. Pumping systems account for a significant share of global electricity consumption, meaning even modest efficiency gains can have a substantial impact on operating costs and carbon emissions.
Manufacturers are responding through innovation: improving hydraulic performance, integrating intelligent controls, and focusing on system-level optimisation rather than standalone components. At the same time, decarbonisation measures such as the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) are advancing rapidly, reinforcing the need for demonstrable environmental performance and transparency.
Alongside sustainability, regulation remains a defining issue. The European Union is progressing the Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR), a wide-ranging framework that will influence how products are designed, documented and placed on the market.
In the UK, the Government is considering legal alignment with aspects of ESPR through an extension of CE recognition. While alignment can reduce barriers to trade, it also introduces complexity for manufacturers operating across multiple markets. The BPMA continues to play an active advocacy role in this area, engaging with UK policymakers and working at a European level through Europump.
The pump industry, like much of UK engineering, faces an ongoing shortage of skilled personnel. Throughout 2026 and beyond, the BPMA will place increased emphasis on careers, skills and training through its Recruitment

Committee and the continued development of its comprehensive training programme. These initiatives are designed to upskill the existing workforce while promoting the pump industry as a modern, technology-driven sector offering long-term career opportunities.
Digitisation is accelerating across the pump sector. Under ESPR, manufacturers will see increasing requirements for digital product information, leading to electronic nameplates and Digital Product Passports.
These tools will improve traceability, compliance, and access to product data across the entire lifecycle. When implemented effectively, these technologies can enhance efficiency, quality, and competitiveness in both domestic and global markets.
The trends shaping the UK pump industry are significant, but they point towards a sector that is adaptable, innovative, and increasingly strategic in its role. The BPMA remains committed to supporting its members through leadership, advocacy and practical guidance, ensuring the UK pump industry is not just responding to change, but helping to shape it.
bpma.org.uk
3-4 JUNE 2026

The UK’s Dedicated Event for Medical Device Design and Manufacturing.
Advance your medical device development with the latest design, materials and manufacturing solutions.
Connect with over 150 specialist suppliers and gain insights into quality, compliance and innovation.
Secure your place today at med-tech expo or scan the QR code

CO-LOCATED WITH:
Nikesh Mistry, Sector Head, Industrial Automation and Test & Measurement, GAMBICA, challenges the current AI narrative of replacement as progress.
The most interesting ideas in manufacturing rarely come from conference stages or glossy technical discussions, they come from the people who keep factories running when the stakes are highest. My views are shaped by those true conversations, when industry struggles and the Industrial Automation members of GAMBICA discuss how they’ve tackled pressure, dealt with constraints and proved themselves resilient, not through theoretical measures but through decisions that have had consequences. That’s why I’m unconvinced by the media narrative that manufacturing’s next leap will come from replacing people with intelligent agents. It’s a clean story, but it doesn’t match history or the lived reality of operations.
For decades, productivity and employment rose in parallel. As we progressed through different revolutions, manufacturers invested in better tools, more efficient processes, and refined skills but these gains were still delivered by the people. It was then that automation and offshoring started to become standard practice for many and productivity began rapidly increasing; however, it was halted when the belief that automation could replace human judgment rather than amplify it became “talk of the town”.
The biggest shortages are still in skilled roles such as process engineers, maintenance technicians, electricians, robotics specialists. These are exactly the people the World Economic Forum identifies as critical to industrial resilience. Yet we keep assuming each role can absorb every new technological wave, as if a process engineer should also be a data scientist and a plant manager a robotics programmer. This becomes more wishful thinking rather than reality. Yes, upskilling is necessary, however, technology only delivers productivity when it aligns with how work is done, and this is usually dictated by a human making the decisions and judgments when time is critical.
AI and Generative AI has the ability to transform manufacturing, but only if it’s founded in real data, real workflows, and human accountability. AI should help people move faster and see more clearly, not replace their judgment.
The future isn’t fully autonomous factories; it’s orchestrated operations with open, composable systems that adapt as technologies evolve, keeping humans in the loop while giving them more influence. If AI doesn’t make frontline work more skilled, more respected, and

more impactful, then it hasn’t solved the real problem. Manufacturing’s future must be written by people, but with AI amplifying what they can do, not replacing them.
Just as other technologies have done in the past, AI will also create new roles, roles we haven’t named yet. As systems become more capable, the demand for people who can interpret, validate, adapt and orchestrate them will grow. Every major technological shift in manufacturing has expanded the scope of human work, not reduced it. We should expect the same here.
The real opportunity isn’t replacing people, but giving them more leverage. If we forget the power of human judgment, creativity and problem solving, we’ll miss the very thing that makes AI valuable in the first place.
gambica.org.uk

This month, MEPCA celebrates Sam Baynham, Founder and Director of ConeX Portal UK. Speaking with our editor, Sam shares how his experiences in engineering inspired the founding of ConeX and highlights the problem-solving power of a community for industry.
Reflecting on his route into industry, Sam said that while he took the conventional STEM subject path, it also felt like a very natural progression for him. “I was always quite handson with things, mainly breaking, not really fixing,” he joked, though he had always taken a keen interest in how things worked.
After studying mechanical engineering at university, Sam began working at Delcam (later purchased by Autodesk), which allowed him to specialise in CADCAM software and gifted Sam with an insight into manufacturing businesses, allowing him to learn properly about the industry, in a hands-on way, something that he believes to be missing from formal education.
While his time at Autodesk was eye-opening, it wasn’t long before he was frustrated with the limited scope of the role and was eager to branch out on his own. At just 26, following a short stint as a self-employed CADCAM specialist, Sam founded Dynamic Edge Innovation Ltd to help businesses with product design, from concept through to prototyping. This ultimately grew into ConeX Portal UK.
“The more manufacturers I’d speak to, the more challenges I’d hear, the more things I’d find out that they were struggling with. The more I’d recognise that the sector isn’t that joined and doesn’t really have that community voice. It doesn’t have that connectivity; there’s no consistent voice or message.”
By connecting companies struggling with similar challenges, ConeX Portal’s community could attempt to solve them together, learning from one another’s experiences, rather than struggling on in their own “silos”.
“When you get in room with people and you decide on the topic and the theme and the main challenge that was holding them back, suddenly everyone’s invested in talking about that.”
Once those ideas gain clarity, ConeX can then put them forward to industry bodies and other groups, creating a consistent voice and message, which is crucial for giving manufacturing SMEs a voice.
Without doing the ground work and defining clearly what the sector needs, Sam explained, the government won’t “see a unified SME engineering manufacturing sector with a list of problems that it can address.”

What can we expect to see from ConeX Portal UK in 2026? Each year Sam starts with a defining word and this year’s is “perception”, referring to both how the industry needs to change, and how ConeX needs to shift its perception as a networking group, to a community connecting people, leveraging skills and “facilitating projects through the entire supply chain.”
To learn more about the important work Sam is doing with ConeX Portal UK, visit the company’s website, or better yet, stop by to speak to him at Southern Manufacturing & Electronics.
conex-portal.co.uk

As the industry looks to artificial intelligence to deliver the next level of production efficiency, data is becoming an invaluable resource and the foundation of operational improvement. Manufacturers that don’t recognise the value of their data, or hesitate in utilising it, risk being left behind.
Manufacturers are operating in an increasingly challenging environment. Supply chain disruption, rising customer expectations, growing product complexity, and persistent labour shortages are pushing operations to the limit. Many organisations have already streamlined processes through automation and lean practices, but the gains from traditional improvement methods are beginning to plateau. To continue progressing, manufacturers are looking to artificial intelligence to deliver the next leap forward.
AI’s value in manufacturing is no longer theoretical. From predicting machine failures to improving yield, optimising schedules, and giving workers instant access to the information they need, AI has become practical, accessible, and increasingly essential. Yet adoption is still slower than the opportunity suggests. Many organisations worry about data readiness, investment requirements, or the impact AI might have on their workforce. In reality, those concerns are often based on outdated assumptions.
One of the strongest signals that the industry is ready for AI is the wealth of data manufacturers already possess, data that is routinely captured through ERP systems, production logs, quality checks, SCADA systems, machine sensors, and maintenance records. Modern AI tools do not require flawless or meticulously structured datasets. Instead, they work with real world operational information, often cleaning and enriching that data automatically as part of implementation.
A persistent hesitation is the fear that AI will replace people. Evidence across manufacturing shows the opposite: AI enhances the role of the workforce by reducing repetitive administration and supporting better, faster decisions. Employees spend less time hunting for information or manually updating spreadsheets and more time applying their expertise to problem solving, process improvement, and customer support. This is especially valuable as manufacturers struggle to recruit and retain skilled workers.
Tools such as Epicor Prism demonstrate how accessible AI has become. Rather than navigating complex ERP screens, workers can simply ask questions, “What’s the status of job 14523?”, “Which orders are at risk?”, “Update

the schedule based on the latest completion times” and receive instant, accurate responses. Manufacturers already using these tools report significant time savings, improved responsiveness, and major reductions in administrative load.
To get started, manufacturers benefit from recognising the wide variety of data sources already available to them. Useful operational data can be derived from several sources, including ERP records such as job orders, materials, inventory and financials; MES data capturing production steps, cycle times, and throughput; SCADA systems monitoring line conditions and process variables; PLC or machine historians capturing real time equipment behaviour; quality inspection results and test logs; maintenance and CMMS histories; and IoT sensors monitoring temperature, vibration, torque, or energy usage.
Increasingly, nontraditional sources such as imagery from automated inspection systems, environmental readings, and energy consumption data are proving highly valuable for AI driven optimisation.
Instead of waiting for data to be “perfect”, manufacturers can begin identifying opportunities where AI would deliver


immediate, measurable benefits. Common areas include:
• Predictive maintenance to prevent unplanned downtime
• Quality prediction and automated visual inspection
• Real time production scheduling and sequencing
• Yield improvement on high variance lines
• Energy optimisation based on machine level consumption
• Conversational access to operational and ERP insights
These use cases work particularly well because they target existing pain points and rely on data that most manufacturers already have.
Starting small is key. A single, well-chosen use case provides an early win that builds internal confidence. Many manufacturers begin by focusing on the issues that disrupt operations most frequently, unexpected breakdowns, scrap spikes, supply delays, or inefficient changeovers. Once AI is applied to solve one of these challenges, momentum builds naturally. Teams can see the benefits firsthand; leaders have measurable outcomes to share and future initiatives face less resistance.
Setting clear goals helps ensure success. Manufacturers may choose to reduce unplanned downtime by a targeted percentage, improve first pass yield on key product lines, shorten changeovers or sequence jobs more efficiently. They may choose to lower energy usage per unit produced, or increase on time delivery by improving schedule accuracy.
Defining these outcomes early provides a shared reference point and makes progress easy to track.
Real world examples reinforce these benefits. Olympus Group has used Epicor Prism to improve quoting accuracy, enhance lead time predictions, and reduce manual coordination. Their leadership sees potential for up to a 20% operational improvement, driven not by new machinery or headcount, but by better use of their existing data. Madsen’s Custom Cabinets offers another compelling example: a previously time-consuming scheduling process involving multiple staff has been replaced with simple natural language instructions, freeing skilled employees to focus on more strategic work.
Success with AI depends as much on people as on technology. Manufacturers who make the strongest progress tend to communicate early and clearly about why AI matters. They will also provide hands on training to build confidence, and involve operations, IT, engineering, and finance from the start. To ensure seamless integration with existing system, they will choose trusted partners whose tools integrate seamlessly with existing systems. What’s more, successful adopters tend to celebrate early wins to build enthusiasm and organisational support.
Leadership plays a decisive role. When executives champion AI initiatives, align them with strategic goals, and highlight the benefits for both the business and its people, adoption accelerates and resistance diminishes.
The path to AI maturity does not require a major transformation. It requires readiness, clarity and momentum. Manufacturers who start small, iterate based on experience and focus on real operational challenges will see rapid gains in efficiency, decision making and resilience.
AI is no longer a futuristic vision, it’s a practical, powerful tool that can help manufacturers work smarter, adapt faster and achieve more with the people and systems they already have. Those who embrace it now will shape the future of the industry; those who delay risk being left behind as competitors turn data into insight, and insight into sustained advantage.
For manufacturers ready to turn their data into a competitive advantage, Epicor can help them take the next step with confidence. With industry specific solutions like Epicor Kinetic, Advanced MES, and the AI powered Epicor Prism, manufacturers gain intuitive tools that fit the way they already work, without costly disruption. Whether the goal is to improve scheduling, unlock real time insights, enhance quality, or empower a workforce with accessible AI, Epicor delivers technology designed for the unique demands of manufacturing.
epicor.com/en-uk/solutions/industries/manufacturing/


Sponsored By
Dave Atkinson, UK Head of Manufacturing SME & Mid Corporates, Lloyds, takes the opportunity to reflect on the key factors that will influence decision making in the year ahead.

As we move into 2026, manufacturers face a landscape defined by heightened security threats, unprecedented cost pressures and geopolitical uncertainty.
Yet alongside these challenges lie significant opportunities – from a £75 billion defence spending commitment to the transformative potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
For SMEs and mid-sized manufacturers, the path forward demands a clear-eyed assessment of the risks, strategic investment in resilience and the agility to capitalise on new growth avenues.Here are seven key factors that will help shape the sector during 2026.
CYBERSECURITY: THE LEADING THREAT
Cybersecurity emerged as a top business risk during 2025,
with the high-profile attack on Jaguar Land Rover.
The threat landscape has evolved. Manufacturing systems increasingly integrate digital technologies with physical operations, creating new attack surfaces. A breach doesn’t just compromise data; it can halt production lines, disrupt delivery schedules and damage customer relationships. For manufacturers integrated into complex supply chains, a vulnerability in one supplier can cascade across multiple organisations.
The challenge is particularly acute for smaller manufacturers who may lack dedicated cybersecurity resources. Yet the cost of inaction – in lost production, remediation expenses and reputational damage – far exceeds the investment required to build digital resilience, including insurance and Cybersecurity as a Service. For manufacturers, cybersecurity is not just an IT problem, but a fundamental business capability.
The government’s Defence Industrial Strategy represents a genuine opportunity for UK manufacturers. The £75 billion commitment over six years aims to make defence “an engine for growth”, with SMEs placed at the centre of this vision.
The strategy explicitly targets regional ecosystems, innovation funds and export support to create jobs and build industrial capacity across the country.
Regional defence clusters are creating pathways for SMEs to integrate into high-value supply chains. These clusters offer access to procurement opportunities, R&D funding and collaborative networks that can help smaller manufacturers scale and compete for contracts that might previously have seemed out of reach.
The strategy also addresses skills development through five new Defence Technical Excellence Colleges and regional training hubs, recognising that a skilled workforce is essential to delivering on defence commitments.
Cost pressures have continued to intensify across the sector; in 2025 Make UK reported that 79% of manufacturers faced raw material cost increases and 70% expected energy costs to rise further1
Rising employment taxes, logistics expenses and persistent inflation are impacting on margins and SMEs are often less able to absorb these increased costs. They typically have less pricing power with customers and have been slower to adopt automation technologies that might help offset labour cost increases.
The UK has some of the highest industrial electricity prices in the world2, creating a structural disadvantage that affects competitiveness, and this will continue to present a significant challenge for manufacturers in 2026, who are particularly exposed.
Geopolitical instability continues to reshape global trade. Disruption in the Red Sea, the ongoing conflict in Ukraine and Middle East tensions have created persistent supply

chain challenges and inflated logistics costs.
This uncertainty is driving a significant shift toward reshoring and nearshoring.
For UK manufacturers, this presents both challenge and opportunity. Building resilient supply chains requires investment and relationship development. However, the trend toward regional sourcing is already creating openings for UK-based suppliers who can offer reliability and proximity advantages.
Manufacturers are making substantial investments in AI, robotics and digitalisation to help offset cost pressures and improve operational resilience. These technologies offer real productivity gains, including better quality control, predictive maintenance and reduced waste.
However, a significant adoption gap exists. Capital constraints, skills shortages and uncertainties over return on investment mean some SMEs are lagging behind larger firms.
But these transformative technologies will undoubtedly be decisive to future competitiveness. The opportunity lies in strategic, phased implementation rather than wholesale transformation.
A good starting point is to contact Lloyds’ long-term strategic partner MTC (Manufacturing Technology Centre), which employs a team of experts who visit manufacturers to carry out free line walks. It’s an opportunity to review how you work and identify opportunities to automate, drive productivity and adopt new technologies that can create the capability to diversify into new supply chains.

According to Make UK, labour shortages are costing the manufacturing sector £6bn in lost output every year3 While the skills pipeline remains weak, wage pressures have continued to rise.
At a time when manufacturers are struggling to attract young talent and retain experienced workers, apprenticeship programmes, upskilling initiatives and retention strategies will prove critical, both for individual businesses and the wider sector.
That will mean a focus on workforce development, creating clear career pathways, investing in training and building workplace cultures that value people.
And the sector must also continue its work to engage with the education sector and promote STEM skills if we are to build the skilled workforce advanced manufacturers need.
The UK manufacturing sector enters 2026 facing significant headwinds, but there are equally substantial opportunities to access. Defence expansion, digital transformation and regional industrial clusters offer strategic growth pathways for manufacturers who can navigate this complex landscape.
The priorities for SME manufacturers must include resilience, agility and targeted investments in productivity, technology, sustainability and cybersecurity, as well as securing access to robust, diversified supply chains.
The manufacturers who thrive won’t necessarily be the biggest or best resourced, but those who invest strategically in capabilities that matter, and remain agile enough to seize opportunities.
As ever, I remain optimistic and look forward to working with the sector during this time of transformation.
See how Lloyds is supporting UK manufacturers to innovate, grow, and lead at.
lloydsbank.com/manufacturing
All Lending is subject to status. Eligibility criteria apply. Lloyds and Lloyds Bank are trading names of Lloyds Bank plc. Registered Office: 25 Gresham Street, London EC2V 7HN. Registered in England and Wales no. 2065. Telephone: 0207 626 1500.
Authorised by the Prudential Regulation Authority and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority and the Prudential Regulation Authority under Registration Number 119278.
1. bit.ly/4svUHd3
2. fullfact.org/economy/uk-world-electricity-prices/
3. makeuk.org/make-uk-industrial-strategy-skills-commission-report-2025

Carried over from the prior year like a persistent hangover, the problem of the growing talent shortage looks likely to be a defining challenge for 2026. In this exclusive feature, MEPCA shares advice from three recruitment experts, Hays, Enginuity and Michael Page.

