WNWR 2019 — 2. ORIGINS AND CLASSIFICATION
22
Mining Milling
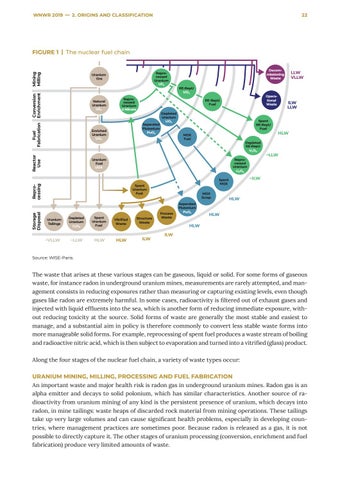
FIGURE 1 | The nuclear fuel chain
Reprocessed Uranium UF6
Conversion Enrichment
Uranium Ore
Fuel Fabrication
Enriched Uranium UO₂
Reactor Use
Natural Uranium UF₆
Uranium Fuel UOX
Reprocessed Uranium U Nitrate
RE-RepU UO2
Depleted Uranium UO2
Spent RE-RepU Fuel MOX Fuel
~VLLW
Depleted RE-RepU U3O8 Reprocessed Uranium U3O8
Depleted Uranium U3O8
Spent Uranium Fuel
Vitrified Waste
~LLW
HLW
HLW
Structure Waste
ILW
MOX Scrap
Process Waste
Separated Plutonium PuO2
LLW VLLW
ILW LLW
HLW
~LLW
~ILW
Spent MOX
Spent Uranium Fuel
Uranium Tailings
Operational Waste
RE-RepU Fuel
Separated Plutonium PuO2
Reprocessing Storage Disposal
Decommissioning Waste
HLW
HLW
HLW ILW
Source: WISE-Paris.
The waste that arises at these various stages can be gaseous, liquid or solid. For some forms of gaseous waste, for instance radon in underground uranium mines, measurements are rarely attempted, and management consists in reducing exposures rather than measuring or capturing existing levels, even though gases like radon are extremely harmful. In some cases, radioactivity is filtered out of exhaust gases and injected with liquid effluents into the sea, which is another form of reducing immediate exposure, without reducing toxicity at the source. Solid forms of waste are generally the most stable and easiest to manage, and a substantial aim in policy is therefore commonly to convert less stable waste forms into more manageable solid forms. For example, reprocessing of spent fuel produces a waste stream of boiling and radioactive nitric acid, which is then subject to evaporation and turned into a vitrified (glass) product. Along the four stages of the nuclear fuel chain, a variety of waste types occur: URANIUM MINING, MILLING, PROCESSING AND FUEL FABRICATION An important waste and major health risk is radon gas in underground uranium mines. Radon gas is an alpha emitter and decays to solid polonium, which has similar characteristics. Another source of radioactivity from uranium mining of any kind is the persistent presence of uranium, which decays into radon, in mine tailings: waste heaps of discarded rock material from mining operations. These tailings take up very large volumes and can cause significant health problems, especially in developing countries, where management practices are sometimes poor. Because radon is released as a gas, it is not possible to directly capture it. The other stages of uranium processing (conversion, enrichment and fuel fabrication) produce very limited amounts of waste.