




Courtney Harris, MSN, APRN, Kaylyn Bourne, DNP, APRN & David Phillippi, PhD
Belmont University Doctor of Nursing Practice Program
Initiation of antiretroviral treatment (ART) within 24 hours of an HIV diagnosis is safe, shortens time to viral suppression, improves retention in care, and is linked to reduced rates of HIV at the community level (Sullivan et al., 2025). Despite this evidence, patients do not universally receive timely HIV care across the United States (Bertolino et al., 2023). Barriers to early ART initiation include lack of staff buy-in, logistics, and socioeconomic patient conditions (Doshi et al., 2023).
To strengthen clinical services and promote health equity through the interdisciplinary co-creation of an HIV testing-to-treatment algorithm.
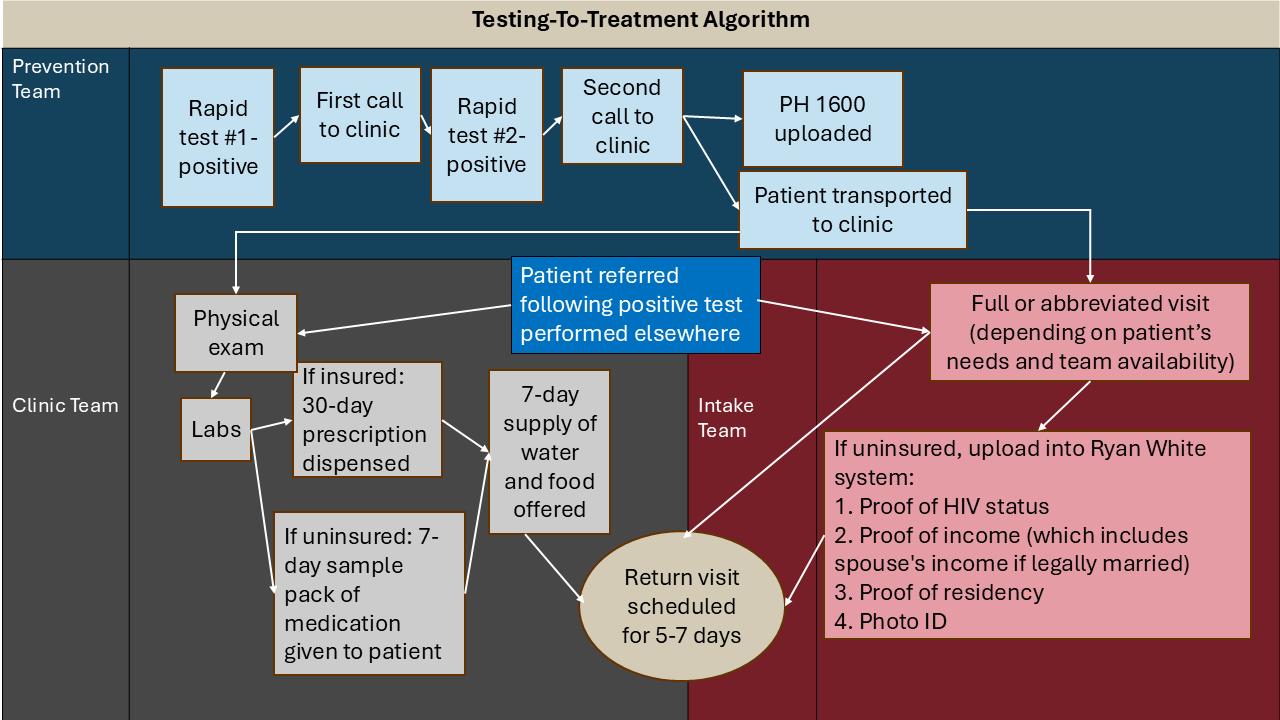
• Mixed-methods convergence design
• Quality Improvement project
• Setting: HIV care clinic and advocacy agency
• Three algorithm design and use surveys sent to 20 staff members at one-month intervals

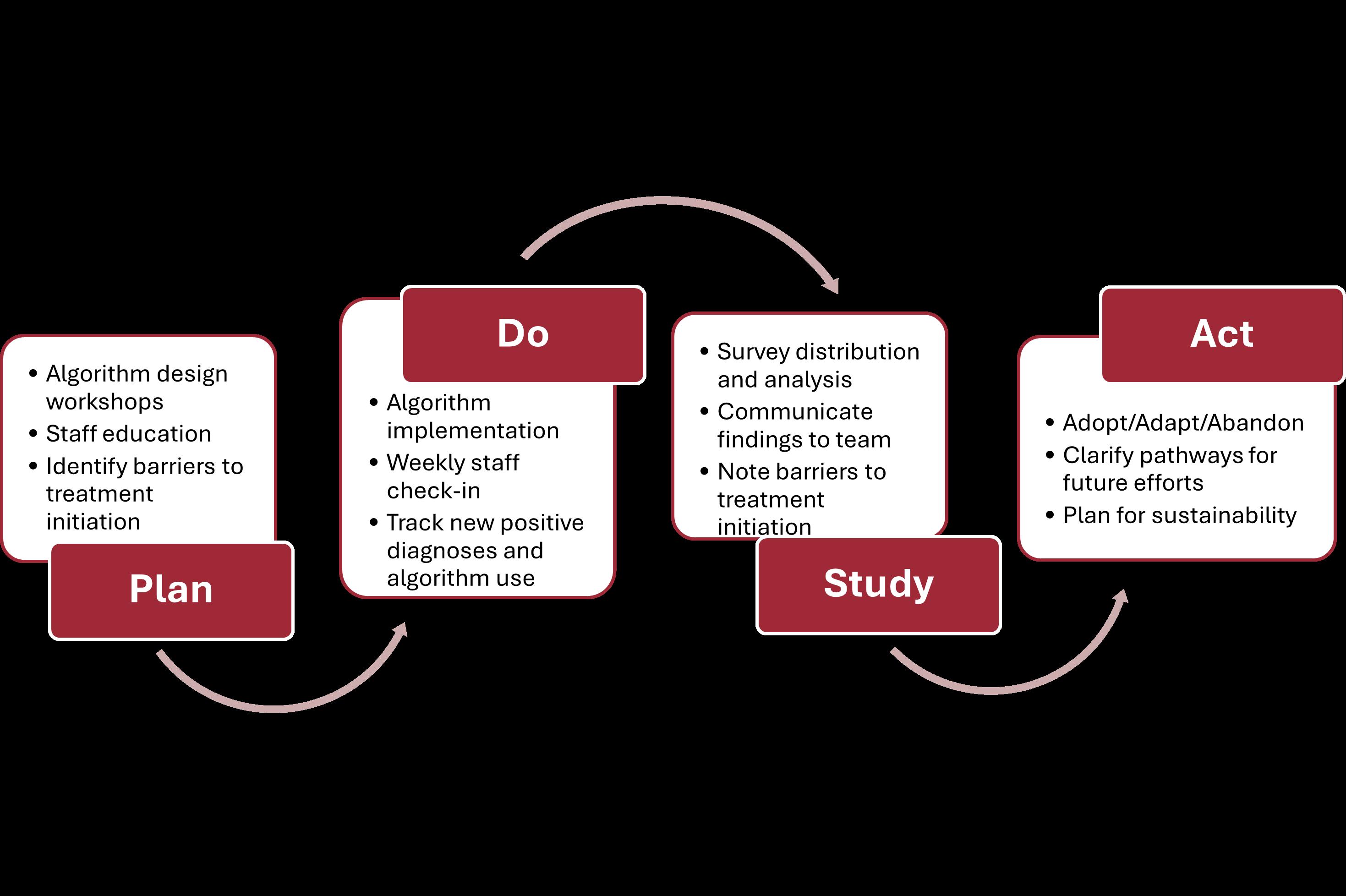
The Institute for Healthcare Improvement’s Model for Improvement:
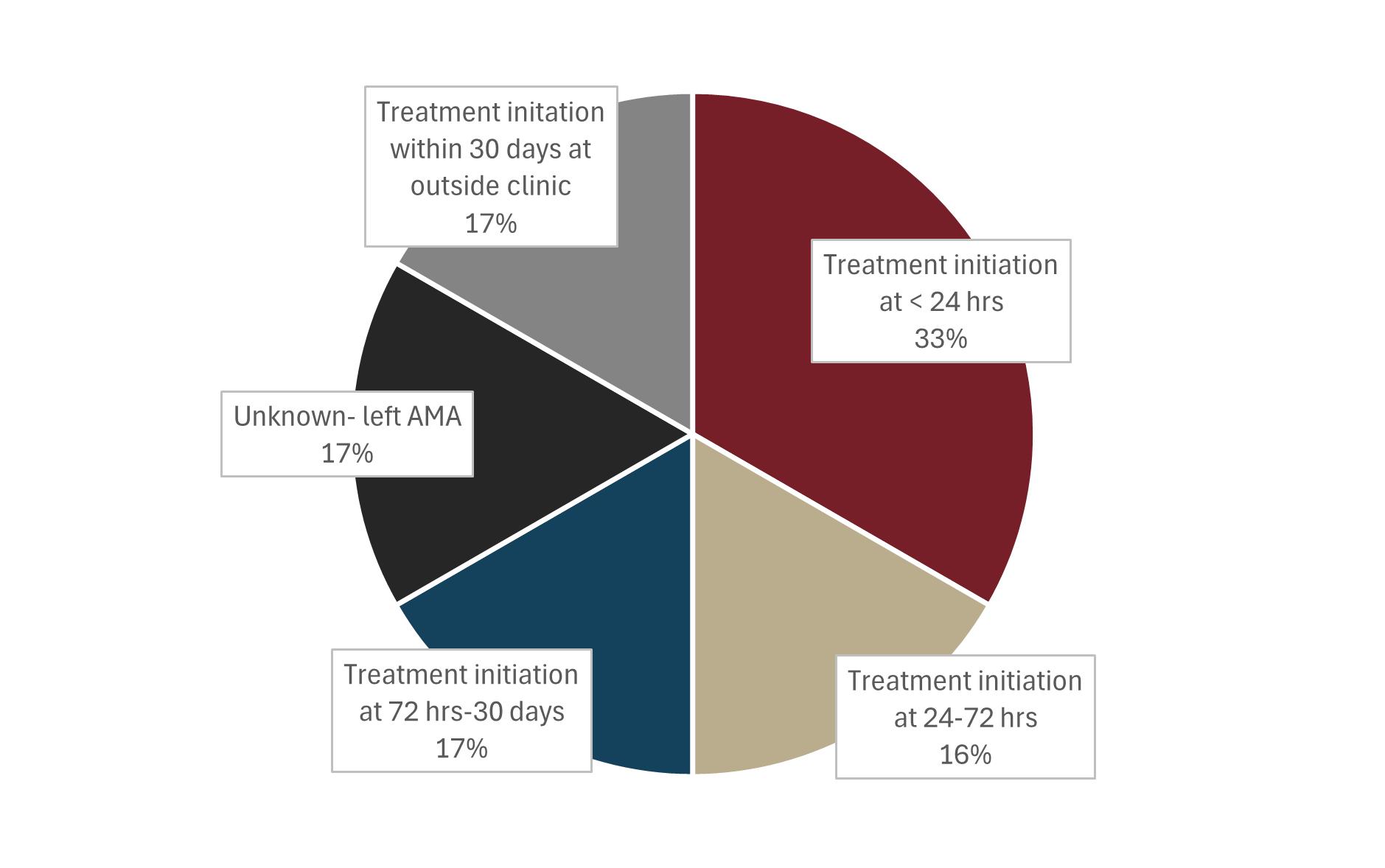
• 83% appropriate use of the testing-totreatment algorithm.
• ART initiated in 83% of HIV-positive cases within 30 days of diagnosis.
• 100% of staff reported that standardized processes improve access to care.
• Qualitative survey responses indicate support for standardized protocols to facilitate timely initiation of HIV treatment.
• Lack of interdisciplinary collaboration functions as a barrier to evidencebased care.
• Interdisciplinary collaboration can be utilized to co-design clinic-specific algorithms that align workflows with evidence-based recommendations for HIV care.
• Collaborative design process highlighted education gaps among professional departments.
• Implementation of a defined testing-totreatment pathway enhances staff engagement, accountability, and attention to timely, coordinated care.