With over 47,000 unfilled vacancies, falling apprenticeship opportunities, the retirement of skilled operatives looming, and rapid technological progress demanding new skillsets, recruitment will be a key challenge for the industry this year. The talent shortfall is putting an increased pressure on businesses, and their employees, as they try to increase output without the people-power required for growth.
To better understand the nature of the recruitment challenges being faced, and to highlight strategies that will help companies put the right people in those vacant positions, we consulted with three manufacturing and engineering recruitment experts.
Providing insights from Michael Page, we have Ruth Hancock, Regional Director, Manufacturing; from Enginuity, we have Fiona McGarry, Sector Engagement Manager; and providing expertise form Hays, Brendan Ryan, Director, Engineering & Manufacturing.
Ruth Hancock had found that senior positions, such as “Supply Chain Manager, Maintenance Engineer,
Engineering Manager, Design Engineer, and Operations Director,” were proving most difficult to fill.
“As organisations focus on strengthening supply chains, maintaining asset reliability, and driving operational transformation, professionals with these skill sets are in high demand,” Ruth explained, which is further driving this by increasing competition.
For Fiona McGarry, “The hardest roles to fill are those requiring practical, technical expertise, particularly welding, maintenance, and advanced fabrication.” While efforts are being made to encourage careers in industry, this was undermined by a reduced access to apprenticeships:
“Over the past decade, the sector has worked hard to raise the profile of engineering careers and the value of apprenticeships. Yet just as young people are switching on to these opportunities, apprenticeship intakes are shrinking or being paused,” Fiona continued, “Fewer apprenticeship vacancies have contributed to the highest NEET (Not in Employment, Education or Training) figures in a decade.”
As well as senior roles, Hays were seeing demand for skillsets needed for Industry 4.0. “Automation, maintenance, project delivery and multidisciplinary
engineering roles are now the hardest to fill as employers modernise operations and prioritise efficiency,” said Brendan Ryan.
“The difficulty” Brendan continued, “stems from the depth of the talent shortage: 95% of organisations reported skills gaps last year, and the biggest hiring obstacles expected ahead include a shortage of suitable applicants (66%), competition from other employers (61%) and unrealistic salary expectations (57%).”
According to ECITB1, 20% of the engineering workforce will be reaching retirement age in 2026. What can businesses do to mitigate the operational impact of retirement?
“Businesses need to act now to protect their skills for the future,” Fiona warned, “Investing in people, by taking on apprentices and helping existing staff develop new skills, is not a ‘nice to have’ but key to keeping operations running smoothly.
“One of the biggest risks is losing valuable, hard-earned knowledge when experienced staff leave. We have seen great success when organisations pair long-standing employees with apprentices, giving them time to share expertise and turn everyday know-how into training that lasts beyond retirement.”
Adding to this, Brendan said: “Organisations should prioritise structured knowledge transfer and succession planning. This includes mentoring, shadowing and documenting critical operational expertise. Strengthening internal development is essential; when it comes to training and upskilling, employees want funded learning (46%), clear development paths (35%) and in house training (32%), all of which help build future capability.
“Hiring strategies must also adapt – positively – 74% of employers across the sector told us they would be open to hiring individuals without all the required skills and upskilling them,” he concluded.
Ruth agreed that business should act proactively: “Building strong apprenticeship and early-career pipelines, implementing structured knowledge transfer, and strengthening long-term workforce planning are all critical.
“Diversifying recruitment channels, exploring returnto-work pathways, and being open to internal moves or transferable skills can also help fill critical gaps. Finding the right recruitment partner is key to executing these strategies effectively.”
As seen above, due to the demand for particular skills sets outstrips the pipeline of talent, competition is increasingly fierce. How can businesses stand out and attract the people they need?
Both Ruth and Brendan, a strong, well communicated (Employee Value Proposition) is a crucial factor to attracting talent.
Brendan: “In a highly competitive market, employers must demonstrate they can provide good pay and benefits, showcase good progression opportunities as well as a good workplace culture.”
Interestingly, he added, “Although 84% of employers

reported that they increased salaries in 2025, over a third of professionals (37%) remain dissatisfied. Clear progression, strong benefits and culture matter: professionals across the industry are prioritising benefits (49%), work atmosphere (41%), job security (35%) and development (35%) when looking for a new role.”
Securing talent now requires a strategic, holistic approach, explained Ruth, “Candidates are taking a ‘waitand-see’ approach, carefully weighing opportunities, while employers seek the right hire. Balancing sector experience with broader capabilities such as agility, systems knowledge, and cross-functional skills opens access to a wider talent pool.
Agreeing that salary wasn’t everything, Ruth continued, “Wellbeing and work-life balance are now decisive factors, alongside clear career pathways and development opportunities.”
Fiona addresses the talent pool at its source: “Employers need to engage with young people early and consistently, creating multiple touchpoints throughout their education. Talent attraction is about showing up and making the sector feel real and reachable.
“That means building school relationships from primary through to post-16 education, supporting work experience and T Level placements, and giving students a clear insight into what engineering and manufacturing look like on a day-to-day basis.”
Solving this complex problem requires tackling it from several angles, from improving routes into industry through STEM subjects and apprenticeships, to retaining staff through upskilling/reskilling and clear EVPs. Added to this, contingencies for knowledge retention will be crucial as staff retire. None of these are easy fixes, but they are feasible, and what’s more they are necessary if UK manufacturing is to flourish.
MEPCA would like to thank the contributors for their invaluable insights. For more information and advice, visit the organisations’ websites.
enginuity.org/enspiring-futures michaelpage.co.uk hays.co.uk/recruitment/manufacturing
1. ecitb.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/EC03-ECITB-ET-ReportFINAL-23.01.18-1.pdf
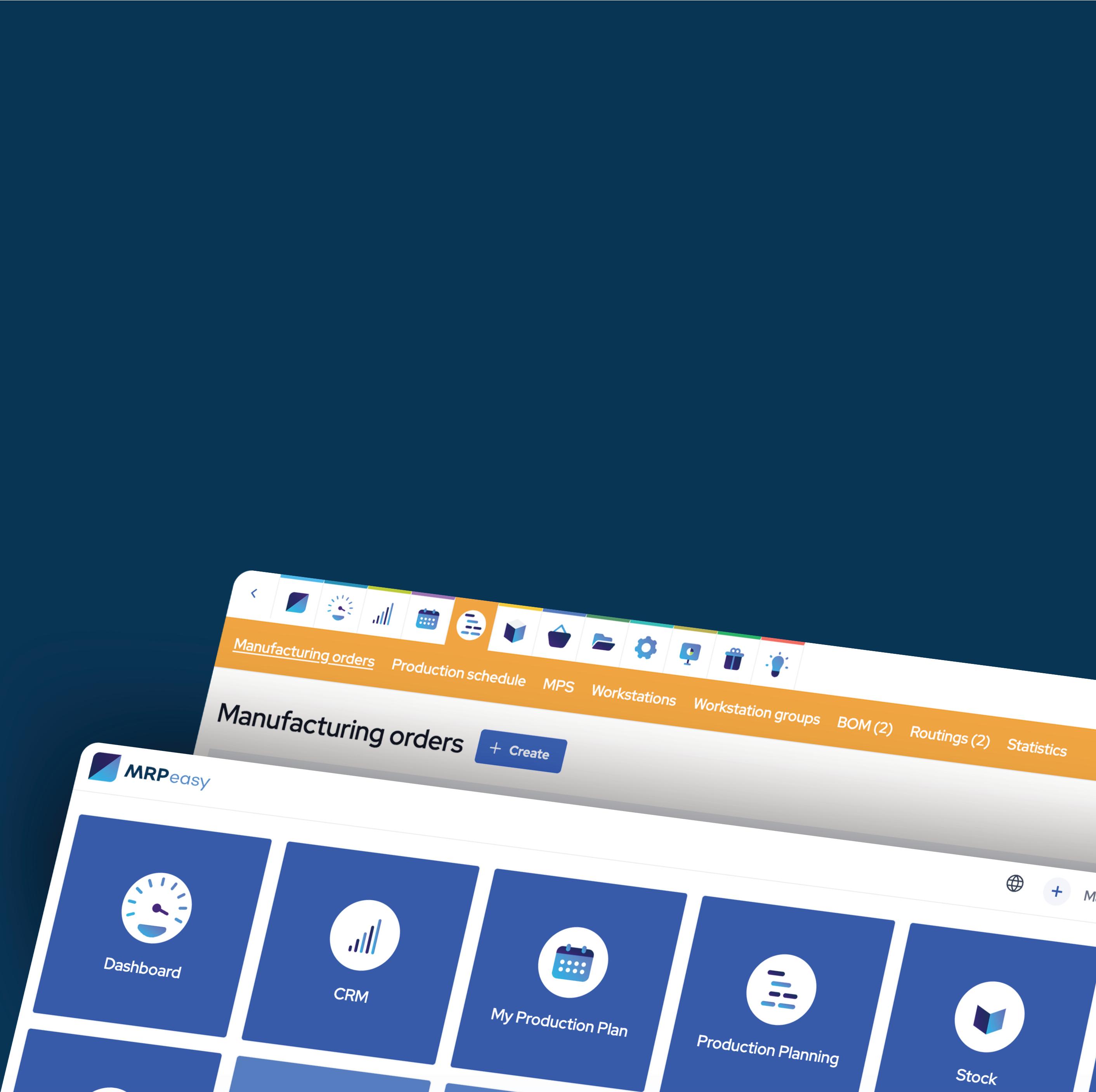
In this insightful case study, a sauna manufacturer brings 45 years of craftsmanship into the digital age with the support of an AI-powered, material requirement planning (MRP) software platform. What began as an internal systems upgrade became a company-wide modernisation project.
Since its inception in the 1970s, Oceanic Saunas has grown into one of the UK’s leading sauna and steam room manufacturers. From compact infrared cabins to bespoke Turkish steam rooms, the Wolverhampton-based company is renowned for designing and building high-quality wellness spaces for homes and commercial locations.
Director Sarah Jones, who joined the family business about two decades ago, has led the company through a major evolution in recent years. Oceanic Saunas used to sell all sorts of bathroom products, like baths, showers, and washroom accessories, aside from their staple product, saunas. “I saw the market saturating and made the decision to focus purely on saunas and steam rooms. That’s what we’re truly good at and what customers know us for today,” says Sarah.
The company’s internal systems had not kept pace with its product innovation, however, as can sometimes happen with long-standing businesses. As a result of the company’s dependence on inefficient productivity tools, the production process was littered with small inefficiencies: duplicate SKUs, inconsistent materials, and non-existent shop floor visibility.
What began as a system cleanup soon became a company-wide modernisation project; a complete realignment of product structures, workflows, and physical space. “And we wanted really good software to underpin it all. Something that would help us tidy up, track things properly, and make the business stronger for the future,” Sarah recalls.
After consulting national manufacturing innovation programs MTC and Made Smarter, Sarah came across MRPeasy. “I loved it immediately. It was intuitive and had a brilliant interface. My logic was that if I find using it easy, my salespeople and the rest of the staff will too,” she says.
MTC put Sarah in touch with independent manufacturing and ERP consultancy, Smart Manufacture, an authorised implementation partner of MRPeasy, who engaged directly to support the setup and implementation of the system.

Since going live, MRPeasy has become central to how Oceanic Saunas runs its operations. It provides Sarah with a full top-down view of how the company is functioning. “I can log in anywhere in the world and see how the business is doing — how many sales we’ve had today, what’s in production, what’s coming in, everything,” Sarah says. She uses CRM filters to monitor quotation conversion rates and track daily sales performance. Something that was previously difficult to see. “It’s all there at a glance now.”
She concludes with the clarity of someone who’s done the hard work: “Going through the process of learning what I needed the software to do was essential. While it took a while, it gave me the confidence to recognise good software when I saw it. MRPeasy is just nice to use, and everything you need, from CRM to production planning, is there. We’ve definitely found new efficiencies with it.”
mrpeasy.com
Companies of any size can show the world the importance and impact of their work to protect lives by entering the Royal Society for the Prevention of Accidents (RoSPA) Health and Safety Awards 2026.
RoSPA is a leading voice in health and safety that campaigns to reduce avoidable accidents. For over a century, it has led the safety agenda, shaping government policy, raising industry standards and driving behavioural change across all areas of life.
This year marks the 70th anniversary of the RoSPA Awards, which began as a small event to recognise the achievements of companies prioritising the safety of workers in UK, and has now grown into the biggest and most prestigious health and safety awards programme in the world, with the 2025 awards attracting 2,000 different entries from nearly 50 countries.
This anniversary presents the ideal opportunity to reflect on how far workplace safety has come since 1956; from unguarded machines and risky practices to today’s culture of prevention and wellbeing. RoSPA Award winners have played a vital role in driving this progress, creating safer workplaces across the decades and around the world.
The 2026 Awards, sponsored by NEBOSH, recognise those individuals and organisations continuing this proud tradition, while also looking to the future and the importance of innovation in ensuring high health and safety standards in the rapidly changing world of work.
The RoSPA Awards welcomes applications from organisations of all sizes, from SMEs to blue chip companies. The main categories recognise health and safety excellence for organisations and their safety management systems, while the Inspiration Awards celebrate the achievements of individuals and teams.
Entries are judged via a rigorous and impartial process by a wealth of highly experienced senior occupational health and safety professionals and consultants.
Entering the RoSPA Awards has never been easier. The organisers have created a free RoSPA Awards Entry Guide, which provides businesses with everything they need to know about the entire entry process.
Companies can gain global recognition for their commitment to safety and benchmark their performance against the best in the industry by entering in this 70th anniversary year.
For further information, download the guide below, or visit RoSPA’s website. bit.ly/3NUFQsI rospa.com/awards
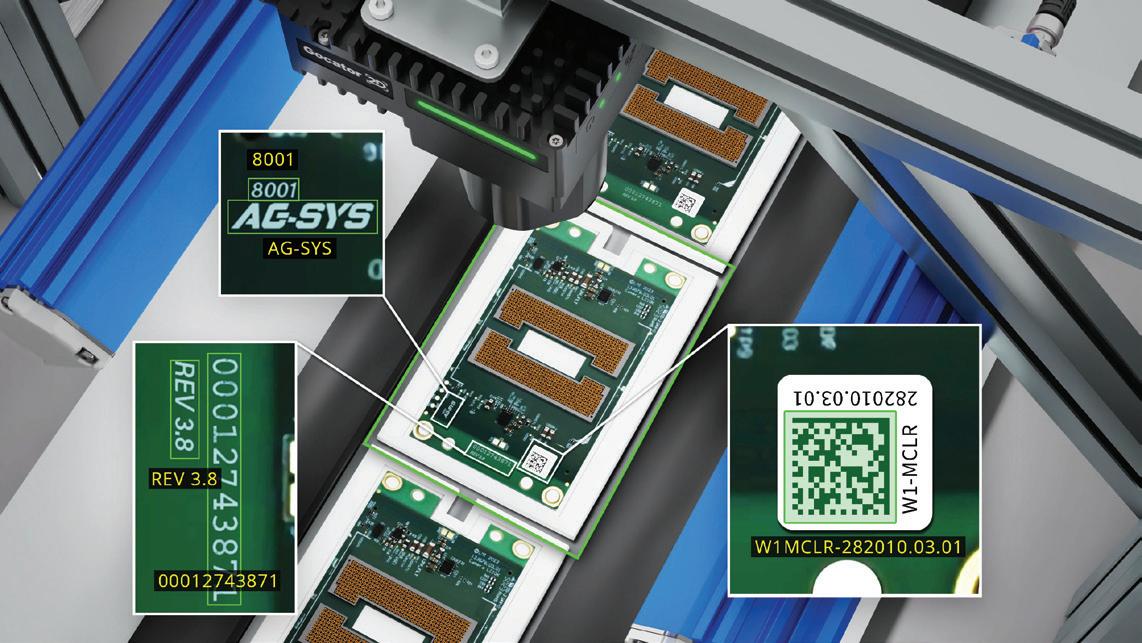
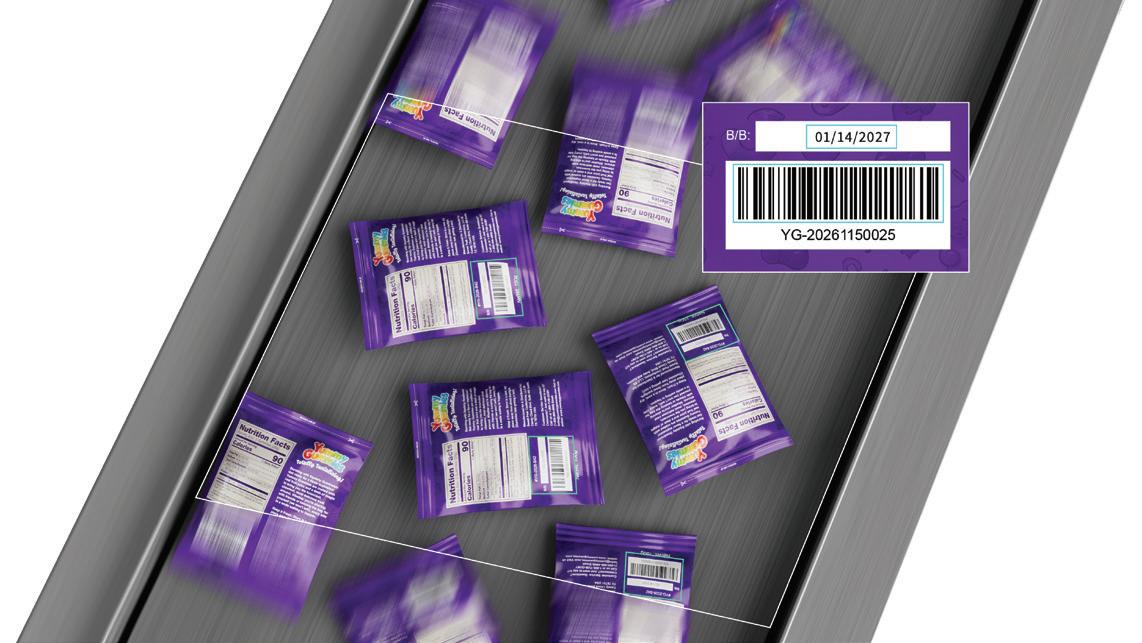





Danny King, Corporate Account Director and member of Gallagher’s Manufacturing Special Interest Group, shares his perspective on why product recall is becoming an increasingly important consideration for manufacturers.
For manufacturers, product recall has long been viewed as a low-probability, high-impact event. Increasingly, however, recalls are no longer rare anomalies but an operational risk that many businesses may face at some point in their lifecycle. Heightened regulatory scrutiny, complex global supply chains and rising consumer expectations mean that even a minor defect or contamination issue can escalate quickly, and publicly.
The frequency of product recalls is increasing across multiple manufacturing sectors, driven by several converging factors. Supply chains are more fragmented, with components often sourced from multiple jurisdictions, increasing the potential for quality control gaps. At the same time, regulatory regimes have become more robust, and enforcement more visible. Social media and digital reporting also mean issues surface faster, leaving organisations with limited time to investigate and respond before reputational damage occurs.
Importantly, recalls are no longer confined to food and pharmaceuticals. Engineering faults, material failures and labelling errors can all trigger recall activity, particularly where safety, compliance or end-user risk is involved. For manufacturers, this has shifted recall from a theoretical risk to a board-level consideration.
Product contamination and recall insurance is often misunderstood or overlooked, yet it plays a critical role in managing the financial fallout of a recall event. Beyond the direct costs of withdrawing products from the market, manufacturers may face expenses linked to logistics, disposal, replacement, specialist consultants and crisis communications. Lost revenue, contractual penalties and long-term brand impact can further compound the issue.
Insurance cannot prevent a recall, but it can provide financial support and access to specialist response services when time is critical. Understanding how these policies operate — what triggers cover, what costs may be included and where exclusions apply — is an important part of wider risk planning. As recall scenarios evolve, so

too has the insurance market, with greater emphasis on preparedness and early intervention.
Perhaps the most effective defence against recall risk is preparation. A clear, well-tested recall readiness plan allows organisations to respond decisively, rather than reactively. This includes defined roles and responsibilities, escalation procedures, supplier traceability, and communication protocols for regulators, customers and stakeholders.
Regular scenario testing can also help identify weaknesses before they are exposed under pressure. In practice, recall readiness is not solely a technical or quality issue; it requires coordination across operations, legal, communications and risk management functions.
These themes will be explored in more detail during Gallagher’s upcoming webinar, “One Defect Away: The True Cost of Product Recall for Manufacturers,” taking place on 10 February 2026. The session will examine why recall risk is changing, how insurance can support response strategies, and steps manufacturers can take to strengthen their resilience in an increasingly unforgiving environment. MEPCA readers can register by scanning the QR code (right):


As one of the largest and most experienced insurance brokers in the world, Gallagher can offer you a complimentary review of your existing insurance programme. Our team can provide detailed insights on how your business benchmarks against others in the industry, identify potential coverage gaps and recommend the appropriate values and limits for your policies. Additionally, we may be able to highlight opportunities where you could save on costs.
For further information, please scan the QR code. CONNECT WITH A SPECIALIST TODAY.

