2 minute read
D. Tirupathi Rao, S.Ravibabu ‘Experimental investigation of cooling performance of an Automobile radiator using Al2O3 Water+ethylene Glycol nanofluid
Investigation on Physical Properties of Al2O3/Water
Nano Fluid (2015)
Advertisement
Performance Investigation Of
Automobile Radiator Using Al2O3 As Base Nan fluid (2016)
Study Of Heat Transfer
Characteristics Of Nano Fluid In An Automotive Radiator (2018)
Experimental Investigation Of Heat Transfer Potential Of
Al2O3/ Water-Mono Ethylene Glycol Nanofluids As A Car Radiator Coolant (2018)
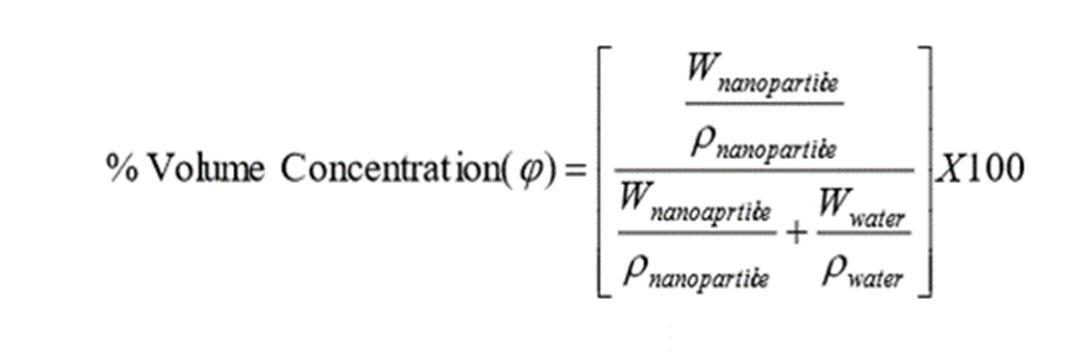
Effect of heat transfer enhancement and NOx emission using Al2O3/ Water Nanofluid as coolant in IC engine Different volume concentration is used to calculate thermal conductivity of nanofluids. Thermal conductivity varies with temperature and volume concentration was studied.
In this paper we studied different physical properties of Al 2 O 3 water nanofluid and
experimentally investigated the effective thermal conductivities and viscosity of
nanofluid. The equipment called KD2 thermal property analyzer uses to measure
thermal conductivity and thermal resistivity. The KD2 analyzer also calculate thermal
data and display thermal conductivity in 90 just seconds. It showed the thermal
conductivity of Al 2 O 3 nanofluids increases with a partial volume concentration & the
viscosity of nanofluid depend on volume percentage. The electrical conductivity is
higher than best fluids available as coolant. This paper concluded that nanofluid having better heat transfer rate as compare to other
coolant. Heat transfer rate increases with the temperature increases. Because of higher heat transfer rate in radiator we can use compact sized radiator for same coolant and this reduced frontal area of automobile and it result in reduced aerodynamic drag and
ultimately increase fuel economy. In this paper detail procedure for preparation of nanofluids is explained. Nanofluid
preparation done by two step method, which involve the use of Ultrasonic Sonicator
for Mechanical Vibration which tends to dissolve nanoparticle in the base fluid.
Followed by Mechanical Exciting to fluid to dissolve the denser particles. And
eventually the use of Magnetic Stirrer to obtain a homogeneous mixture of Al 2 O 3
nanoparticles with base fluid.
By virtue of experimentation the overall heat transfer coefficient, Nusselt number and Reynolds number increase with coolant flow rate which gives higher heat transfer rate compare to base fluids. It is concluded that nanofluid has higher heat transfer
properties than other base fluid like water and ethylene glycol and good economy. Ethylene glycol / water is a normal coolant used in a car radiator. In this paper Al2O3 water–mono ethylene glycol nanofluids is used as a coolant for car radiator. This
coolant have higher thermophysical properties than normal coolant. Heat transfer rate increases with concentration of nano particle. It has higher heat transfer rate. By experimentation it is concluded that use of nano fluid provides scope for design of
compact radiator size & reduce weight of system because of this the car can possess better aerodynamics at similar rate of heat dissipation.
NOx emission from engine reduce to 12.5 % at full load for nanofluid as compared to distilled water based coolant because of the lower overall operating temperature of the IC engine. Overall heat transfer coefficient was increased by 20%, 25% and 29% for Al2O3/water nanofluid with volume concentration of 1%, 1.5% and 2% respectively at Peclet no