The pandemic makes it necessary to accelerate efforts to increase the tax contribution of the digital economy through multilateral agreements to avoid harmful fiscal and trade effects, and to increase the participation of the countries of the region in global negotiations on taxation of the digital economy, so that regional needs and interests are considered. At the same time, the widespread use of management algorithms for telework, information and communications technologies, big data for creating contact tracing applications, artificial intelligence, e-health and e-commerce has highlighted the need to establish standards that take into account existing antitrust regulatory frameworks. At the heart of the disruptions are the business strategies of big tech companies, based on greater access to data. This calls for a policy and regulatory discussion, covering both data protection and privacy and interoperability, access to data for development purposes, intellectual property and competition rules. Some countries and organizations are concerned by privacy issues relating to the competitive practices and the growing market power of these tech giants. Even before the pandemic some platforms, such as Twitter, had announced restrictions on political content that is considered harmful. While it does not seem to be the general rule, the declaration of a pandemic has opened the door to content monitoring by platform owners. Clear guidelines or rules are needed that balance the prohibition of harmful content with freedom of expression. These companies argue that is their responsibility to ensure that relevant and truthful official information is disseminated on the spread of the pandemic and the measures taken by governments to tackle it. It is an important argument, but there is concern that these tools may become established as a new means for these companies to exercise market control and dominance.
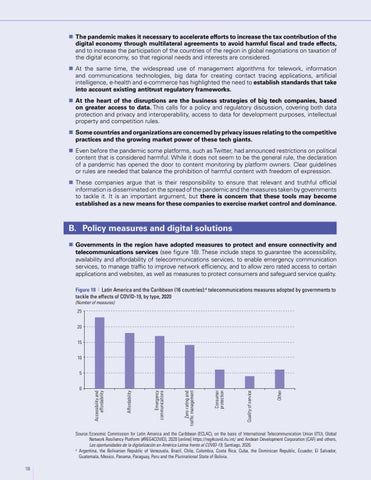
B. Policy measures and digital solutions Governments in the region have adopted measures to protect and ensure connectivity and telecommunications services (see figure 18). These include steps to guarantee the accessibility, availability and affordability of telecommunications services, to enable emergency communication services, to manage traffic to improve network efficiency, and to allow zero rated access to certain applications and websites, as well as measures to protect consumers and safeguard service quality. Figure 18 | Latin America and the Caribbean (16 countries):a telecommunications measures adopted by governments to tackle the effects of COVID-19, by type, 2020 (Number of measures) 25 20 15 10
Other
Quality of service
Consumer protection
Zero-rating and traffic management
Emergency communications
Affordability
0
Accessibility and affordability
5
Source: Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC), on the basis of International Telecommunication Union (ITU), Global Network Resiliency Platform (#REG4COVID), 2020 [online] https://reg4covid.itu.int/ and Andean Development Corporation (CAF) and others, Las oportunidades de la digitalización en América Latina frente al COVID-19, Santiago, 2020. a Argentina, the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, the Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Mexico, Panama, Paraguay, Peru and the Plurinational State of Bolivia. 18