Barclays’ defence research finds that almost 6 in 10 UK manufacturing businesses expect positive impact from defence investment, but leaders call for targeted support.
The Barclays Business Prosperity Index1 shows strong support for the Government’s increased defence spending (74 per cent)2. This sentiment is consistent across business sizes and regions, reflecting a broad consensus that defence sector investment is both necessary and potentially beneficial for the wider economy.
Of those surveyed, 24 per cent have been involved in defence contracts or supply chains on one occasion, 17 per cent on multiple occasions and 25 per cent have never been but are interested in future opportunities.
Among those expecting a positive impact, 56 per cent see boosting research and development in new technologies as the main benefit to their business. Half (50 per cent) highlight the creation of new contracts and opportunities within local supply chains as a key benefit, while 53 per cent anticipate enhanced skills and workforce development.
More broadly, 51 per cent believe defence spending will attract new investment or partnerships to their region, and 40 per cent expect it to support SME growth, innovation, and job creation locally.
Yet despite optimism, a third of businesses (32 per cent) said they require simplification of regulatory requirements, such as compliance reporting, clearer guidance on the procurement process (33 per cent) and a trusted supplier white list to streamline due diligence (30 per cent).
To unlock the full potential of defence-driven growth, business leaders are calling for three key things: improved access to sector-specific skills and training (34 per cent); greater transparency around ESG expectations and reputational safeguards (34 per cent); and financial incentives or support schemes (34 per cent).
Almost four in 10 (38 per cent) say a Defence Guarantee Scheme, where the government would offer financial guarantees for capital and investment, would encourage them to enter the supply chain.
The findings from the Barclays Business Prosperity Index defence research were featured at the Department for Business and Trade’s Global Space Finance Summit on Wednesday 10 December 2025.
Matt Hammerstein, CEO of Barclays UK Corporate Bank said: “Our research shows that businesses are increasingly

interested in supporting the defence sector, with many ready to innovate and enter supply chains.
“To unlock the full potential of defence-driven growth, we urge the Government to sustain momentum on defence investment by streamlining export and compliance regulations and providing targeted support such as a Defence Guarantee Scheme. These steps will help more UK businesses seize the opportunities presented by increased defence investment.”
To support businesses to invest for growth, The Barclays Business Prosperity Fund is available for new and existing Business Banking customers and UK Corporate Banking clients across the UK to apply for lending and refinancing on existing projects. Businesses can find out more via the website below.
£22bn is the total amount of lending Barclays has available to lend and support business growth among Business Banking and UK Corporate Banking clients in 2025. Subject to normal lending assessment, status and application. Terms and conditions apply.
1. home.barclays/insights/business-prosperity-index/ 2. gov.uk/government/news/uk-to-deliver-on-5-nato-pledge-as-government-drivesgreater-security-for-working-people
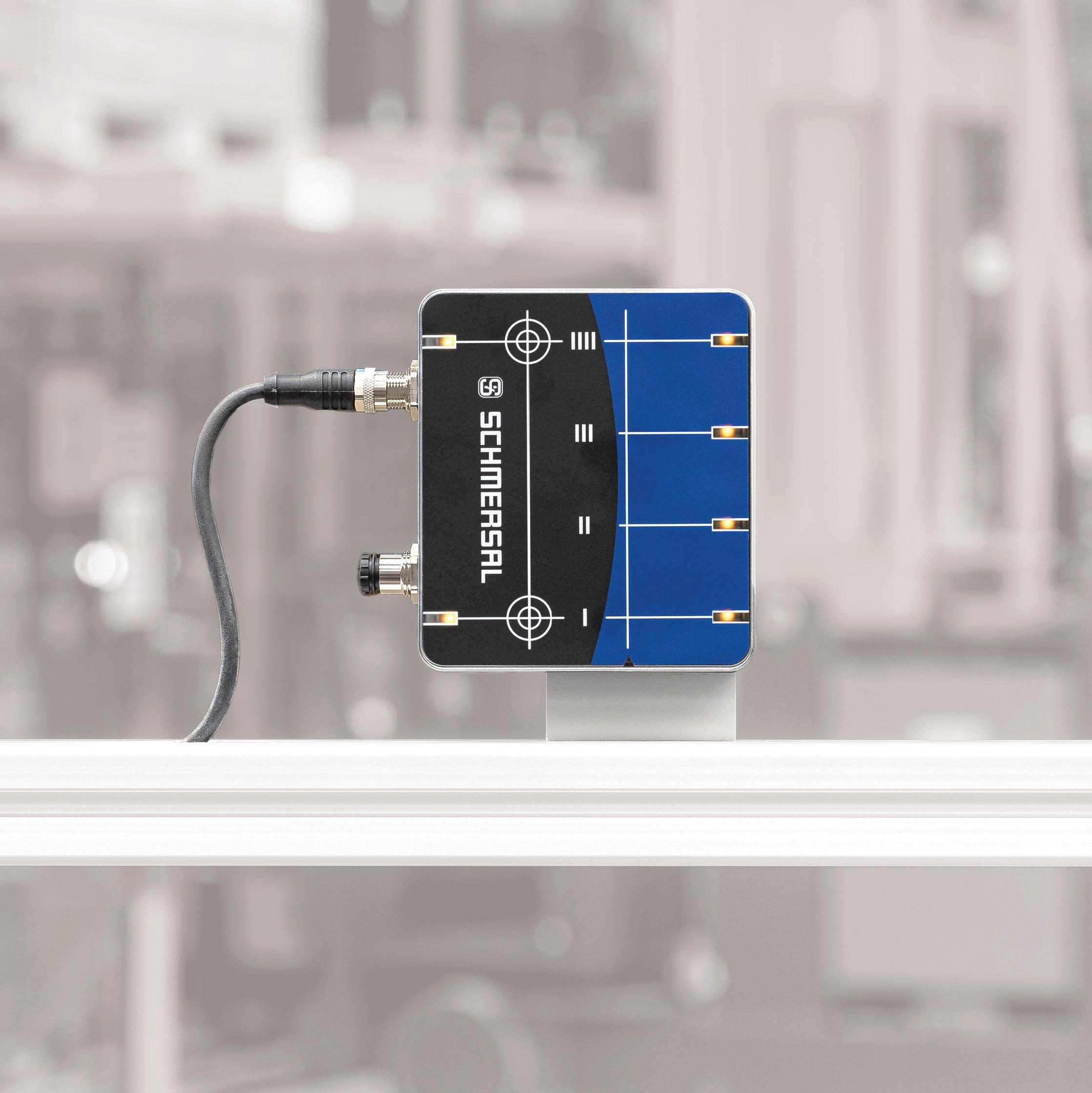

Magnetic switches are used for positioning and control in electric monorail systems and in lift construction, they are characterised by wide-ranging wear resistance and tolerance in the event of misalignment.
A connected control unit uses the signals to determine the position and section of the sensor box and controls the speed and holding positions of the drive motor. In addition, two angle sensors enable fine positioning.
Electric monorail conveyors are used to transport workpieces, tools and other purchased parts in almost every industry. The SSB-R magnet sensor box is used to define route sections for speed regulation for electric monorail conveyors in a manner that is cost efficient and maintenance free. It also allows park positions to be approached with careful accuracy.
Magnetic switches are used for positioning and control in electric monorail systems and in lift construction, they are characterised by wide-ranging wear resistance and tolerance in the event of misalignment.
A connected control unit uses the signals to determine the position and section of the sensor box and controls the speed and holding positions of the drive motor. In addition, two angle sensors enable fine positioning.
SCHMERSAL | Enigma Business Park Malvern, Worcestershire, WR14 1GL
www.schmersal.co.uk uksupport@schmersal.com
Electric monorail conveyors are used to transport workpieces, tools and other purchased parts in almost every industry. The SSB-R magnet sensor box is used to define route sections for speed regulation for electric monorail conveyors in a manner that is cost efficient and maintenance free. It also allows park positions to be approached with careful accuracy.

Consumers expect the same taste in every box, but as supply and climate pressures cause the old playbook to fail, manufacturers can leverage end-to-end data visibility to protect brands and margins, says Ted Combs, Industry Principal, Consumer Products at AVEVA.
Disruptive uncertainty is now the default state for industry, as the IMF pointed out in October. Behind the headlines, the real competitive gap opens up inside factories and supply chains. The only durable path is to treat product and performance as co-equal levers: design the product so it can be produced from a range of inputs, and design the process so it can flex without breaking quality.
In a state of permanent disruption, the winning companies are those with the fastest response times.
First, design for ingredient flexibility with responsive product and process innovation. Supply chain fluctuations lead to ingredient volatility. Creating a golden batch each time requires end-to-end visibility of every aspect of the production line: from metrics such as temperatures and cook cycles to context such as information about production orders and stock keeping units (SKUs). When Maple Leaf Foods exported its existing data to a digital twin in the cloud, teams were able to adjust recipes each week to get the optimal product each time. Within three months, the company improved yields of bologna production and increased gross profit 10-12%.
Second, optimise in real time. Every stage of production generates a stream of data, but silos and legacy technology mean few organisations use this data to drive live decisions. Smart manufacturing draws on AI-infused predictive insights using operational and historical data, so companies enjoy proactive maintenance, reduce unplanned downtime and preserve throughput. When Bakoma, one of Poland’s largest dairy producers, replaced outdated systems with a centralised platform that integrates SCADA, MES, and ERP functionalities, the company reduced manual processes and streamlined production order management, enhanced data visibility and improved sustainability by optimising resource consumption and cutting water usage by 25%.
Third, connect the ecosystem to enable business agility. Future-proofing the manufacturing value chain depends on end-to-end data visibility from across the business lifecycle by connecting all players in the value chain –

suppliers, manufacturers, distributors and even retailers – within a single platform ecosystem. For consumer goods leader Henkel, such a digital backbone gave workers access to new insights using digital analytics. The result? Savings upwards of €37 million since project inception with a growth in overall equipment effectiveness growing 15% in just two years.
A tech stack that leverages IoT data with advanced AI analytics and generative AI capabilities is essential to deliver both efficiency and agility, giving operators a dynamic new path to do better work with less guesswork. That is the durable advantage in a world that will not stop changing.
aveva.com/en/
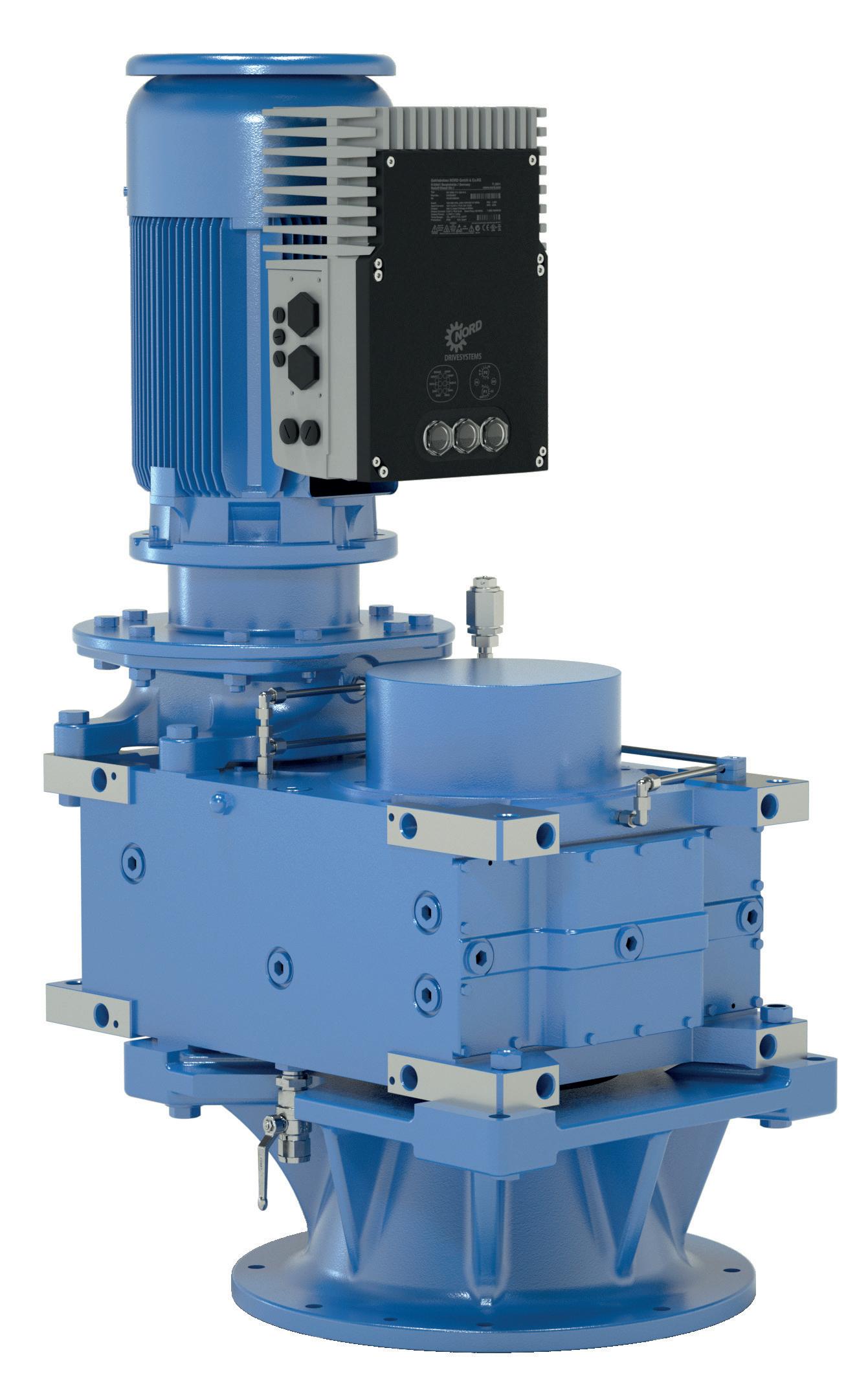
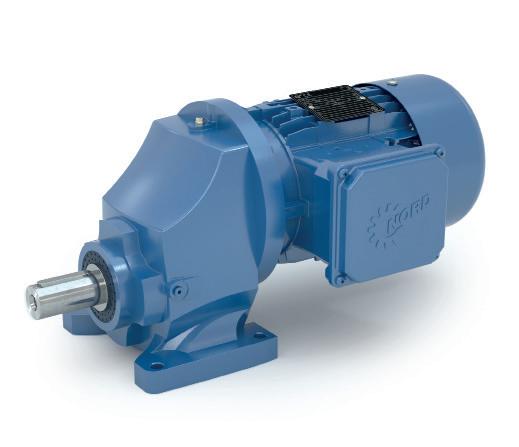
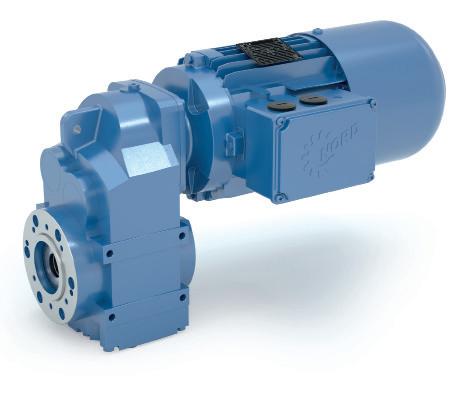





Scan for more information

You have the application, we have the drive solution.
A flexible, modular range of high efficiency, robust gearboxes with output torques up to 250kNm.
Motors with efficiency levels up to IE5+.
Intelligent frequency inverters with PLC onboard and parameter selectable multi-protocol ethernet interface.
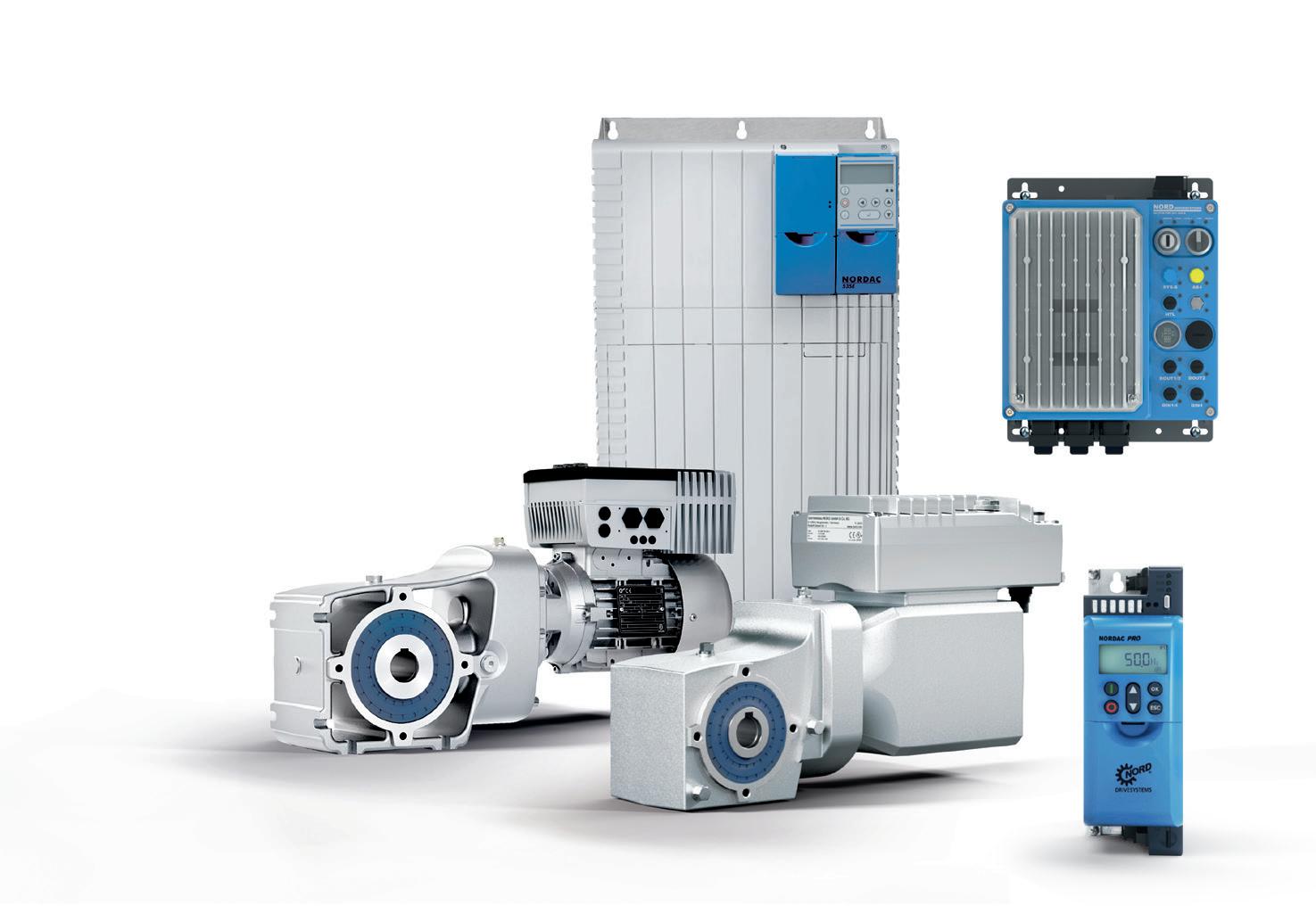





