
Simon Philip
Computational Design Course Portfolio
Novatr 2023-2024
AlbertRhino 3D Basics
SubD
Visual Scripting Basics
Stadium Concept
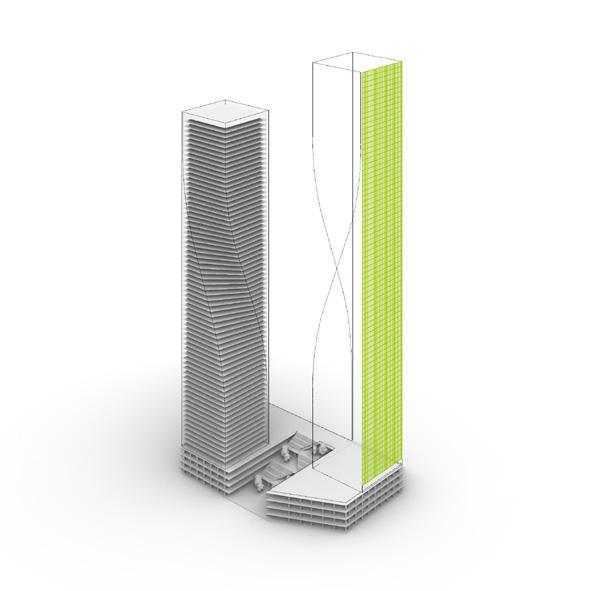
Twist Museum
Phyllotaxis
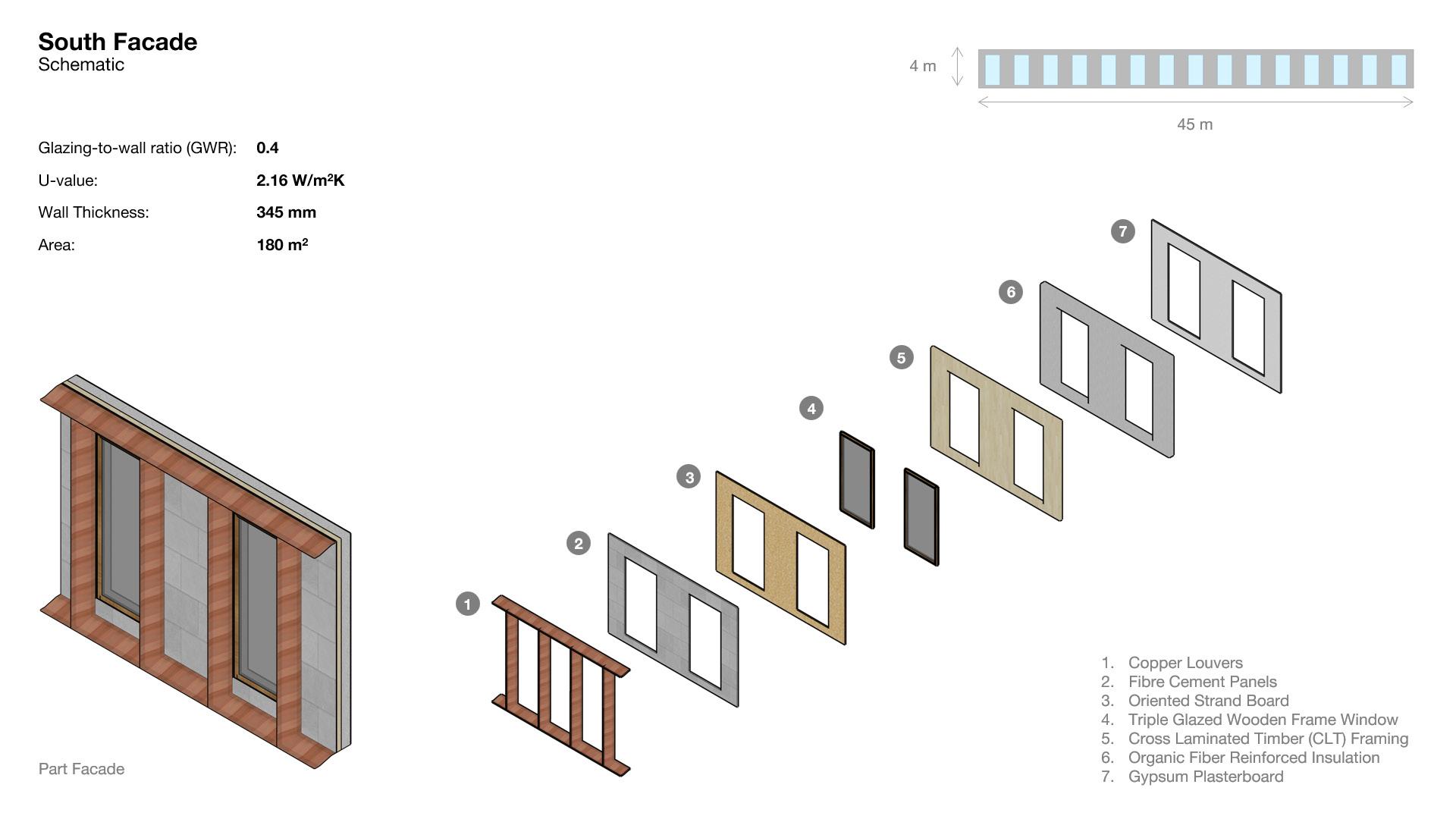
Facade
Attractor Based Modulation
Jacob
NSW Pavilion
Capstone