Energy Efficient Drive Systems Since 1965
ESI Technology Ltd has spent more than forty years at the forefront of pressure measurement innovation, delivering precision engineering and purpose-built sensing solutions that serve industries where accuracy is demanded.
Founded in the mid-1980s, ESI’s journey from specialist aerospace projects to global deployment in oil & gas, marine, hydrogen and beyond is a testament to adaptability, ingenuity and technological resilience.
At the core of ESI’s capability lies its signature Silicon-onSapphire (SOS) sensor technology, a remarkable leap in pressure sensing. Instead of relying on conventional strain gauges, ESI’s SOS sensors combine a thin silicon sensing layer grown directly onto a sapphire substrate. This fusion delivers near-zero hysteresis, superb repeatability, wide temperature stability, excellent overpressure resilience and chemical compatibility that few alternatives can match. Technically elegant and notoriously robust, SOS technology unlocks measurement ranges from ultralow pressures to as high as 5000 bar and thrives in environments where traditional sensors simply won’t survive. Titanium alloy diaphragms and durable housings — often machined from single pieces for high-integrity operation — further elevate “rugged” into a new category of dependability.
ESI’s sensor and transmitter portfolio stretches across diverse industries, each with its own challenges:
• Oil & Gas and Subsea: from topside platforms to deep hydrocarbon wells, ESI pressure solutions monitor critical conditions under high pressures and corrosive environments. Dual redundant subsea units and hyperbaric rated devices demonstrate ESI’s readiness for extreme underwater applications.
• Aerospace & Defence: aerospace demands meticulous accuracy and durability, and ESI has over three decades of supplying sensors into aerospace and defence programmes. From aircraft systems to military hydraulics and test rigs, precision under vibration, temperature swings and long service life is indispensable.
• Marine & Offshore: with DNV qualifications embedded across key product ranges, ESI sensors meet the rigours of marine classification standards — essential for ship systems, ballast and fuel monitoring, and offshore energy platforms.

• General Industrial & Process: whether it’s industrial automation, process control loops, or safety monitoring, ESI delivers pressure transducers and transmitters built for uptime and accuracy across harsh factories and chemical plants.
• Hydrogen & Emerging Energies: in the rapidly evolving hydrogen economy, ESI’s pressure measurement units are engineered to function in hydrogen refuelling, storage and production systems with robust media compatibility and safety-centred design.
As industries pivot toward energy transition, automation and extreme environment exploration, ESI Technology Ltd stands primed to measure what matters most: pressure with steadfast precision. Its blend of innovative SOS technology, global certifications and engineering fluency keeps ESI ready for tomorrow’s challenges, from offshore rigs and marine fleets to hydrogen infrastructure and aerospace platforms.
With decades of expertise behind them and a broad portfolio ahead, ESI continues to be a name synonymous with trustworthy and resilient pressure measurement solutions.
esi-tec.com
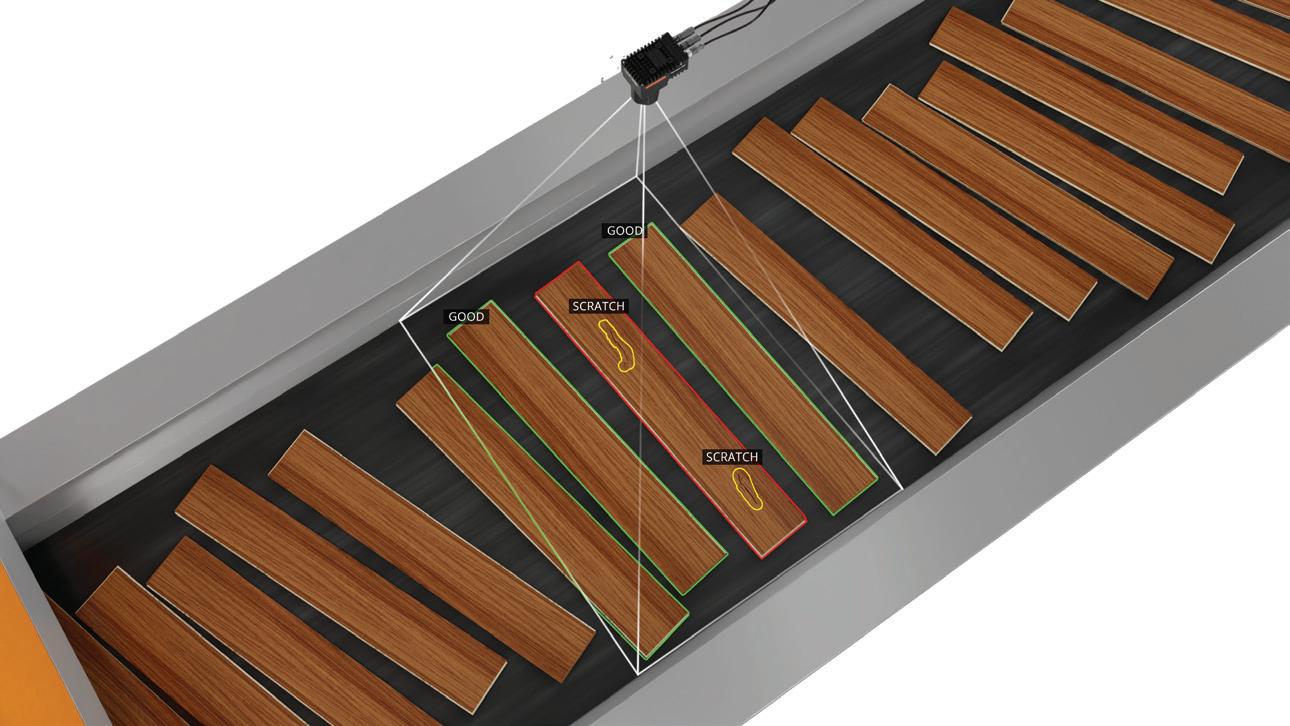
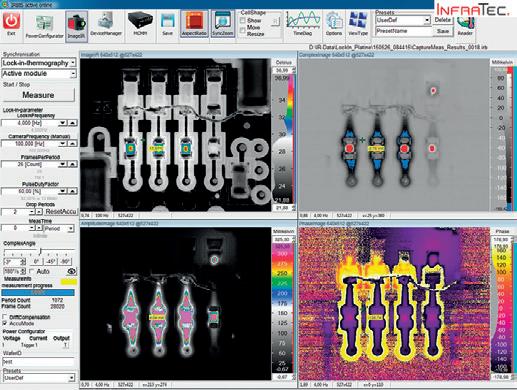
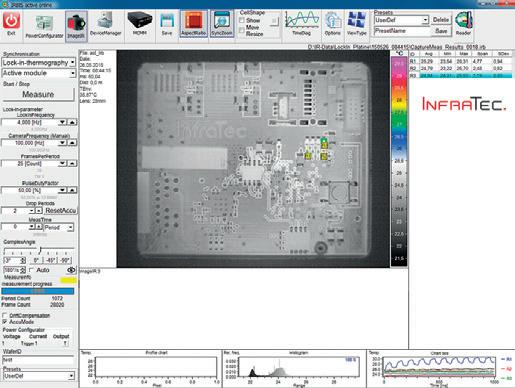
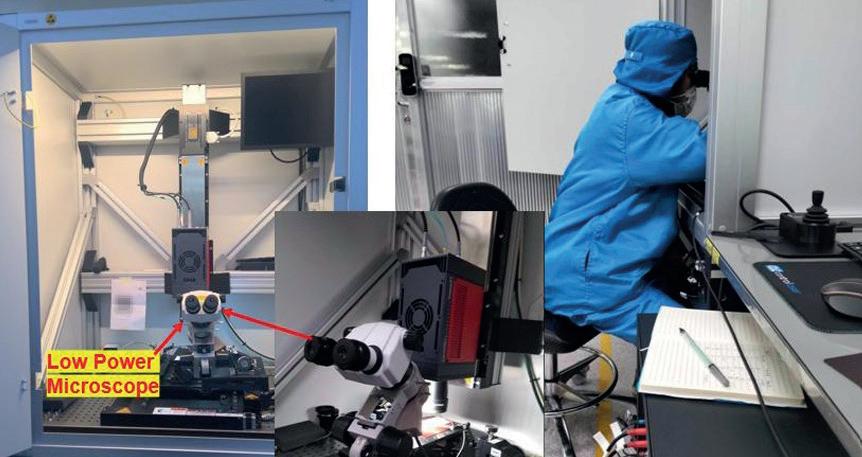
The E-LIT automated testing solution from InfraTec allows non-contact failure inspection of semiconductor material during the manufacturing process. Inhomogeneous temperature distribution, local power loss can be measured with Lock-in Thermography.
This is achieved by using the shortest measurement times combined with a high-performance thermographic camera and a specialised lock-in procedure. The power supply for this process is clocked with a synchronisation module and failures that produce mK or even µK differences are reliably detected. Smallest defects like point and line shunts, oxide failures, transistor and diode failures on a PCB surface and in IC´s can be detected and displayed in x and y positions. Additionally, it is possible to analyse stacked-die packages or multi-chip modules in z-direction with merely changing the lock-in frequency.
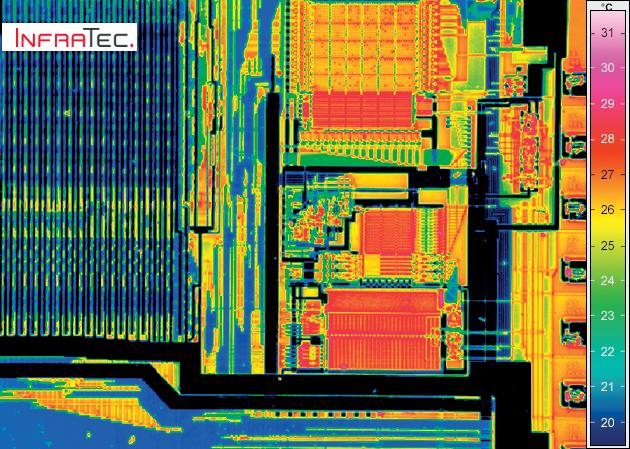
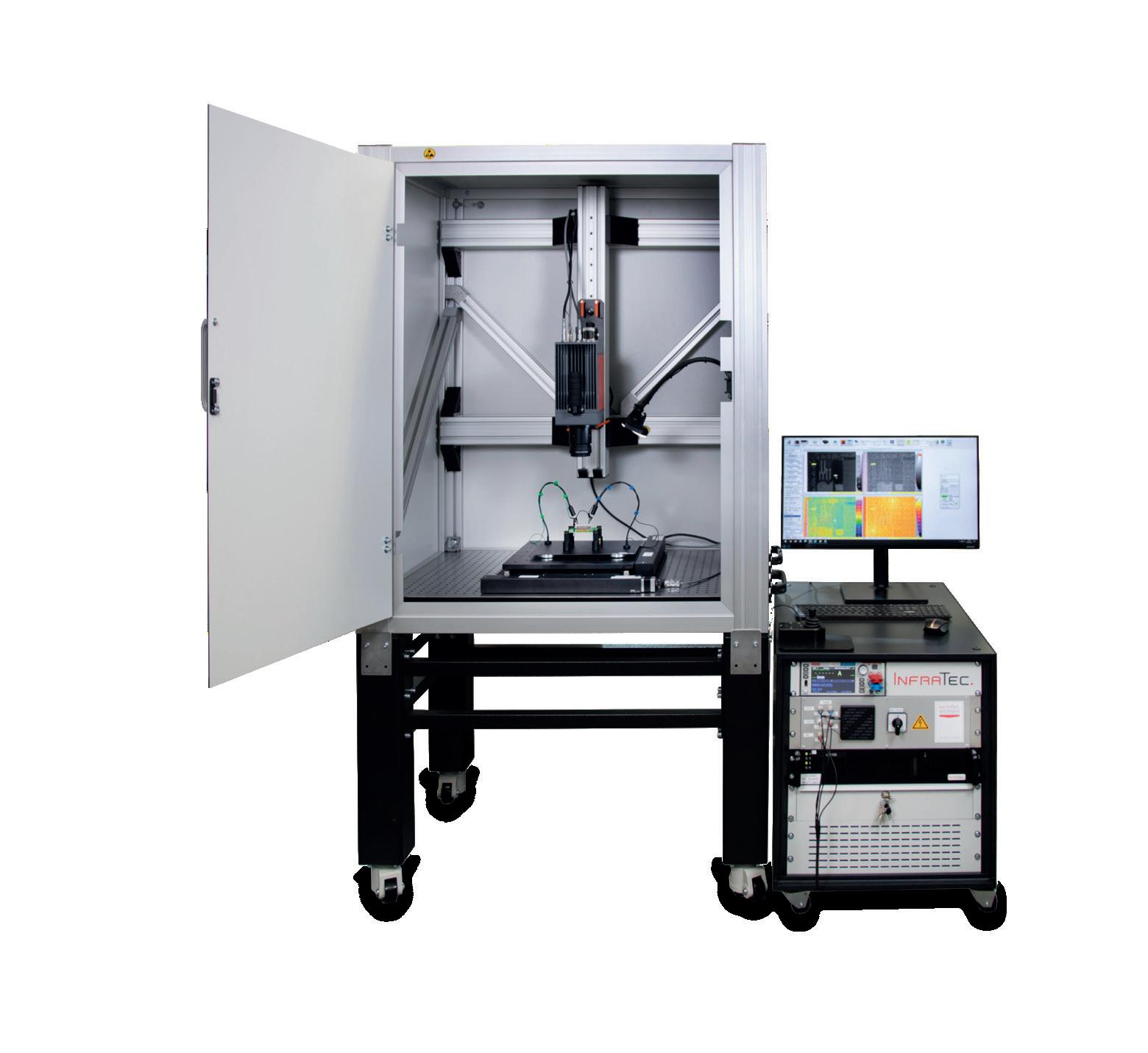


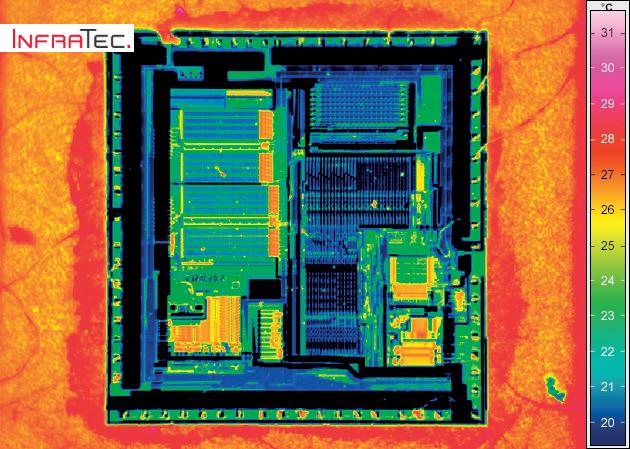
The modular test bench offers the following benefits:
• Online lock-in measurement with the highest sensitivity
• Complete and detailed microscopy analysis
• Geometrical resolution up to 1.3 µm per pixel with microscope lenses
• Thermal resolution in the microkelvin range
• Multi-layer analysis
• Automatic scanning of larger samples due to precision mechanics





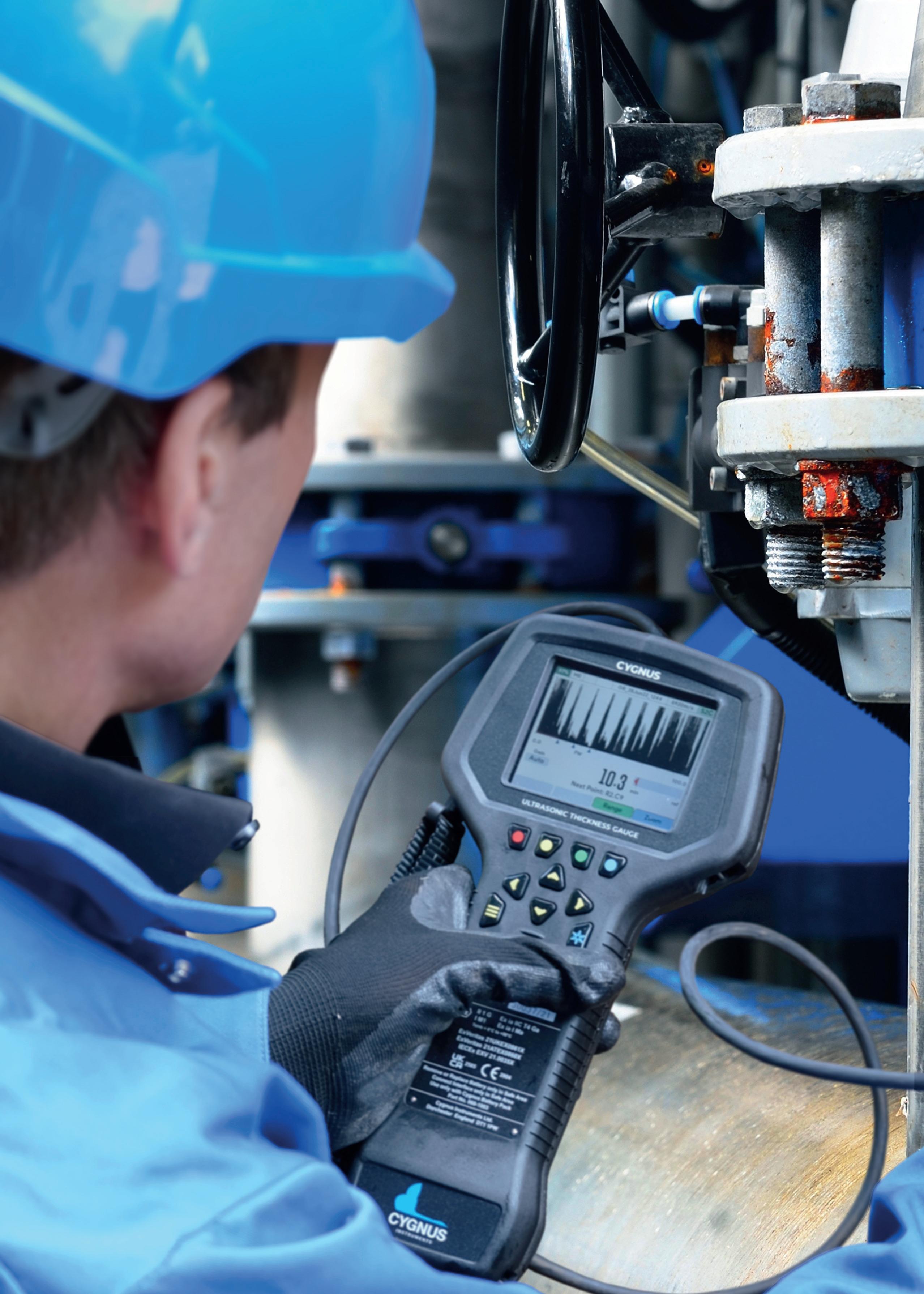
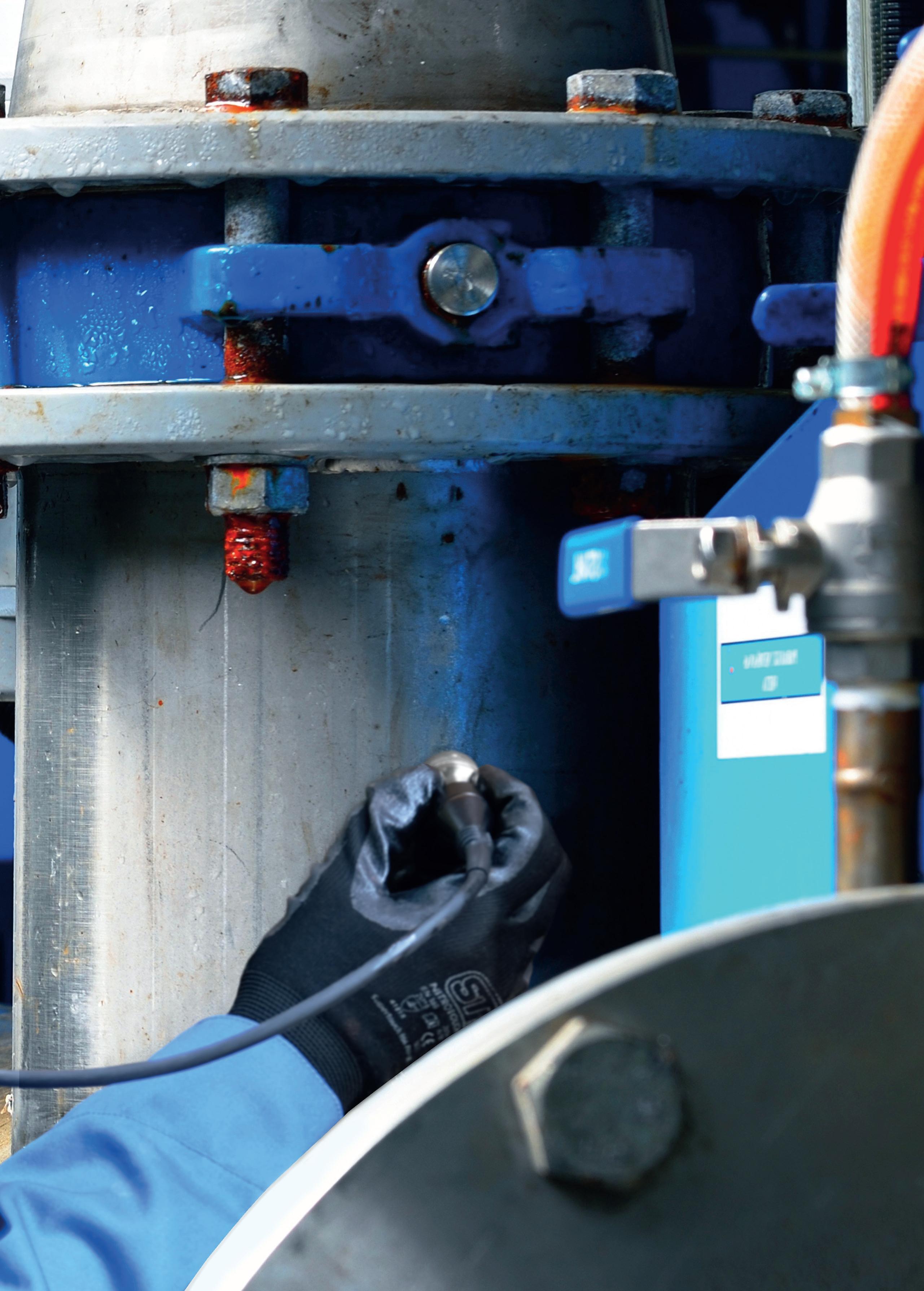
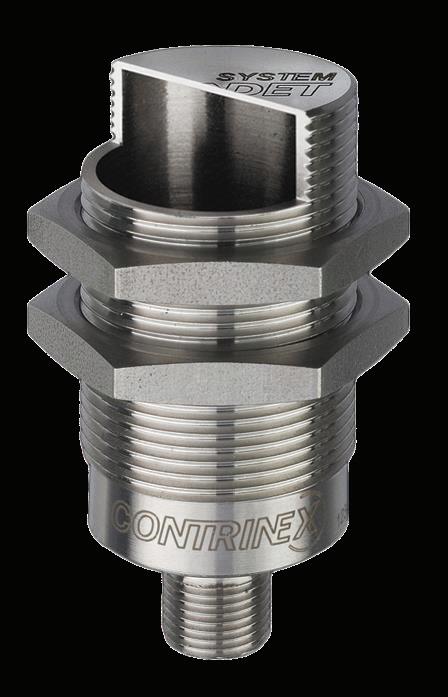
Over three years since the launch of the Cygnus 1 Ex, an ultrasonic thickness gauge (UTG) engineered for use in hazardous areas, Cygnus Instruments Ltd reveals why it continues to be one of its most celebrated products in this exclusive Q&A.
Founded by George Edes in 1983, Cygnus Instruments Ltd brought to market Edes’ pioneering UTG products for the non-destructive testing of ships’ hulls. Headquartered in Dorchester, South West England, the company has since cemented its position as a leading manufacturer of multiple-echo ultrasonic thickness gauges used for measuring remaining metal thickness.
While initially serving the marine industry, Cygnus’ solutions are used in a wide range of industries, including in civil engineering, Oil and Gas, and plant maintenance. In the following Q&A, Chih Ju Wei, Cygnus Marketing Director, provides insights into one of Cygnus’ leading solutions: the Cygnus 1 Ex.
The Cygnus 1 Ex is unique in that it is a fully certified intrinsically safe UTG capable of operating in ALL hazardous gas environments (Zone 0, 1, 2), coal mines and combustible dust environments (Zone 21, 22).
Unlike many UTGs that require hot-work permits or shutdowns, Cygnus 1 Ex allows safe, frequent in-service thickness measurement in explosive atmospheres, combining ease of use and the accurate multiple-echo technology for through-coat measurements (ignoring coatings up to 20mm thick).
Coupled with Cygnus’ high-temperature Ex probe, Cygnus 1 Ex thickness gauge can perform on-stream corrosion inspection of hot assets without shutdowns. It is certified to IECEx, ATEX, UKEX, and is the only ultrasonic thickness gauge approved for ATEX Zone 0 – the highest safety classification – and for combustible dust Zones 21 and 22.
For operators, live measurement in hazardous zones means improved safety, reduced downtime, and lower inspection costs. Inspections can be carried out without shutting down plant, depressurising systems, or removing protective coatings; significantly increasing efficiency and productivity.
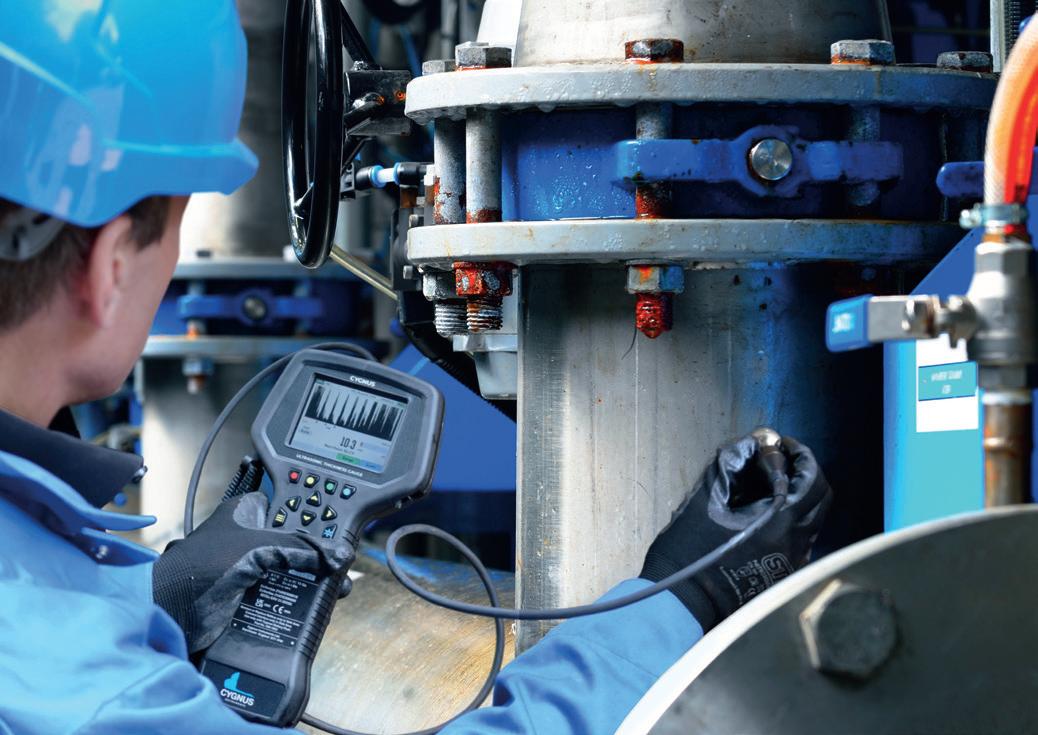

Further benefits of using the Cygnus 1 Ex include that it does not require a Hot Work Permit, which can be a lengthy and costly process. This allows Cygnus 1 Ex UTG to be used anytime, anywhere in hazardous zones, enabling more frequent inspections as part of preventative maintenance and better asset integrity management.
Cygnus Instruments pioneered the Multiple-Echo technique, which Classification Societies have specified for Ultrasonic Thickness Measurement (UTM) in shipping.
Unlike other conventional gauges that measure from the first returned echo, Cygnus UTM gauges use the MultipleEcho technique to analyse multiple back-wall echoes from the metal substrate, automatically ignoring the first echo from the coating surface. This ensures accurate thickness readings of the remaining metal without removing protective coatings. This preserves corrosion protection, preventing further corrosion or damage, and saves significant time and costs.
Additionally, when combined with the Deep Coat function, Cygnus 1 Ex can ignore coatings up to 20mm thick.
bit.ly/3YEXQK3
Work with Ideal Power from the start of your project to get the right PSU first time.
Our expert-led support, bespoke products, and flexible call-off service help you avoid delays, reduce risk, and stay in control. Visit our Website









To derive actionable data from the factory floor means overcoming the divide between Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT). Sensor to cloud solutions offer a scalable and robust way of bridging this gap. Turck Banner, industrial connectivity specialist, and Accenture, digital transformation consultancy, discuss the benefits of this approach.
In their efforts to reach Industry 4.0, manufacturers face a host of challenges, from the growing labour and skills shortage, to increasing operational costs squeezing profit margins and reducing CapEx investment. Gaining actionable insights from the factory floor and using it via enterprise intelligence systems will be pivotal to solving these problems and driving manufacturing towards Industry 4.0, and beyond.
Speaking at a press event late last year, Tony Coghlan, Managing Director of Turck Banner, explained that cloud to sensor technology simplifies the journey of data from the factory floor to enterprise systems – such as MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) and CMMS (Computerised Maintenance Management Systems) –by circumventing the connectivity and compatibility challenges present between the two. While Turck Banner’s focus is on turnkey solutions, its end customers are increasingly interested in the IT-OT crossover and Industry 4.0.
In the spirit of bridging the OT-IT divide, Turck Banner had invited guest speakers Jonathan Parr and Daniel Winter from Accenture, a consultancy that helps companies to reinvent products, processes and business models through digital technologies, to provide insight from an IT-centred perspective and help build a broader picture of the challenges faced by the industry and the benefit cloud to sensor can offer.
Jonathan Parr, Managing and Operations Lead, had often found that Accenture’s clients want reassurances around the value of Industry 4.0., before fully investing in it, but this can be challenging with Proof of Concepts (POCs) as they only provide value at scale, which, he advised, requires a clear strategy from the outset.
Using AI adoption as a fitting example, Jonathan pointed out that for AI to be effectively implemented requires having the right data, and that was where companies such as Turck Banner come in; the “ability to get the data off the shop floor quickly, surface it, and what we call contextualise it, which is basically providing clarity around where it’s come from, is what the real step change in the ability to get data, and get value from AI.”
Addressing how this advancement is moving away