Simon Philip
Computational Design Course Portfolio
Novatr 2023-2024
AlbertRhino 3D Basics
SubD
Visual Scripting Basics
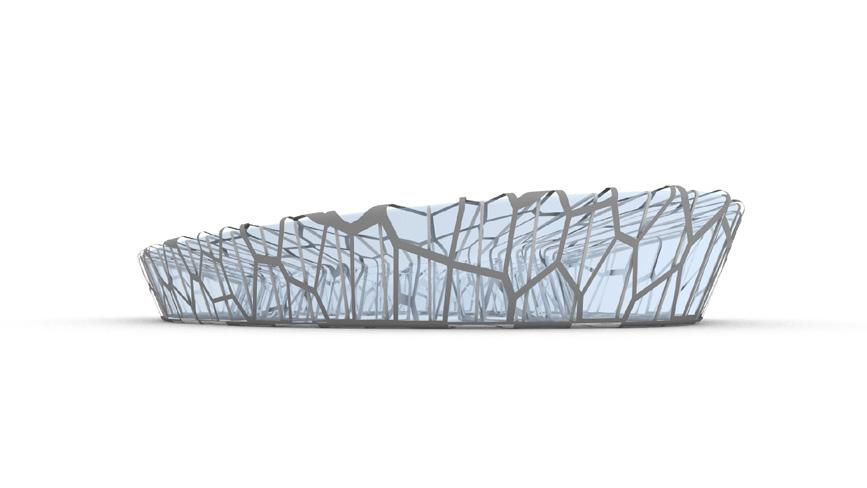
Stadium Concept
Twist Museum
Phyllotaxis
Facade
Attractor Based Modulation
Jacob
NSW Pavilion
Capstone








subdivide, subd loft edge loops, crease










concepts extrude, loft, boolean operations, graph mapper, sets tools rhino 3D, grasshopper

























concepts
graph mapper, voronoi, gradients






concepts
divide domains, md slider, relative items, branches tools grasshopper




concepts orient, attractor curve
tools
grasshopper




concepts solid difference, tree branch
tools grasshopper


































concepts
evolutionary solving, pareto front
tools
grasshopper, wallacei



concepts variables, functions, definitions
tools
grasshopper, gh python










concepts
blend curve, loft, sweeps, extrude
tools
rhino 3D, grasshopper, kangaroo, galapagos, ladybug, honeybee, dragonfly














































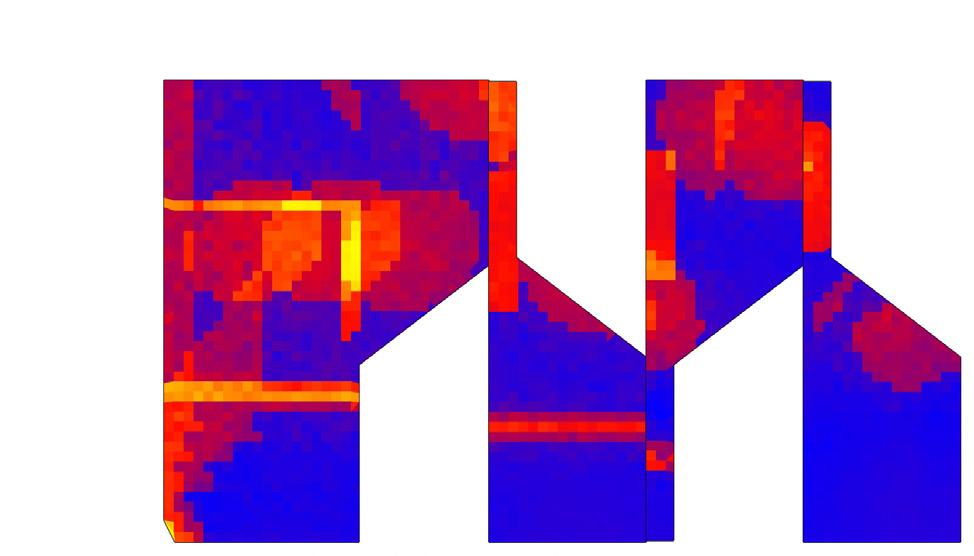

The Spatial UTCI analysis performed on the podium levels justifies the use of a canopy above to mitigate heat gain during summers. The hourly UTCI plot shows that the overall feels-like temperature remains hotter during the summer months (Jun-Aug).
About 65% of the podium area experiences hotter temperatures, with the central and bottom areas most exposed. With the canopy, the temperature all across the podium significantly drops by ~1.5°C.
 Canopy
Without Canopy
With Canopy
Spatial UTCI map at the Podium for 29 Jun @1300 hours
UTCI hourly plot
Hottest day: 29 Jun @1300 hours
Canopy
Without Canopy
With Canopy
Spatial UTCI map at the Podium for 29 Jun @1300 hours
UTCI hourly plot
Hottest day: 29 Jun @1300 hours



































The building’s Energy Use Intensity (EUI) was measured with the Regular EPW and an Urban EPW generated with Dragonfly, for daytime & nighttime occupancies.
As a result of Urban Heat Island, the difference between cooling loads during nighttime is 13kWh/m2, much more than 3kWh/m2 difference in daytime.
The urban model created reveals higher feels-like temperatures that contribute to a higher temperature difference between day and night.







Optimized Shading Currrent Shading



The current shading derived from panelling which is the same across all four facades, is optimized using Galapagos as solver. The genomes considered are all four horizontal depths and horizontal angle.
The optimized shading using the metric of Direct Sun Hours shows significant improvements, especially in the east and west facades with 26.6% and 22.6% improvement respectively.




24,867

 Albert Simon Philip Computational Design
Albert Simon Philip Computational Design