from the traditional data journey topography (see Fig.1), Daniel Winter, Manufacturing & Supply Chain System Manager, explained that sensor to cloud allowed them to “bypass” the usual layers of complexity between the two, a
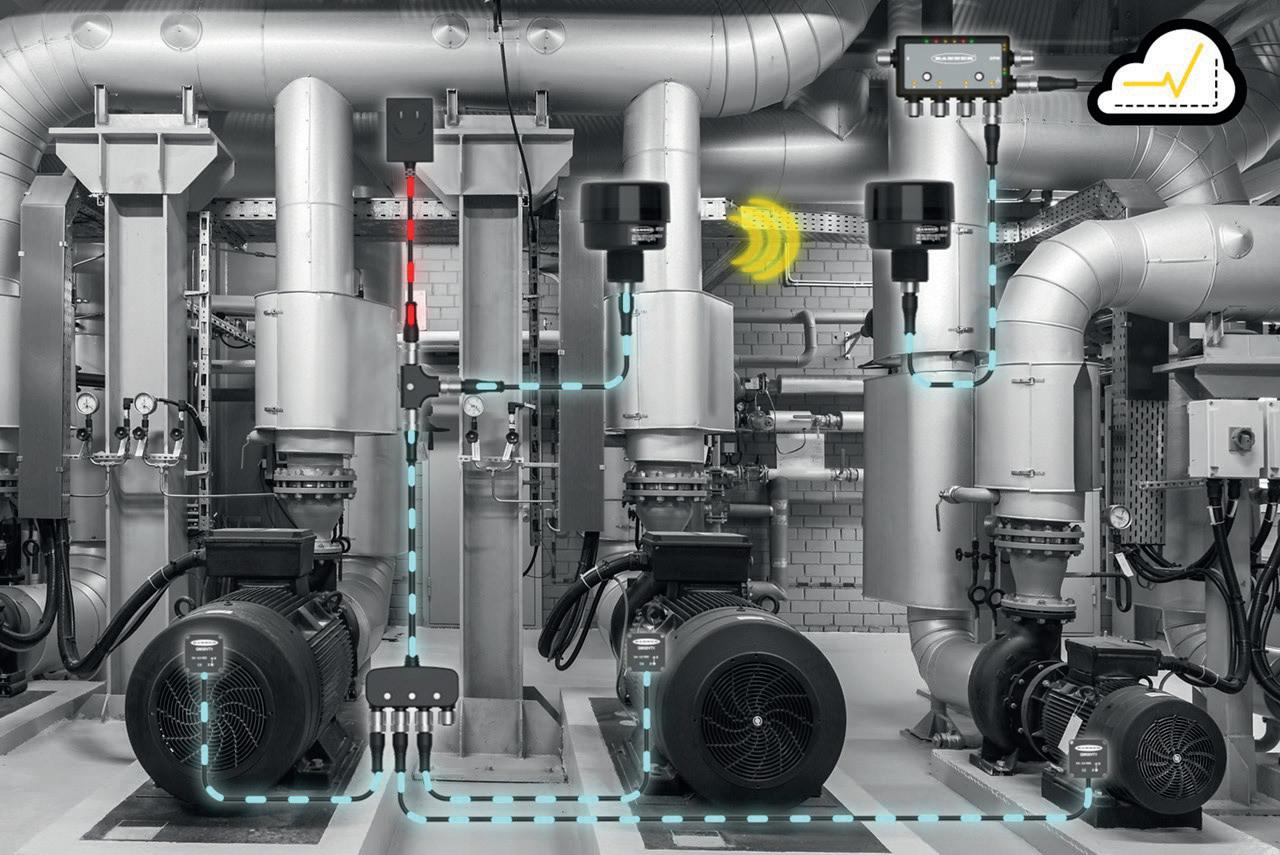
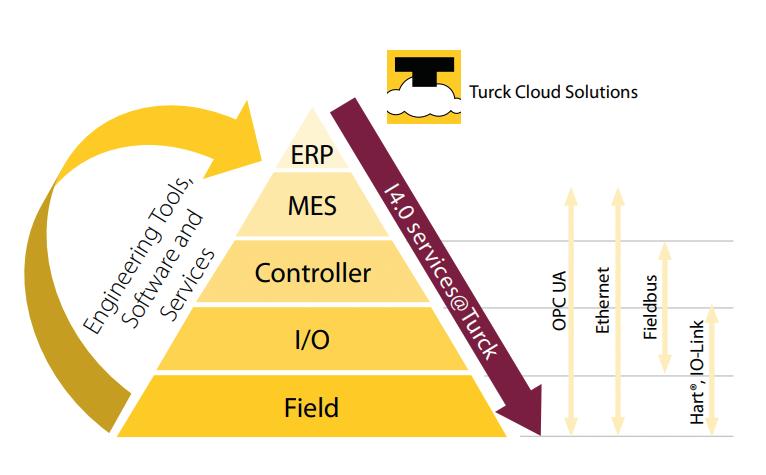
The beauty of this new approach is getting raw data, unfiltered data from the shop floor to intelligence in the cloud with minimum transition and transformation and handling of the data.
Daniel Winter, Manufacturing & Supply Chain System Manager, Accenture.
particularly attractive proposition for a Brownfield facility, where the equipment is legacy, or even obsolete, and extracting data in the traditional way is an arduous and highly skilled process.
“The beauty of this new approach” Daniel summarised, “is getting raw data, unfiltered data from the shop floor to intelligence in the cloud with minimum transition and transformation and handling of the data.”
Traditionally, getting data from the hardware on the factory floor is challenging due to the varying formats (OPC UA, REST APIs, MQTT, RFID, IO-Link, etc.), and this is then exasperated by legacy systems, which traditionally requires OT-skilled people to resolve.
In an economic climate where CapEx spend is increasingly hard for companies to get approved, being able to benefit from digital transformation utilising existing hardware is an attractive prospect, and Turck Banner prides itself on being able to facilitate this with its multiprotocol approach. Despite being a sensor manufacture, Turck Banner often use an existing hardware, made possible by methods of digital shadowing and parallel networks. In these instances, the company acts as a systems integrator.
Circling back to the IT-OT divide, while having sensors in place and getting that data to a cloud system makes it actionable, it doesn’t follow that this will lead to process optimisation or improve overall operational efficiency. This is where higher level conversations with the IT department are required, as they would typically drive a digital transformation project.
Turck Banner is offering an holistic approach to this challenge. In the first instance, it will work with companies from the point of scoping the project and selecting the appropriate hardware, through to Functional Design Specification (FDS) and deployment of the selected hardware and software, including connectivity, before then
assisting with data integration to ensure real-time insights are communicated in the desired format, to where they are needed most.
However, those businesses need to have a clear understanding of what they want to do with that data. Otherwise, they risk what Jonathan termed “pilot purgatory”, where a solution works but won’t scale. To avoid this, businesses should start with scalability in mind and support this with Proof of Value (POV); measurable, tangible benefits, which can only be proved with real data.
But what is viewed as a desirable Return on Investment (ROI) to a business can vary. Broadly speaking, Jonathan sees businesses taking two paths:
“The first is to identify some of the really key challenges that they want to go and solve, that they can use digital or availability of data to solve it. But actually, the longerterm value comes from being able to understand how the entirety of your process can be improved and getting greater visibility.”
Another ROI-pertinent factor is that decentralised data collection reduces the need of intervention by OT staff, an expensive overhead, best applied on more skilled tasks.
Summarising the benefits of sensor to cloud and Turck Banners end-to-end approach, Tony explained that they can near guarantee a scalable solution because they know that their systems will scale. Whatever stage of the process a company wishes to save money on, the goal will always be improving that company’s bottom line.
With sensor to cloud technology, Industry 4.0 will be more accessible to manufacturers than ever before. But to maximise the value, manufacturers must have a clear understanding of how to utilise this data, and recognising the insights it provides on their end-to-end operations.
For more information on sensor to cloud solutions, visit Turck Banner Ltd’s website. turckbanner.co.uk
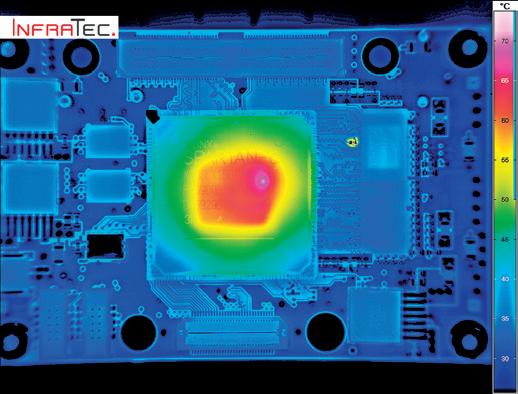
Introducing STMicroelectronics, a European manufacturer of semiconductor devices and integrated circuits with locations worldwide. In the following case study, the company demonstrates the technical benefits of deploying an E-LIT thermography solution for non-destructive failure analysis at two plants.
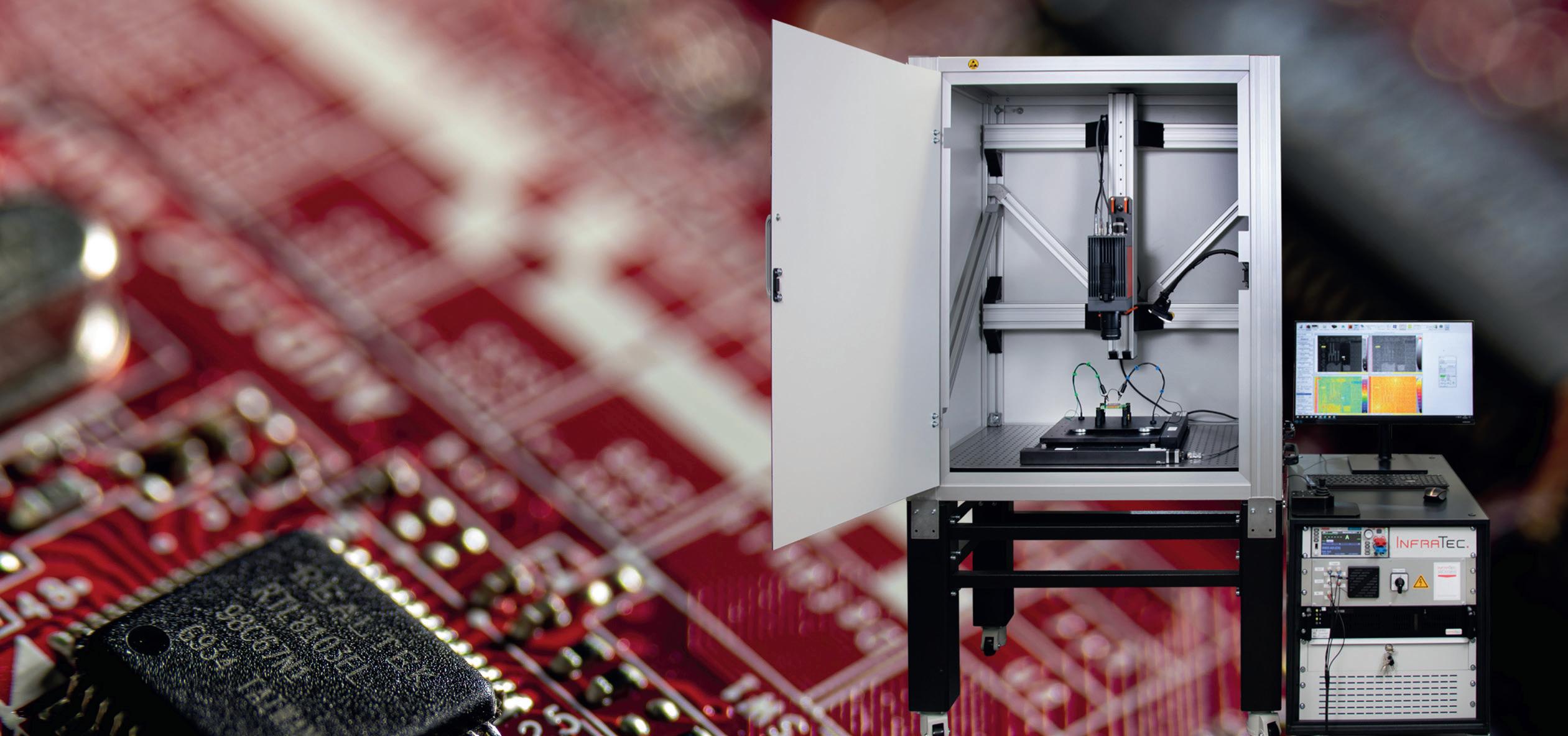
STMicroelectronics’ products are mainly used in the automotive industry and for the Internet of Things (IoT). The company performs nondestructive failure analysis of chips, discrete components, sensors, LEDs and power modules using InfraTec’s E-LIT system at plants in Shenzhen (China) and Calamba (Philippines).
The E-LIT solution employs lock-in thermography, a method in which local defects are detected and analysed based on thermal anomalies generated by defined electrical excitation of an electronic component or assembly. At STMicroelectronics, the test system –comprising an excitation source, an infrared camera with adjustable Z-axis positioning and various lenses, an X-Y table, and additional accessories – was integrated into the failure analysis laboratory. The E-LIT system was further enhanced with a binocular to enable the connection of
power supply contacts to the tested components.
During electrical activation of components under investigation, changes in surface temperature are measured using a high-end infrared camera from the ImageIR® series to identify so-called “hot spots”. This allows even the smallest defects, such as point and line short circuits, oxidation, and faults in transistors and diodes within circuits, which cause only minimal temperature deviations in the millikelvin (mK) or microkelvin (μK) range, to be detected.
For the analysis of large components, the E-LIT system is equipped with 25 mm lenses that provide a wide field of view, along with several microscope lenses capable of resolving fine details up to 1,3 µm. Hot spots can be detected with high sensitivity at chip level using as little as 2 μA. To excite power modules, high voltages up to 3 kV are applied.

The analysis is performed using InfraTec’s IRBIS® 3 active online operating software, which offers a wide range of comprehensive analysis functions. The use of various colour palettes, including inverted and weighted modes, has proven particularly effective for fault detection. By sharing their practical experience, users help InfraTec continuously enhance the E-LIT system for new test objects and faster result; and in return, they promptly benefit from updates and advancements.
Lock-in thermography is a key method at STMicroelectronics for identifying faults in electrical components. The user-friendly method is especially effective in exactly locating short circuits and other anomalies.
Users particularly appreciate the simple visual identification of faults and the flexibility of the system for measurements on different components such as ICs, sensors, LEDs or power modules. The E-LIT solution played a crucial role in the approval of a new mass production project in Calamba, where it was used to quickly pinpoint hot spot locations across multiple batches.
Smallest defects like point and line shunts, oxide failures, transistor and diode failures on a PCB surface and in ICs can be detected and displayed in x and y positions. Additionally, it is possible to analyse stacked-die packages or multi-chip modules in z-direction with merely changing the lock-in frequency.
Specific features that proved advantageous in the Calamba application are below, following by details of the supporting software.
An interface for incoming and outgoing control signals: the trigger signals to or from the camera can be used to control and synchronise image data acquisition. Thermographic measurements can also control the processes.
Measurement of high temperatures & spectral ranges: up to two individually combinable wheels equipped with filters and apertures allow the camera sensitivity to be adjusted to the specific requirements of demanding measurement tasks

Remote-controlled focussing of the thermal image: interchangeable standard lenses in the ImageIR® series can be equipped with a motor focus unit. This enables precise, remote-controlled and fast focussing via the operating software.
Fast measurements in defined subsections: this enables the capture of very fast temperature and motion sequences in full, half, quarter and sub modes, as well as in sub image formats defined by click-and-drag, using highframe rates.
Quadruple geometrical resolution: by using a fast-rotating MicroScan wheel, the number of pixels used can be quadrupled compared to the native pixel count of the FPA detector, significantly improving image quality.
Ultra-fast data transfer: high-resolution detectors and high frame rates generate large amounts of data. With the 10 Gigabit Ethernet interface, this data can be transferred quickly, reliably and without loss.
Software:
• Operational software with comprehensive analysis options in laboratory conditions
• Software add-on for automatic error classification based on parameter settings
• Intuitive user interface for easy operation
• Real-time display of the object being measured in various states
• Multifaceted memory options for image data and measurement results
• Alternative 0°, 90° or customised set phase angle image for representation of complex intensity information
• Merging live and amplitude image
• Optional: IV measurement, under sampling, drift compensation, DC-mode, power loss measurement, user and protocol administration, interface preparation: e.g. Profibus, Ethernet
The InfraTec E-LIT system is available exclusively in the UK and Ireland through Quantum Design UK and Ireland. More information can be found on the website below.
qd-uki.co.uk
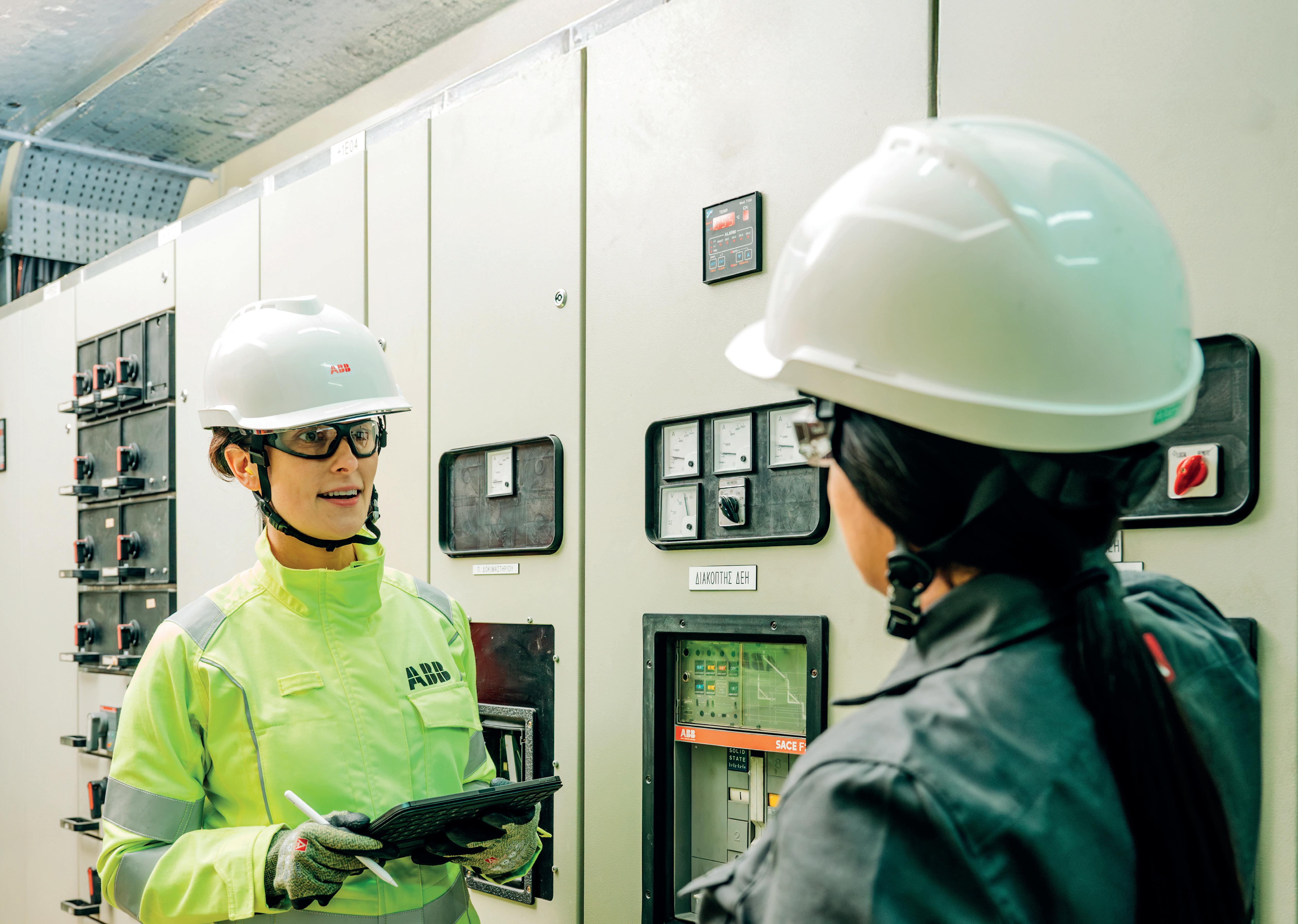
Maintaining process continuity can feel like a non-stop battle. A holistic understanding of a plant’s electrical systems is fundamental to implementing asset management strategies. Here, Carlo Collotta, Global Product Manager, ABB Electrification Service, explains how to eliminate unplanned downtime.

As plants and processes grow larger and more complex, there’s a heightened need for betterinformed strategies to minimise the risk of electrical failure impacting on revenues and corporate reputation.
Today’s holistic approach to asset management and maintenance demands a deep understanding of the interactions between an electrical system’s constituent elements and their overall impact on plant efficiency, safety and sustainability.
Take the example of a brand-new circuit breaker boasting the latest functions and features. If that breaker’s installed in an environment where it faces high levels of physical stress, the chances of premature wear and
sudden failure rise rapidly. When it does fail, the traditional response is replacement of the device to get back online quickly. However, this quick fix may overlook the root cause of failure, triggering an inevitable cycle of failure, downtime and replacement.
The latest technologies found in many process plants often coexist with decades-old components and systems. This patchwork of old and new systems adds to the challenges of effective management and maintenance, hampering efforts to achieve significantly more reliable and efficient operations. Key to escaping this resourcesapping cycle is a step-change from reactive maintenance to more proactive strategies that can also uncover hidden opportunities for optimisation across a facility’s operations.
While the battle to maximise efficiency and uptime can appear daunting, the chances of success for plant operators are increased by paying due attention to some fundamental but easily overlooked essentials.
An example of this is the Single Line Diagram (SLD) that offers a simplified schematic representation of a facility’s electric power systems. Essential for ensuring electrical safety and simplifying troubleshooting, the SLD is arguably the most important single document relating to a facility’s electrical systems. An up-to-date SLD is fundamental to understanding system interconnectivity and power flows. Without it, the efficiency and safety of electrical systems – and the entire plant – can be seriously compromised. Electrical contractors tasked to perform system upgrades or expansion will typically insist on access to a current SLD, making it essential for plant managers to maintain documentation that’s accurate and up to date.
Maintenance processes typically combine numerous separate elements and connections, some more visible than others. It’s simple enough knowing how many people are in a maintenance team. However, it can be harder to understand exactly what’s in the current spares inventory, or the replacement and lifecycle strategies for hundreds or thousands of individual pieces of equipment.
The reliability of each asset is contingent on numerous factors including its age, condition, load and running hours as well as the environment it’s operating in. Factor in that asset’s interaction with other devices and systems plant-wide, and it quickly becomes incredibly difficult to understand its impact on overall system performance.
A 50 kA circuit breaker may quietly do its job for years without incident. However, changes or upgrades to the wider system can affect short circuit levels, rendering that breaker unfit for purpose. For operations and maintenance teams without the requisite skills and experience, it can be hard to understand the ramifications of these changes and how to address them.
Help is at hand for plant owners who are struggling to fully understand and successfully manage their electrical systems. Advisory services provided by an expert partner –such as ABB Navigate – can help operators build a forensic picture of what’s actually happening in their plant. These insights can then be used to optimise asset management and maintenance strategies that transform operational resilience and dramatically reduce the costly danger of unplanned downtime.
If something can’t be measured, the opportunities for improvement are slim. The latest generation of smart circuit breakers and switchgear deliver a constant stream of instrumentation and diagnostic data. However, this information is of little value unless it can be harnessed to drive meaningful improvements. With electrical distribution systems offering few outward signs of wear, it can be easy to miss the clues of impended failure.

This is where data-driven condition monitoring plays an increasingly critical role, flagging subtle trends and signals of anomalous asset behaviour hidden in a torrent of process and diagnostic data that even the most experienced human engineer would miss unaided.
While no two plants are the same, the goals of optimised performance and profitability while maintaining safety and sustainability are common across every industry sector. Irrespective of an organisation’s size or location, realising these objectives demands electrical systems that are secure, reliable and resilient.
The journey to maximum uptime starts with a clear understanding of an organisation’s overarching business priorities. Whether it’s driving production efficiency and profitability, improving staff safety or promoting greater sustainability, there can be many ways of reaching the same goal. A common driver, however, is the shift from reactive maintenance to more proactive strategies that can dramatically improve the reliability of equipment and even extend its working lifespan.
Delivered by ABB’s hugely experienced Electrification Service team, ABB Navigate is a suite of solutions and services that can help plant operators understand what is really going on in their plant. This consultancydriven capability encompasses a wide range of different disciplines that embrace the maintenance and management of electrical equipment and systems.
Through Power System Studies, assessments, operational benchmarking and advisory services, ABB Navigate smoothly guides plant owners and operators towards more reliable and resilient operations. Building a profound understanding plant operations at a granular level, it drives actions that push the needle towards greater reliability, safety, sustainability and long-term profitability for operators.
For more information and to take a survey, visit ABB’s website.
bit.ly/3NFOT0z

Discover how a collaboration between identification solutions manufacturer Brady and distributor Milexia has optimised the maintenance of France’s railways.

With 28,000 km of service lines, Société Nationale des Chemins de Fer Français (SNCF) maintains and assures the safety of hundreds of thousands of technical components every day. Maintenance operations are tracked with accurate and reliable labels. Thanks to a unique collaboration between Brady and distributor Milexia, the railway company now benefits from the cutting-edge technology of the Brady M611 and BMP61 printers.
Working closely with Milexia and SNCF, Brady’s Software Development Kit (SDK) was utilised to seamlessly integrate SNCF’s existing software with Brady’s printers. Ludovic Leclere, Brady Territory Manager, explains:
“SNCF’s maintenance management relies on a database containing thousands of references. Using Brady’s SDK, they developed a custom-built interface with pre-designed label templates, enabling technicians to create and print inspection labels directly from their familiar system. By selecting the correct references within their existing interface, the necessary label information is automatically populated from SNCF’s database. This integration eliminates the need to learn new software or manually input data, ensuring a smooth, error-free and efficient labelling process.
“Additionally, users can automatically add a barcode or illustration to their label design. Another advantage is the ability to work in series, retaining specific elements and integrating variables. Labels to validate the inspection of 70
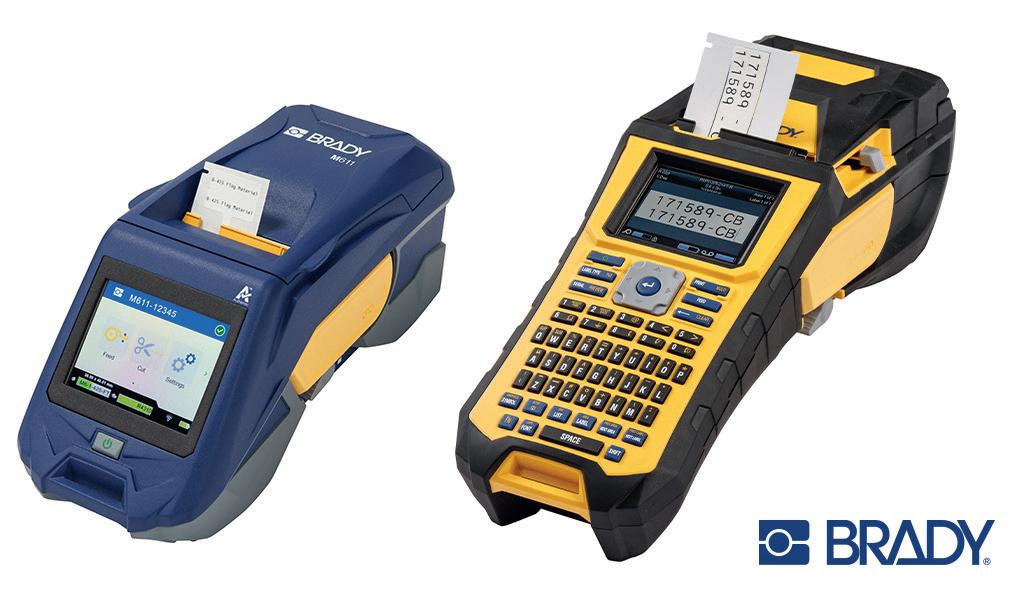

safety helmets, for example, can all be printed at once, with unique serial numbers.”
The Brady M611 printer and the BMP61 – now improved to the M610 – Label Printer perfectly meet the complex needs of SNCF. Users only need to load a consumable to initiate automatic printer calibration. Unlike with most competitor models, there is no need to waste labels to calibrate the printer, saving consumables and valuable time. Consumables can be switched quickly to print a few labels on a first material, one more on another, and then switch back, all in a matter of seconds. The printer always prints the first label right.
In addition, label reliability played a major role in SNCF’s decision: “Their rail network spans the entirety of France. The labels they use to identify its components must withstand the cold of the Jura as well as the sunshine of Nice” continues Ludovic Leclere.
“Weather and UV are not the only adverse conditions to be taken into account. Heavy traffic vibrations, solvents and grease... The label must have reliable legibility in all circumstances and it must also stay attached to a variety of surfaces (plastic, wood, metal and others).”
“Brady’s experience in rail vehicle manufacturing, aerospace and mass transit industry identification enabled us to provide a reliable solution for these extreme conditions.”
brady.co.uk
















Pumps are vital to industry, but often get overlooked as critical pieces of engineering equipment. Here, pump technology specialist Verder provides a checklist for choosing the right pumping solution to empower processes and maintain uptime.
Pumps and Pumping Systems are the backbone of multiple industries that keeps modern society moving. From HVAC and domestic water to drainage and fire protection, food production to wastewater treatment, pumps and pumping systems underpin the reliable operation of almost every commercial and industrial building to keep fluids moving safely, efficiently and reliably.
Despite their importance in modern production, pumps are often treated as commodity items rather than critical pieces of engineered equipment. As pump specialists, Verder understands that choosing the right pumps is not simply a matter of operational efficiency; it directly impacts product quality, safety, regulatory compliance, and overall process reliability, which is why Verder offer a range of pumps specifically designed with the application in mind and aligned to industry standards and certification requirements – ATEX, FDA, ISO etc.
Successful pump selection begins with a clear understanding of the system it serves – flow rates, head requirements, fluid characteristics and operating conditions all need to be considered – correctly matching the pump to the system is fundamental to ensure better performance and increased longevity.
Start the new year with pumps that are engineered for uptime by following Verder’s Pump Selection Checklist:
1. What is the lifecycle cost? Rather than looking at only the initial purchase price of the pump, selection should be based on the cost over a pump’s lifespan considering energy consumption, which typically represents the largest cost.
2. Is fixed speed pumping or variable speed pumping required? Variable speed pumping has now become standard practice across most industries as this can deliver substantial energy savings, improved system stability and reduced mechanical wear.
3. What are the maintenance requirements? Accessibility, reliability, availability of spare parts, and manufacturer support all contribute to long-term value. A slightly higher initial cost can often result in significantly lower total cost of ownership.
4. How does digitalisation impact pumping systems? Smart pumps and integrated controls now provide real-time performance data, fault alerts, and predictive

maintenance capabilities. These technologies allow operators to identify inefficiencies early, reduce downtime and move from reactive to proactive maintenance strategies, particularly valuable in large or complex installations.
5. Installation quality should never be underestimated. Poor pipework layouts, inadequate supports, air entrainment, or misalignment can quickly negate the benefits of good pump selection. Early collaboration between consultants, contractors and manufacturers is key to delivering coordinated, efficient pumping solutions and achieving smooth handover.
As systems become smarter, more efficient and more resilient, pumps must be recognised not as secondary components, but as critical assets that deserve careful design attention from concept through to operation. From hygienic food-grade pumps to heavy-duty chemical transfer systems, reliability is built into every design of Verder Pumps.
Verder’s pump solutions are helping food, beverage, chemical, and water treatment operations move liquids safely, efficiently and consistently throughout 2026, contact Verder today to find out how it is enabling progress in 2026.
bit.ly/45LsYeB
✓ Peristaltic Pumps – Ideal for abrasive, corrosive and shear-sensitive media.
✓ Diaphragm Pumps – Handles aggressive, viscous and solids-laden fluids with safe dry-run capability.
✓ Lobe Pumps – Hygienic, low-shear pumping with smooth, pulsation-free flow for sensitive and high-viscosity applications.
✓ Dosing Pumps – Accurate, repeatable chemical dosing delivering precise flow control and reduced chemical consumption.


Winter puts industrial cooling systems through their paces, increasing risk of downtime. Fortunately, Summit Process Cooling is on hand with top tips for protecting cooling systems during cold snaps.
As temperatures fall, industrial cooling systems face increased pressure from freezing conditions, corrosion risk and bacterial growth. Glycol plays a critical role in protecting chilled water circuits through the winter months, yet it is often overlooked until a problem occurs. Carrying out a structured glycol check before colder weather sets in can help prevent breakdowns, protect equipment and maintain stable production.
The first and most important step is to verify glycol concentration. For UK conditions, a concentration of around 25 - 30% is typically required to provide freeze protection down to approximately -12°C to -16°C. Concentrations below this level significantly increase the risk of freezing and can encourage bacterial growth.
Over time, systems that are regularly topped up can become diluted without operators realising. Water ingress, corrosion products or biological contamination can all reduce freeze protection and thermal efficiency. Visual checks are useful here. Healthy glycol should be clear, consistent in colour and free from odour or suspended particles. Investigate any deviation.
Strainers and filters naturally collect debris, rust flakes and organic matter. Before winter, these should be cleaned or replaced to maintain proper flow and prevent restrictions. Pipework should also be checked for signs of corrosion or small leaks, both of which can lead to unnoticed dilution of the glycol mix.
Even when concentration appears correct, the actual freeze point should be confirmed. Different glycol types behave differently, meaning concentration alone is not always a reliable indicator. A handheld refractometer or test kit can quickly verify true freeze protection and highlight any discrepancies.

It is important to ensure the correct glycol is being used for the application. Mono Ethylene Glycol offers excellent heat transfer performance, while Propylene Glycol is often chosen where lower toxicity is required. DTX glycol provides a non-toxic alternative with strong inhibitor protection. Mixing glycol types or using an unsuitable product can compromise system protection and shorten fluid life.
If adjustments are required, always top up with the same inhibited glycol type. Using incompatible fluids can accelerate corrosion. If glycol concentration has dropped below 20% at any stage, bacterial activity may already be present, with symptoms such as cloudy fluid, odour, sludge formation or reduced flow.
A thorough winter glycol check provides confidence that cooling systems are ready for colder conditions. For processors seeking additional reassurance, Summit Process Cooling supports customers with a proactive approach that helps protect assets, maintain performance and reduce the risk of unexpected downtime when temperatures drop.
bit.ly/Summit-Glycol-Frost-Protection
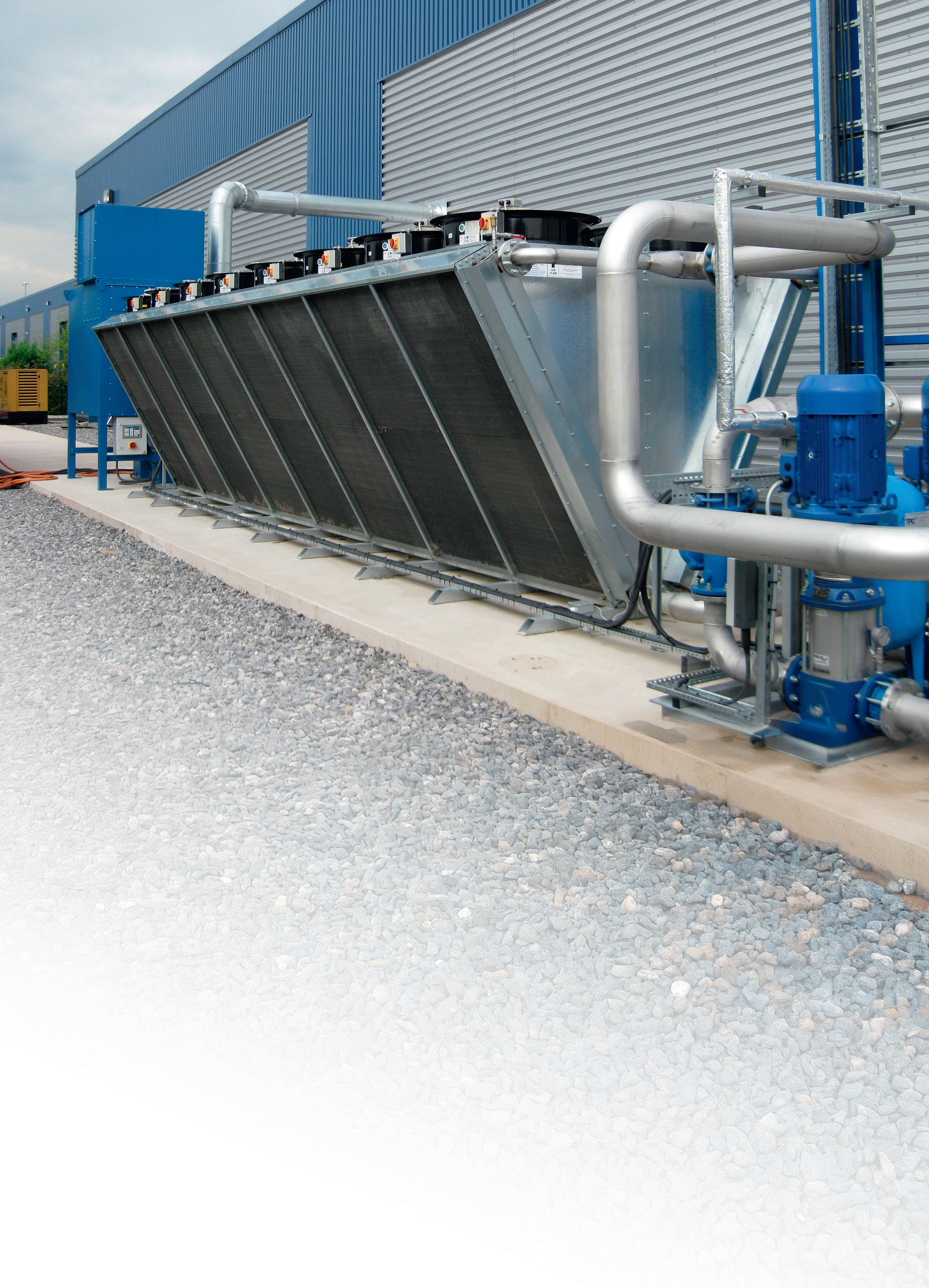





For manufacturers seeking to improve energy efficiency, the first step is gaining a granular understanding of how energy is used across their operations, explains Gemini Data Loggers, provider of environmental data solutions.

With rising energy costs and increasing pressure to improve operational efficiency, UK manufacturers are being challenged to do more with less. The government’s recent commitment of £2 million to support energy efficiency through the Made Smarter Adoption Programme reflects a growing recognition that digital tools and data-led decision-making are essential for sustainable growth, particularly for SMEs.
However, before manufacturers can invest in new equipment, automation or energy-saving technologies, they must first understand how energy is being used across their operations. Without accurate, granular data, efficiency initiatives risk being based on assumptions rather than evidence.
This is where energy monitoring becomes a powerful enabler. Tinytag Energy Loggers by Gemini Data Loggers provide manufacturers with a clear, objective view of electrical consumption by measuring voltage, current, power and power factor either across an entire facility or at critical points throughout. By establishing reliable energy baselines, businesses can identify inefficiencies, uncover hidden waste and prioritise improvements with confidence.
For operations managers and facilities teams, this data supports smarter decisions. From validating the impact of process changes and equipment upgrades, to justifying investment cases and supporting funding applications. Crucially, it turns energy efficiency from a theoretical goal into a measurable, manageable operational discipline.
For manufacturers looking to go further, energy monitoring can also highlight areas where deeper investigation is required. Uneven energy demand or unexplained consumption patterns may indicate issues with airflow, insulation or thermal performance. There are areas where targeted diagnostic services such as Thermal Mapping can provide further insight.
With over 40 years of experience designing and manufacturing robust, reliable data loggers in the UK, Tinytag by Gemini Data Loggers helps manufacturers take the first, most important step toward energy efficiency: understanding their environment. Armed with accurate data, UK SMEs are better placed to take advantage of initiatives and funding and build more resilient, efficient operations for the future.
geminidataloggers.com/energy
Turn energy costs into actionable insight.
Gain clear visibility of where, when and how energy is being used, so inefficiencies can be identified and addressed with confidence.

Build a data-driven case for efficiency improvements.
Establish accurate energy baselines to justify investment, validate change and support funding or grant applications.


Reduce waste without disrupting operations.
Monitor energy consumption non-intrusively across processes and infrastructure, without interfering with production or uptime.
Move to evidence-based decisions and control.
Replace guesswork with reliable data that supports smarter operational decisions and longterm efficiency planning.
Learn here how the extensive mk conveyor range was used to provide a compact conveying solution for bulky car body parts through a robot cell.
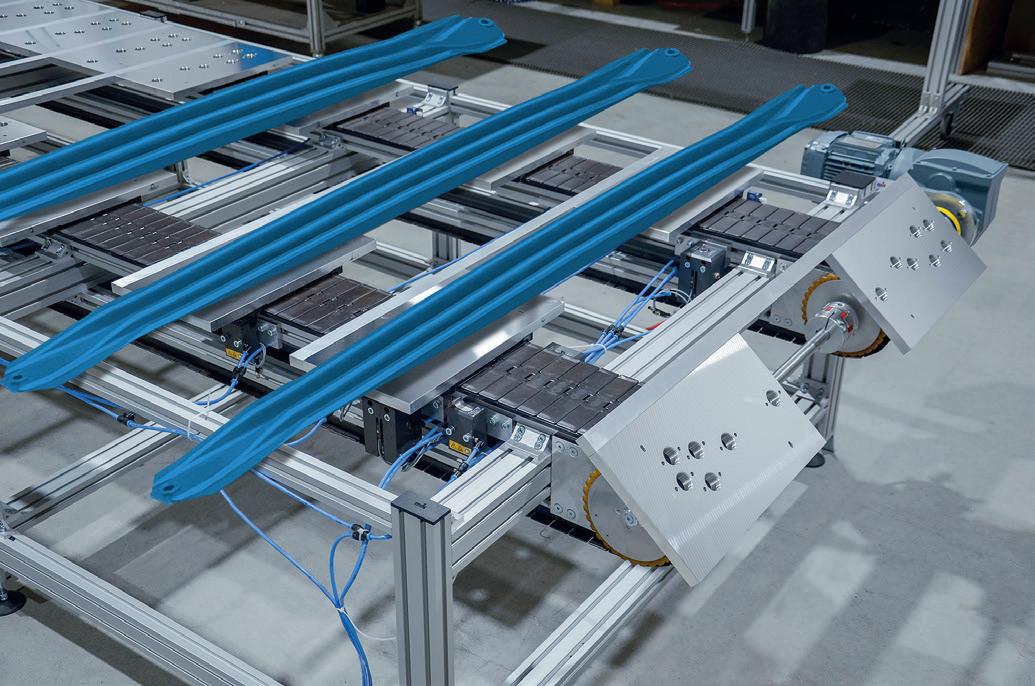

Vehicle manufacturers fit side impact beams in the car body to ensure that drivers are protected in the event of a lateral impact. To mitigate the noise and vibration that these elongated metal reinforcements cause, they are generally coated with a damping material. In many cases, this process is now automated. In a robot cell, the side impact beams are transferred to a granulating machine and removed. A complex process, in which the precise interaction of numerous automation components is vital.
A crucial factor is the conveyor technology, which supplies the side impact beams to the cell in a cycled manner and transports them away again after processing. In this case, finding a suitable supplier proved to be a challenge for the manufacturer of the robot cell because the conveyors not only have to position the beams, which are up to 1,250 mm long, with repeat accuracy and precision so that the robot can pick them up, but also to allow for a buffer of twelve components, so the line can run autonomously. Finally, the conveying path needs to be compact and adaptable to achieve a seamless transfer to a customer-side conveyor offset by 90°.
To solve this, mk’s experts implemented two individually configured conveyor systems. An SPU 2040 accumulating conveyor, a 5,500 mm long and 800 mm wide, two-track chain conveyor with aluminium pallets, to transport the parts into the robot cell. The pallets of the left and right tracks are connected by a beam, forming a rigid and stable connection. The corresponding sensor system allows the precise stopping, separating and positioning of the

pallets at a cycle time of approximately 30 seconds. The workpieces are manually placed on the pallets of the SPU 2040. After removal by the robot, the pallets then travel back to the starting position on the underside of the conveyor. This creates a space-saving recirculation system that allows up to twelve side impact beams to be buffered without additional conveying levels or complex lifting and lowering mechanisms.
After granulation, the robot places the side impact beams on another conveyor system from mk: a ZRF-P 2040 dual-lane timing belt conveyor, 5,600 mm long and 500 mm wide, with customer-supplied workpiece holders on the top side of the timing belt. The solution boasts one special feature: at the end of the conveying path, mk has fitted a compact GUF-P Mini belt conveyor between the two lines, 400 mm long and 200 mm wide. The cross conveyor lifts the side impact beams with a pneumatic lifting device and transfers them to a belt conveyor provided by the customer. This realises the 90° corner transfer.
Thus, a continuous and compact material flow solution was developed that reliably buffers the side impact beams, delivers them to the robot in a cycled manner and discharges them safely after processing.
As the only UK and Ireland distributor of the mk conveyor range, please visit AdaptTech’s website for more information.
adapt-tech.co.uk

One Controller. One Network. One Software. Maximize your freedom to innovate

#MakeitIntegrated
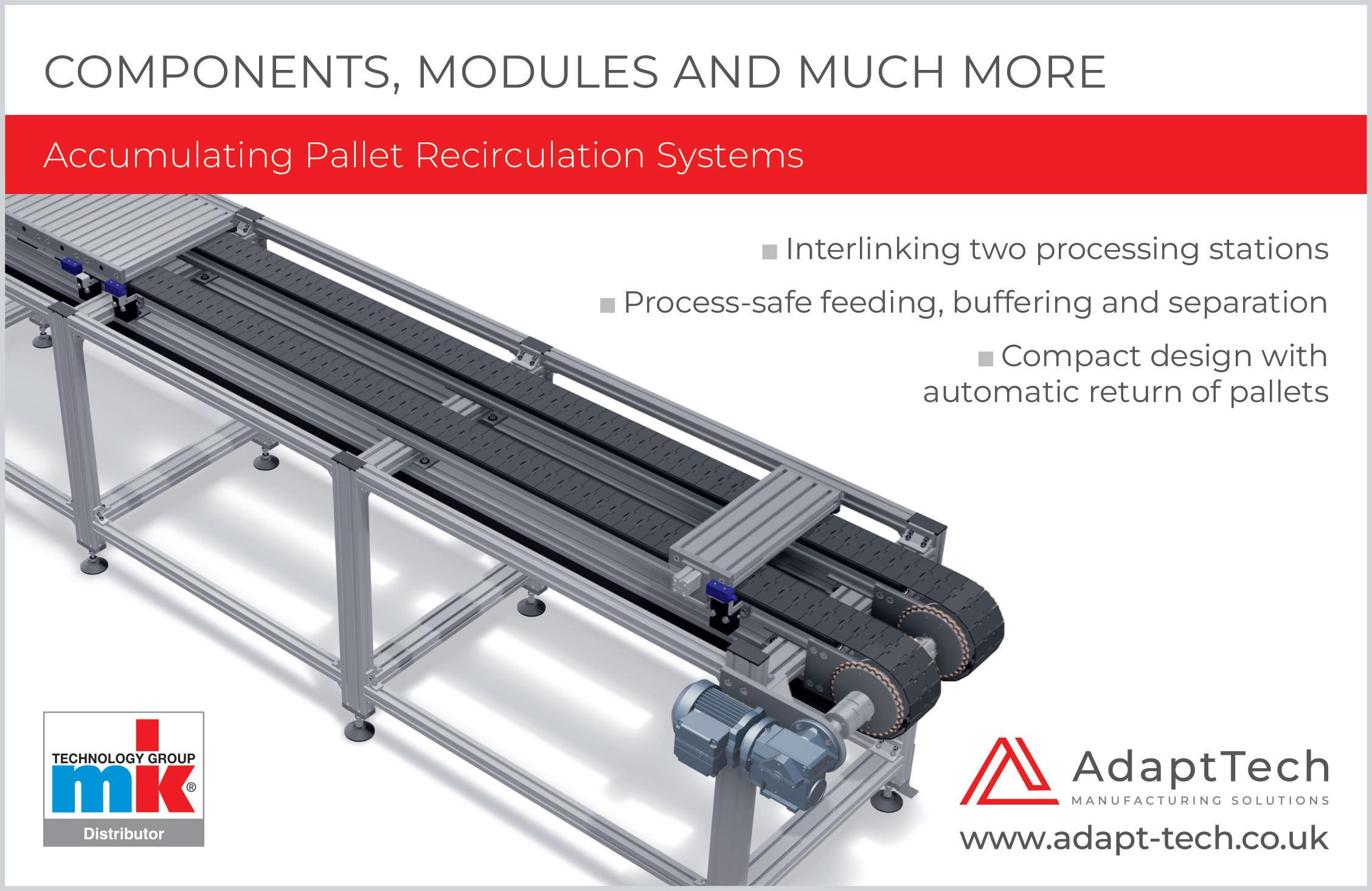
Precision in process automation is crucial, especially when handling flexible components. Introducing the scanCONTROL 3010-200 laser profile scanners from Micro-Epsilon, which enable robots to precisely detect and handle flexible cables in real-time.
In modern production, process automation plays a crucial role in creating cost-efficient and high-quality products. High precision is particularly important when assembling complex and flexible components such as cable harnesses. The precise handling of flexible components is extremely challenging, as they are easily deformed and their position can change. To make this process efficient and reliable, non-contact position detection is required so that robots can precisely detect cables and insert them into the connector housing.
High-resolution laser profile scanners from Micro-Epsilon’s scanCONTROL 3010-200 series have proven effective for these tasks. The sensors measure the position and geometry of the cables in real time so that the robot can grip them securely and fit them in the designated slots. Another building block for successful implementation is software, which processes the measurement data and synchronises it immediately with the movement of the robot. In this way, the manufacturer can ensure that the robot determines the exact pick-up point and inserts the cables precisely into the intended connectors – a decisive advantage for cable harness assembly automation.
Real-time synchronisation between the sensor and the robot ensures precise position detection and reliable processing. It is also a flexible automation cell that can be reprogrammed at any time without the need for complex mechanical modifications. The combination of standard components creates an economical solution that replaces cost-intensive, rigid special machines and significantly increases production efficiency.
The wide selection of sensor models and measuring ranges now available in the scanCONTROL range of laser scanners enable engineers to solve every profile measurement task. Smart laser scanners with integrated data processing allow users to solve common measurement applications without the need for external data processing. For more complex applications, sensors with programmable software are available. With Micro-Epsilon’s Configuration Tools software,

more than 40 measurement programs with a total of more than 90 evaluations are available. The programs are transferred to the SMART sensor, which performs the measurement, evaluation and output in standalone mode.
The scanCONTROL 30x0 series is among the highest performing profile sensors in terms of their size, accuracy and measuring rate. They provide calibrated 2D profile data with up to 7.37 million points per second. A profile frequency of up to 10kHz enables precise profile measurements in dynamic high-speed processes. The high-resolution sensor matrix offers a resolution of 2,048 points with an ultimate point distance of just 12µm, enabling extremely fine details to be detected reliably. The sensors are available with either blue or red laser diodes.
For more information on the scanCONTROL 3010, please visit Micro-Epsilon’s website.
bit.ly/4sNWkmz



Titan Enterprises is a leading design and manufacturer of innovative end user and OEM high-performance flowmeters and flow measurement instrumentation, used within a wide range of processes, environments and applications.
• Compact, robust, reliable
• Excellent accuracy and repeatability
• Measure low to high flow ranges
• High chemical resistance
• NSF-Approved mini turbine flowmeters Titan’s liquid flowmeters are designed and manufactured to ISO 9001 with traceable calibrations.




With new and returning exhibitors showcasing the full spectrum of UK manufacturing technologies, MACH 2026 is poised to be the catalyst for UK manufacturing to deliver economic growth and sovereign resilience.
In just over four months, MACH 2026 will open its doors at the NEC, Birmingham to over 30,000 members of the manufacturing community, bringing together buyers, sellers, specifiers and designers. The biennial event offers an unmissable opportunity to experience new technology, live and in action and is perfectly timed for UK manufacturers preparing for growth in capacity and capability.
Registration is now open for the event owned and organised by the Manufacturing Technologies Association (MTA), and sponsored by Lloyds, which is the UK’s largest for inspiring, innovating and connecting the manufacturing community and is due to take place across five halls of the NEC from 20 to 24th April 2026.
Building on the overwhelming success of their debut at MACH 2024, the Knowledge Hubs will return and are even bigger and better for MACH 2026. These interactive hubs are designed to provide manufacturers with practical guidance on adopting new technologies, helping them tackle challenges, boost performance and improve competitiveness by connecting with the right experts and suppliers.
The Machining & Tooling Knowledge Hub is a particular focus for MACH 2026 and is supported by a wide range of tooling companies including Ceratizit, Iscar Tools, Horn, Guhring, ZCC Cutting Tools, Kyocera, Europa Tools, Mapal and Mitsubishi.
Commenting on the exciting plans for MACH 2026, James Fudge, Head of Operations at the MTA, said: “MACH is the only show that offers thousands of visitors a fantastic opportunity to explore and see live demonstrations of a wide range of the latest manufacturing technologies and techniques, all under one roof, in one week – without leaving the UK. This year’s event is a fabulous opportunity to learn about new technology and how this can be harnessed to improve productivity and efficiency. The Knowledge Hub areas are spearheading our drive to help manufacturers integrate new technologies into their processes and manufacturing systems. The event also offers invaluable face-to-face opportunities to meet new suppliers and strengthen existing relationships, helping businesses stay ahead in a rapidly evolving sector.”
The Education and Development Zone (E&D Zone), sponsored by Iscar Tools, is the educational hub at

MACH 2026, designed for students keen to explore what engineering-based manufacturing can offer them as a future career and to help them find their ‘pathway to engineering’.
The cutting-edge manufacturing technology on display at MACH 2026 will include machine tools, cutting tools, metrology equipment, additive manufacturing (3D printing), surface engineering, robotics and automation, sheet metal, metal forming and fabrication technology, and specialist software which is both enabling and driving the digitalisation of manufacturing.
To find out more about MACH 2026 and to register your attendance, please visit:
machexhibition.com

Subcon is a free-to-attend exhibition taking place on the 3-4 of June at the NEC, Birmingham. It is a must-attend for buyers across all industry sectors. Read on for a host of compelling reasons to attend or exhibit, including a sneak peek at this year’s conference programme’s themes.
Subcon is the premier event for procurement teams from both OEMs and tiered suppliers to benchmark their subcontracting manufacturing capabilities and refine their supply chain.
The event brings together 6,000+ visitors, 200+ exhibitors, and 50+ industry experts and speakers. With hundreds of the latest innovations, products and services to explore, visitors come to Subcon to source, network, learn and benchmark.
Highlights include 200+ suppliers showcasing products made in Britain or made for British manufacturers, live product demo sessions, expert-led practical workshops, peer-to-peer roundtable panel discussions, and dedicated work and meeting spaces. There will also be networking drinks open to all visitors, a VIP Buyers Programme for senior manufacturers, a motorsport games zone and The Manufacturing Solutions Show Awards, celebrating the best and brightest in the industry.
• Circular Economy & Remanufacturing – how UK manufacturers can design products and supply chains for reuse, refurbishment and remanufacture, cutting waste, and improving resilience.
• Supply Chain Resilience & Sourcing – building robust, flexible supply networks through nearshoring, supplier diversification, digital visibility and risk mapping to withstand disruption and price volatility.
• Workforce & Skills Transformation – addressing the skills gap by blending traditional manufacturing expertise with automation, data, robotics and AI to create agile, future-ready teams.
• Sustainable Materials & Processes – practical innovations in low-carbon materials, energy-efficient production and waste reduction that improve environmental performance and competitiveness.
• Cyber & Physical Security – protecting connected factories from cyber threats, IP theft and supply-chain risks through technology, training and governance.
• New Business Models (MaaS) – moving beyond “make and sell” with outcome-based and subscription models enabled by digital twins, IoT and cloud platforms.

• Geopolitics & Trade – navigating reshoring, tariffs, export controls and critical-materials security to maintain supply continuity and seize growth opportunities.
• Smart Supply Chains – using digital logistics, traceability and data-driven transparency to boost efficiency, compliance and ethical sourcing.
• Human-Robot Collaboration – integrating cobots to enhance safety, productivity and job satisfaction without replacing skilled workers.
• Digital Validation & Virtual Commissioning – using simulation and digital twins to reduce time-to-market, cut costs and optimise production before deployment.
The organisers are looking for passionate and unique industry voices to be a part of this exciting programme.
In just two years, Subcon has seen an 85% surge in visitors and a 30% increase in exhibitors. It is the UK’s go-to event for sourcing, supply chain solutions and manufacturing innovation.
Pooja Jha, Director, Sahasra Electronics UK Limited said: “Subcon is a fantastic opportunity to network with existing and prospective clients”.
For companies wishing to showcase their capabilities, meet serious buyers and grow their pipeline, Subcon delivers. Visit Subcon’s website to learn more.
subconshow.co.uk












































Southern Manufacturing & Electronics announces details of its speaker programme for the 2026 exhibition, providing opportunities for strategic learning and practical insights.
Southern Manufacturing & Electronics 2026 will present a high-calibre speaker programme alongside free-to-attend, CPD-accredited seminars, bringing together industry leaders, technology experts and manufacturers to address the industry’s most pressing challenges. Taking place from February 3 to 5 at Farnborough International Exhibition & Conference Centre, the seminar programme is designed to deliver practical insight, strategic perspective and real-world learning.
The programme will kick off on Tuesday, February 3, with a keynote speech from Stephen Phipson, CEO of Make UK. This will be a 60-minute overview of the current manufacturing landscape and upcoming opportunities for those in the industry.
Over the three days, visitors can hear from speakers representing leading organisations including Siemens, Rolls-Royce, Renishaw, Airbus and Sourceability, as well as other technical specialists and solution providers. Sessions will explore topics ranging from electronics design and manufacturing scalability to supply chain resilience, sustainability and advanced automation. Presentations such as “The Journey Towards Sustainable Electronics”, “Mitigating Knowledge Loss and Component Unavailability” and “Agentic AI – Automating the Mundane” are designed to offer actionable takeaways that attendees can apply directly within their organisations.
The seminar programme will be split across two separate conferences. The Manufacturing Conference will explore topics including process optimisation, operational excellence and digital transformation. Meanwhile, the Electronics and Semiconductors conference will focus on the latest innovations driving the industry, including the impact of automation and Industry 4.0 and cutting-edge technologies, such as additive manufacturing.
“This year, we’re looking forward to welcoming some of the biggest names in manufacturing and electronics, including Siemens, Rolls-Royce and other high-profile partners,” explains Simon Farnfield, portfolio director at Easyfairs, organiser of Southern Manufacturing & Electronics. “Today, our industry is facing some of its toughest challenges, whether it’s skills shortages, reduced productivity or digital transformations. We wanted a seminar programme that would address these issues headon.

“We wanted this year’s event to bring together industry leaders and technical experts, giving our visitors practical insights they can take back to their businesses,” added Farnfield. “Now more than ever, the focus is on actionable learning that supports long-term resilience, innovation and growth.”
With expert speakers, in-depth sessions and a programme focused on industry needs, Southern Manufacturing & Electronics 2026 offers visitors the opportunity to combine strategic learning with hands-on discovery across the show floor.
southern-manufacturing-electronics.com/seminars

Returning to the NEC, Birmingham this June, Smart Manufacturing Week (SMW) will focus on strategies for tackling the most pressing challenges facing the industry.
The UK manufacturing sector stands at a critical junction, navigating the demands of digital transformation, supply chain resilience and the urgent push towards Net Zero. Finding actionable strategies to balance these priorities is the central challenge facing industry leaders today.
This will be the core focus of Smart Manufacturing Week, which returns for its 5th edition at the NEC in Birmingham on 3-4 June 2026.
Curated by The Manufacturer and informed by deep industry insight, this year’s event structure moves beyond general technology showcases to tackle the sector’s most pressing challenges. The event is built around five key strategic pillars: Digital Transformation, Sustainability and Circular Economy, Supply Chain Resilience, Innovation and Smart Technologies, and Workforce and Skills.
The five pillars closely align with the eight dedicated Solution Theatres across both days. Building on previous successes, visitors can expect over 170 free-to-attend sessions led by global manufacturing and technology experts.
Key topics under the microscope include AI-driven productivity and machine learning applications; the deployment and practical value of digital twins; strategies for Net Zero manufacturing; and workforce transformation and skill development in the automation era.
By concentrating on the next wave of innovation and adaptation, the Solution Theatres promise attendees actionable takeaways to accelerate progress and foster industry-wide collaboration.
Joining the exhibitor line-up in 2026 are industry leaders including Beckhoff, Solutions PT, Epicor, Ericsson, Prod Utech, Fanuc, and Sage and many, many more.
Grace Gilling, Event Director at Smart Manufacturing Week said: “Smart Manufacturing Week 2026 is all about bringing the future of advanced manufacturing and

engineering to life. This year, we’re introducing brand-new features designed to showcase the very best the industry has to offer.
“Our Meet the Buyer programme helps visitors source the most efficient and profitable solutions for 2026, ensuring every moment delivers real value.
“Experience the stand-out new Factory of the Future is a fully immersive, walk-through demonstrator bringing connected, intelligent, and sustainable manufacturing to life. See live, hands-on demonstrations of robotics, AI, digital twins and predictive maintenance working together to make transformation tangible and bridge the gap between ambition and implementation.
“The Future Stage will showcase breakthrough thinking and bold ideas from pioneering innovators, offering debate on the strategies shaping the next decade. Plus, the expanded Ambassador Programme brings more industry leaders for enhanced networking, learning and inspiration.
“Together, these features make Smart Manufacturing Week 2026 an ever-growing festival for all facets of industry. It’s the destination for industrial transformation and a glimpse of what manufacturing and engineering can achieve.”
Register now to secure a place at the UK’s major manufacturing event and keep up to date on the latest information.
smartmanufacturingweek.com















